Thinking about a real-world microservice architecture is a bit like imagining how an e-commerce site works behind the scenes. Instead of one giant application, you have smaller, independent services for things like user authentication, product catalog management, and payment processing. Each one runs on its own, which means you can update or scale them individually without taking the whole system offline. It's a key strategy for building apps that can scale to meet any user demand and for modernizing your software with the latest AI integrations. A little fun fact: making this switch can feel like turning a tangled ball of yarn into a neatly organized set of Lego blocks—way easier to build with!
The trick, however, is managing all those new pieces, especially when AI enters the picture. That’s why we built the Wonderment Apps prompt management system. It's an administrative tool you can plug right into your app to modernize it for AI. It gives developers a central command center to manage, version, and monitor all AI interactions, taking the complexity out of building truly intelligent, scalable software.
Moving Beyond Monoliths: A Practical Revolution
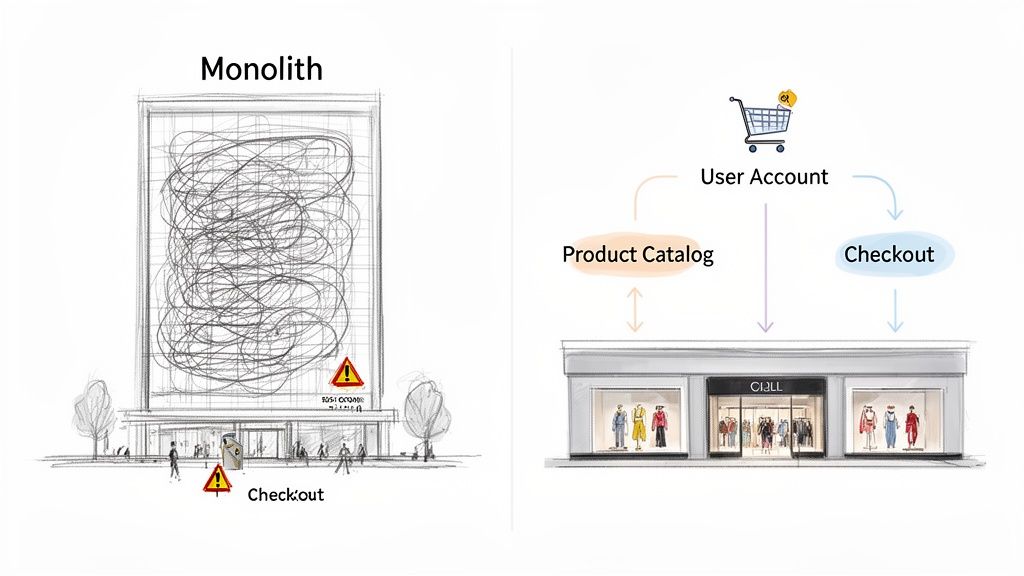
Imagine your entire application is a massive, single department store. If the checkout system goes down, the whole store grinds to a halt. That’s the reality of a traditional monolithic architecture—all the parts are tangled together in one big codebase. A glitch in one area often spells disaster for the entire operation.
Now, picture a modern shopping mall filled with independent boutiques. You’ve got a dedicated store for User Accounts, another for the Product Catalog, and a separate one for Checkout. If one boutique closes for maintenance, the others stay open for business. Shoppers can still browse for products even if the payment system is temporarily down.
This shopping mall analogy gets right to the heart of microservice architecture. It’s a strategic move away from a single, clunky application toward a collection of small, independent services that collaborate. Each service is built around a specific business function, owned by a small, focused team, and can be deployed on its own schedule.
Why Does This Shift Matter Today?
This isn't just another tech trend; it’s a direct answer to the pressures of modern business. Companies need to move fast, scale on a dime to meet user demand, and integrate new tech like AI without blowing up their existing systems. Microservices give them the flexibility to do just that.
The big wins with this approach are pretty clear:
- Enhanced Agility: Small, independent teams can build, test, and deploy their services whenever they're ready. This massively speeds up how quickly you can get new features out the door.
