Building a Fortress, Not Just a Fence
Let's get straight to the point: most API breaches aren't the work of criminal masterminds cracking impossible codes. They happen when an attacker finds an unlocked front door—often an authenticated session with way too many permissions—and simply walks right in.
This new reality has completely reshaped the threat landscape, making rock-solid API security an urgent priority for any modern application, especially as businesses look to integrate AI into their custom software. This guide will walk you through the tips and tricks business leaders need to make their software initiatives successful and secure.
Why Weak API Authentication Is a Ticking Time Bomb
The days of just slapping an API key on an endpoint and calling it a day are long gone. Today's interconnected software, especially with the rise of AI integrations, creates a massive attack surface. Every single endpoint is a potential entry point, and if your authentication is weak, it's a huge liability.
Ignoring API security isn't a calculated risk; it's a guaranteed future cost. The fallout goes way beyond a temporary system outage. We're talking direct financial losses, eroded customer trust, and serious reputational damage that can take years to rebuild.
The stats paint a pretty stark picture. A recent report found that a staggering 99% of organizations had at least one API security incident in the last year. What's more telling is that 95% of these attacks came from authenticated sessions, which proves that just verifying who someone is isn't nearly enough. These breaches aren't cheap either, costing businesses an average of $591,404 to clean up. You can dig into the full research about these API security stats to see just how big the problem is.
This is exactly why at Wonderment Apps, we don't just tack security on at the end. We build it into the core of every AI-ready application from day one.
API security isn't just about keeping unauthorized people out. It's about making sure that even authorized users can only do what they're explicitly supposed to do. This minimizes the blast radius if their credentials ever get compromised.
As businesses integrate powerful AI models into their software, the need for stringent access controls becomes even more critical. These integrations often need access to sensitive internal data and can rack up huge operational costs if they're misused. To tackle this, Wonderment has developed a prompt management system—an administrative tool that developers and entrepreneurs can plug into their existing app or software to modernize it for AI integration securely. We'll go into more detail about this tool later on, but if you're curious now, you can schedule a demo to see it in action.
Choosing Your Armor: A Guide to Modern Authentication Schemes
Not all authentication methods are created equal. When it comes to securing your API, think of your authentication scheme as a suit of armor—you need the right type of protection for the battle you're facing. Choosing the wrong one can leave you vulnerable, while the right one becomes the foundation of your entire security posture.
This isn't just a technical decision; it's a strategic one that directly impacts your application's risk profile and scalability. To make an informed choice, we need to move beyond jargon and understand how each method works in a real-world context. A clear grasp of these options is a core component of strong API authentication best practices.
The following decision tree shows just how quickly a seemingly secure, authenticated API can become the primary breach vector if security isn't layered correctly.