- Improved Scalability: You can scale services based on their specific loads. If your product search gets slammed with traffic, you just scale up the Product Catalog service, not the whole application.
- Greater Resilience: When one service fails, it doesn't bring the whole system down with it. This "fault isolation" keeps your application mostly available, even when things go wrong.
A Gateway to AI Modernization
This freedom is a game-changer when it comes to modernizing software. Trying to shoehorn complex AI features into a rigid monolith can be a nightmare. But with microservices, you can introduce new AI-powered services—like a recommendation engine or a fraud detection unit—piece by piece, without risking the whole platform. To successfully modernize legacy systems, this modular strategy is often the first, most crucial step.
This is exactly where Wonderment Apps' AI modernization toolkit shines. Our platform is built to help you plug powerful new capabilities into your applications with ease. For instance, our advanced prompt management system gives your development teams a central hub to control, version, and monitor AI interactions, taking the usual headaches out of AI integration and helping you build software that’s truly ready for the future.
The Core Principles of Microservice Design
Before you can really grasp any microservice architecture example, you have to understand what makes it all work. These aren't just abstract rules for engineers; they're core business philosophies that dictate how flexible, scalable, and resilient your software will be. Moving away from a monolith isn't just a technical swap—it’s a whole new way of thinking about building products.
There's a reason this architectural style is taking over. The global market for microservices was already valued at $2,073 million back in 2018 and is on track to hit a staggering $8,073 million by 2026. This isn't a fad; it's a fundamental shift in how modern, adaptable applications get built. You can learn more about the rapid adoption of microservices and see just how big this trend has become.
To see what this shift really means in practice, it helps to compare the old way with the new.
Microservices vs Monolith Core Principles Compared
This table breaks down the fundamental differences in philosophy between building with microservices and sticking with a traditional monolith.
| Principle | Microservice Approach | Monolithic Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Responsibility | Each service does one thing and does it well (Single Responsibility Principle). | One large application handles all responsibilities and functions. |
| Team Structure | Small, autonomous teams own their services end-to-end. | Large, interdependent teams work on a shared codebase. |
| Technology Stack | Teams can choose the best tech for their specific service (polyglot). | Everyone is locked into a single, standardized technology stack. |
| Deployment | Services are deployed independently, allowing for frequent, low-risk updates. | The entire application must be redeployed for any change, no matter how small. |
| Failure Impact | If one service fails, the others continue to run (failure isolation). | A failure in one component can bring down the entire application. |
| Data Management | Each service manages its own database, preventing shared bottlenecks. | A single, large database serves the entire application, creating dependencies. |
Seeing them side-by-side makes the contrast pretty stark. Microservices trade the simplicity of a single codebase for the immense power of flexibility and resilience.
Single Responsibility and Bounded Context
At the very core of microservices is the Single Responsibility Principle. It’s simple: instead of having one giant application that tries to do everything, you break it down into specialized services. Think of it like a restaurant. You don't have one person greeting guests, cooking the food, mixing the drinks, and handling the bill. You have a host, a chef, a bartender, and a server—each with one job to do, and they do it well.
This clear focus is defined by a bounded context. It’s an explicit boundary that says, "This is what my service is responsible for, and this is the data it owns." For example, a "User Authentication" service only cares about logging users in and out and securing their accounts. It knows nothing about what’s in their shopping cart. This separation is what saves you from the tangled mess that makes monoliths so painful to change.
Key Takeaway: By giving each service a single, clear job, you empower small, focused teams to become true experts in their domain. This ownership leads to higher quality code, faster development cycles, and less organizational friction.
Decentralized Governance and Data
Here’s where things get really interesting: decentralized governance. In a monolithic world, everyone is forced to use the same technology stack, whether it’s the best tool for the job or not. Microservices throw that idea out the window.
Your team building the user-facing "Shopping Cart" service might choose fast and lightweight Node.js for its speed. Meanwhile, the team handling the critical "Order Processing" service might opt for the robust stability of Java. This "polyglot" approach means every part of your application is built with the optimal tool, driving innovation and better performance. This idea also applies to data—each service owns its database, preventing the system-wide bottlenecks that plague monolithic architectures.
Independent Deployment and Failure Isolation
Finally, let's talk about the two principles that your operations team will love: speed and safety. Independent deployment is the ability to update one small piece of the application without taking the whole thing offline. Found a bug in the "Product Review" service? Your team can fix it and deploy the update in the middle of the workday without anyone using the checkout process even noticing.
That leads directly to failure isolation. If the "Recommendation Engine" service suddenly crashes because of a weird data bug, it won’t bring down your entire e-commerce site. The rest of the application just keeps on chugging along. This containment makes your system incredibly resilient, which is absolutely critical for keeping users happy and the business running.
These principles are the bedrock of a solid microservices architecture. Of course, knowing the principles is one thing; putting them into practice is another. For a deeper look at how to implement them effectively, check out our complete guide on microservices architecture best practices.
An Ecommerce Microservice Architecture Example in Action
Theory is one thing, but seeing a real microservice architecture example in the wild is where the lightbulb really goes on. Let's step away from the abstract and get our hands dirty by designing a system for a modern e-commerce platform. Instead of building one massive, tangled application, we're going to break it down into a team of specialized, independent services.
This isn’t just some textbook exercise. Retail giants like Amazon and streaming pioneers like Netflix famously ditched their cumbersome monoliths for microservices. Why? To handle incredible scale and innovate faster. Their stories prove this isn't just for startups; it's a battle-tested strategy for any business that needs to stay agile and resilient.
Deconstructing the Ecommerce Platform
A successful online store is a master of multitasking. Shoppers are browsing products, filling carts, trying promo codes, and checking out all at once. Behind the scenes, inventory is being updated in real-time and orders are flying to fulfillment centers. In a microservice world, each of these core functions gets its own dedicated service.
Here’s how we'd break down the essential services for our e-commerce platform:
- User Management Service: This is the bouncer at the front door. It handles everything about customer accounts—sign-ups, logins, password resets, and managing profiles and addresses. It owns all the user data, acting as the single source of truth for who your customers are.
- Product Catalog Service: Think of this as the digital stockroom. It manages every bit of product information: descriptions, photos, prices, SKUs, and how many are left on the shelf. When other services—like the shopping cart or search function—need product details, they ask this service.
- Shopping Cart Service: This service is all about managing a user's temporary selections. It's lightning-fast and built to track what customers add, remove, or update in their cart. Since so many carts get abandoned, it's designed for speed and lots of short-lived interactions.
- Order Processing Service: As soon as a customer clicks "buy," this workhorse service takes over. It's responsible for the entire journey of an order: creating the official record, talking to inventory, connecting with the payment gateway, and telling the shipping department what to do.
- Payment Gateway Service: This is a high-security specialist. Its only job is to handle money. It integrates with payment providers like Stripe or PayPal, processes credit card info, and confirms that a payment went through. Security and reliability are non-negotiable here.
- Recommendation Engine Service: This is where the cool stuff happens. This service crunches data on user behavior, purchase history, and browsing patterns to suggest products people might actually want. It often runs on machine learning models and can be updated and scaled on its own, so you can test new algorithms without breaking the checkout process.
The infographic below really brings to life the principles of responsibility, governance, and deployment that allow these services to work together while staying independent.
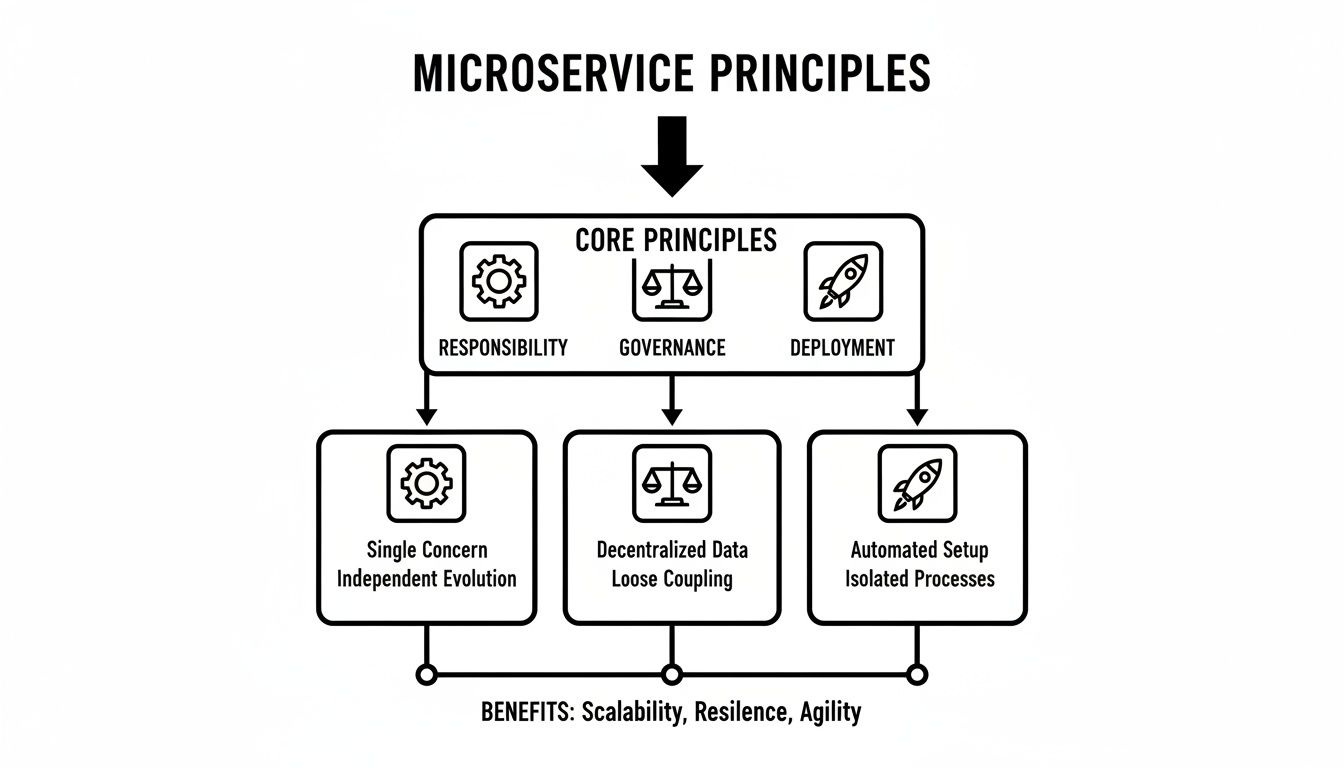
This diagram shows how each service is built on the principles of single responsibility, decentralized governance, and independent deployment, allowing the entire system to be more agile and resilient.
How These Services Talk to Each Other
These services aren't working in silos; they're constantly chatting. This is where Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and message queues come into play. For instance, when you add an item to your cart, the Shopping Cart service makes a quick API call to the Product Catalog service to double-check the price and stock level. This is synchronous communication—it needs an immediate answer.
But not everything needs to happen instantly. When an order is placed, the Order Processing service might just drop a message onto a queue. The Shipping and Notification services can then pick up that message and act on it asynchronously, whenever they're ready. This decouples the services beautifully. A slowdown in the email system won't grind the entire order process to a halt.
Key Insight: This mix of synchronous and asynchronous communication is the secret sauce. It makes the system feel responsive for user-facing actions (like adding to a cart) while being incredibly resilient for backend processes (like fulfillment). It prevents a bottleneck in one small service from causing a system-wide meltdown.
The Power of the Polyglot Approach
One of the biggest wins with this structure is technological freedom, often called a polyglot approach. Different services have different problems to solve, so why force them all to use the same tech stack?
Let’s look at our e-commerce platform again:
- The Shopping Cart Service needs to be incredibly fast. A team might pick Node.js for its amazing performance with I/O-heavy tasks.
- The Order Processing Service demands transactional integrity and rock-solid stability. A proven, enterprise-grade language like Java or C# (.NET) is a perfect fit here.
- The Recommendation Engine is all about data science. The team building it would almost certainly use Python with powerhouse libraries like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
This flexibility lets each team choose the absolute best tool for their specific job. The result? Better performance, happier and more productive developers, and more room for innovation. It's a world away from the one-size-fits-all prison of a monolith. This practical microservice architecture example shows how breaking a complex system into focused, manageable pieces creates something far more scalable, resilient, and ready for whatever comes next.
Navigating the Challenges of Microservices
While the benefits of going with a microservice architecture are huge, it’s best to go in with your eyes wide open. This approach is powerful, but it’s definitely not a magic bullet for every single project. Adopting microservices brings a whole new layer of complexity that can easily become a massive headache if you’re not ready for it.
Think of it like this: you're swapping a single, reliable family minivan for a fleet of high-performance motorcycles. Suddenly you have way more speed and agility, but you also have more engines to maintain, more parts to track, and a whole crew of drivers to coordinate. The operational overhead can multiply in a hurry.
The Rise of Distributed Complexity
One of the biggest hurdles is simply managing a distributed system. Instead of one application to keep an eye on, you might suddenly have dozens of independent services. This creates some very specific challenges that teams have to tackle head-on.
- Increased Operational Overhead: Every single service needs its own deployment pipeline, its own monitoring, and its own alerts. This demands a mature DevOps culture and serious automation to keep your operations team from getting completely swamped.
- Complex Troubleshooting: When a bug pops up, it might not be neatly contained in one service. Tracking down an issue that spans multiple services—each with its own set of logs—is like solving a mystery where the clues are scattered all over town.
- Data Consistency Conundrums: Since each service is in charge of its own database, keeping data consistent across the entire system gets tricky. Simple database transactions are off the table, forcing teams into complex patterns like sagas to handle operations that touch multiple services.
This distributed complexity isn't just a hypothetical problem. We're actually seeing a growing trend of "re-monolithing," where teams switch back because of these unforeseen operational nightmares. A recent Gartner report found that 60% of development teams regret using microservices for small-to-medium-sized apps. Some companies are even seeing cost reductions of up to 25% by consolidating back to a simpler monolith. You can dig into some more of these market trends and challenges if you're curious.
When Is It Overkill?
For a small startup with a straightforward app or a team that’s still finding its groove, jumping straight into microservices can be a costly and unnecessary distraction. The investment in tooling, infrastructure, and specialized skills often far outweighs any benefits you might get.
Honestly, a well-structured monolith can be much faster to build and easier to manage in the early days. The trick is to avoid building a "big ball of mud." Instead, focus on creating a modular monolith that can be more easily broken apart into microservices down the road, if and when the business complexity actually calls for it.
Crucial Consideration: Before you commit to a microservice architecture, take a hard, honest look at your project's scale, your team's expertise, and your business goals. The most successful moves to microservices happen when the architecture directly solves a specific, painful problem—not just because it's the trendy thing to do.
At the end of the day, the goal is to build a system that's both scalable and maintainable. That requires a rock-solid foundation in automation and continuous delivery. To make sure your deployment strategy is up to the task, it’s worth reviewing some CI/CD pipeline best practices that can support either architectural style. This kind of prep work will help you sidestep the common traps and make a smart decision that sets your project up for success in the long run.
Modernizing Your App with AI-Powered Microservices
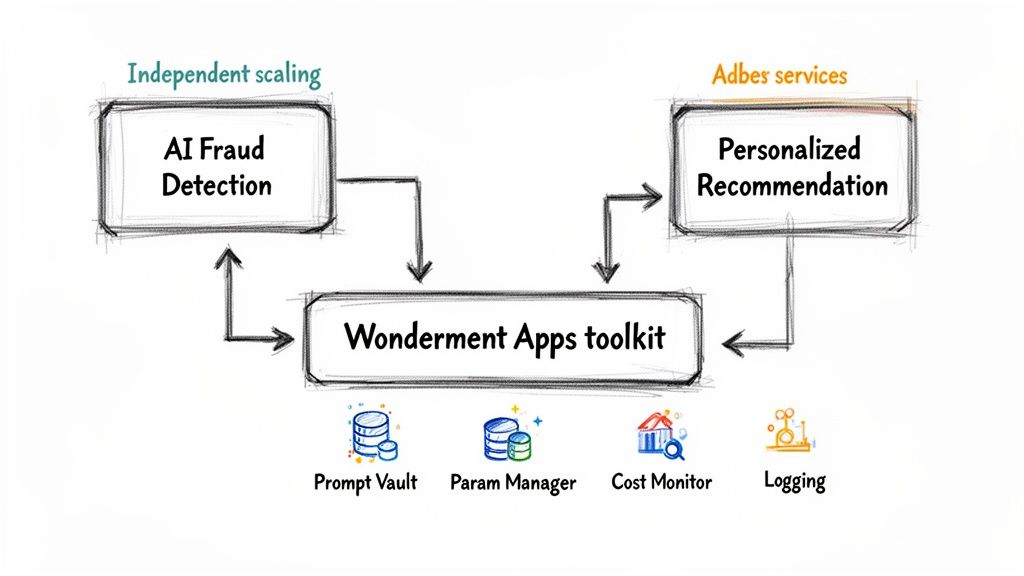
This is where a microservice architecture example becomes a real game-changer for innovation, especially when you start weaving in Artificial Intelligence. The very nature of microservices—small, independent, and focused—makes adding sophisticated AI features much simpler and safer than trying to shoehorn them into a rigid, monolithic app.
Think about upgrading your e-commerce platform. Instead of a high-stakes, system-wide overhaul, you can spin up dedicated, independent services for new features. You could build an "AI Fraud Detection" service that analyzes transactions for sketchy patterns, or a "Personalized Recommendation" engine that learns from customer behavior on the fly.
Each of these AI-driven units can be built, tested, and scaled entirely on its own. This independence is everything. Your core application—handling checkouts, user accounts, and product catalogs—stays stable and untouched, while your AI teams have the freedom to experiment and deploy new models without breaking things.
Taming the Complexity of AI Integration
While adding AI features one service at a time is a powerful approach, it does bring its own kind of complexity. Suddenly, you're juggling multiple AI models, fine-tuning countless prompts, and trying to keep track of new costs. This is exactly the problem Wonderment Apps' toolkit was built to solve, giving you the administrative layer needed to stay in control.
Our platform is designed to manage the unique challenges that come with an AI-powered microservice ecosystem. It essentially acts as a central nervous system for all your AI integrations, making sure everything is consistent, observable, and cost-effective.
Here’s how our toolkit helps you modernize with confidence:
- Version-Controlled Prompt Vault: Keeps every AI interaction across all your services consistent and repeatable. You can test new prompts, roll them back if needed, and deploy with confidence, always knowing which version is live.
- Parameter Manager: Gives you a secure, central hub to manage access to internal databases and other data sources. This allows your AI models to get the information they need without putting your security at risk.
- Unified Logging System: Pulls logs from every single AI service into one place. This delivers complete observability, making it much easier to troubleshoot issues and see how different AI components are working together.
- Comprehensive Cost Manager: Provides a clear, real-time dashboard showing your cumulative AI spending across all providers. This transparency helps you manage budgets and avoid nasty surprises as you scale your AI features.
As you start modernizing your app with AI, it’s worth digging into a practical guide to AI software engineering, which breaks down the essential tools, workflows, and principles for success. This kind of knowledge helps you build a solid foundation for any intelligent, scalable system.
Building Intelligent and Scalable Applications
When you combine a microservice architecture with a strong management toolkit, you create the perfect environment for building truly intelligent apps. You get the agility to innovate quickly without sacrificing the stability of your core business functions.
For instance, your e-commerce site can keep running its rock-solid payment processing service while your data science team deploys a brand-new version of the recommendation engine. The risk is completely isolated, but the potential upside is huge. This separation of concerns lets you build a system that’s not just powerful today but is ready to adapt to whatever AI advancements come next.
The Wonderment Advantage: We help you tap into the full potential of AI within a scalable, manageable framework. Our tools are built to give you firm control over your entire AI ecosystem, turning what could be overwhelming complexity into a strategic advantage.
By treating AI features as their own independent microservices, you’re creating a future-proof architecture. This approach, backed by the right administrative tools, lets you build applications that can learn, adapt, and scale to meet your users' needs for years to come.
Your Questions About Microservices Answered
Making the leap to a new architectural style always kicks up a lot of questions. It doesn't matter if you're a business leader thinking about strategy or a developer deep in the technical weeds—you need clear, straight answers. This section is here to cut through the jargon and tackle the most common questions people have when they see a microservice architecture example.
We’ll get into team structures, how services talk to each other, migration plans, and data management. The goal is to clear up any confusion so you can move forward with confidence.
What Is the Ideal Team Size for Managing a Microservice?
You’ve probably heard of the "Two-Pizza Rule," made famous by Amazon. It’s a simple but brilliant idea: a development team should be small enough that you can feed the whole group with two large pizzas. That usually works out to a team of five to ten people.
This isn't just about being frugal with the food budget; it’s a core organizational philosophy. Smaller teams naturally create a stronger sense of ownership and autonomy, and communication is just plain easier. In a microservices world, each two-pizza team can own the entire lifecycle of its service—from coding and design all the way to deployment and maintenance. This setup is a perfect mirror of the architecture itself, letting teams ship updates independently, which is really the whole point.
How Do Microservices Communicate with Each Other?
Since microservices are self-contained, they need a solid way to talk to one another. They do this through APIs, which usually fall into two main camps.
First, there’s synchronous communication. Think of it like a phone call. One service sends a request and then has to wait for an immediate response before it can do anything else. This is usually handled with HTTP/REST protocols and works great for things that need a fast answer, like a real-time inventory check on an e-commerce site.
The other style is asynchronous communication, which is more like sending a text. A service shoots a message or an event to a message broker (like RabbitMQ or Apache Kafka) and then gets back to its own work without waiting for a reply. Other services can then grab that message and deal with it on their own time. This asynchronous method is key for building resilient, scalable systems because it decouples services. A delay in one service won't cause a massive traffic jam across your whole application.
How Do You Migrate from a Monolith to Microservices?
Whatever you do, don't try a "big bang" rewrite where you replace the whole monolith in one go. That approach is incredibly risky and almost never works out. The smarter, proven path is a gradual one called the Strangler Fig Pattern.
The name comes from a vine that slowly wraps itself around a host tree until it eventually takes over. In the software world, you start by building new features as separate microservices that live alongside your monolith. Then, over time, you strategically pick pieces of the monolith—like user authentication or payments—and carefully carve them out, rebuilding them as new, independent services.
The Strangler Fig Pattern in Action: These new services gradually steal responsibilities from the old application, piece by piece. This methodical process keeps disruption to a minimum, lowers risk, and gives your team time to learn the new architecture as you go, making the entire transition much smoother.
How Do You Handle Data Consistency Across Services?
This is easily one of the biggest headaches in any distributed system. Because each microservice has its own database, you can't use traditional database transactions that lock multiple tables at once. You have to get comfortable with a concept called eventual consistency.
A common way to pull this off is with the Saga pattern. Imagine a business process that touches multiple services, like placing an order. In a saga, each service does its own local transaction and then fires off an event to say, "I'm done." The next service in the chain is listening for that event and kicks off its own task.
If something goes wrong along the way, the saga initiates a series of compensating transactions to undo the work that was already completed. For instance, if the payment service fails, a compensating transaction tells the inventory service to put the item back in stock. It’s how you keep your data in sync across the system without tying all your databases together.
Modernizing your application with a microservice architecture, especially one enhanced with AI, opens up incredible possibilities for scalability and innovation. But managing the new complexity requires the right tools. Wonderment Apps provides a complete AI modernization toolkit, including a version-controlled prompt vault, a parameter manager for secure data access, unified logging, and a cost manager to keep you in full control.
Ready to see how you can build intelligent, scalable applications without the headaches? Schedule a demo with Wonderment Apps today.
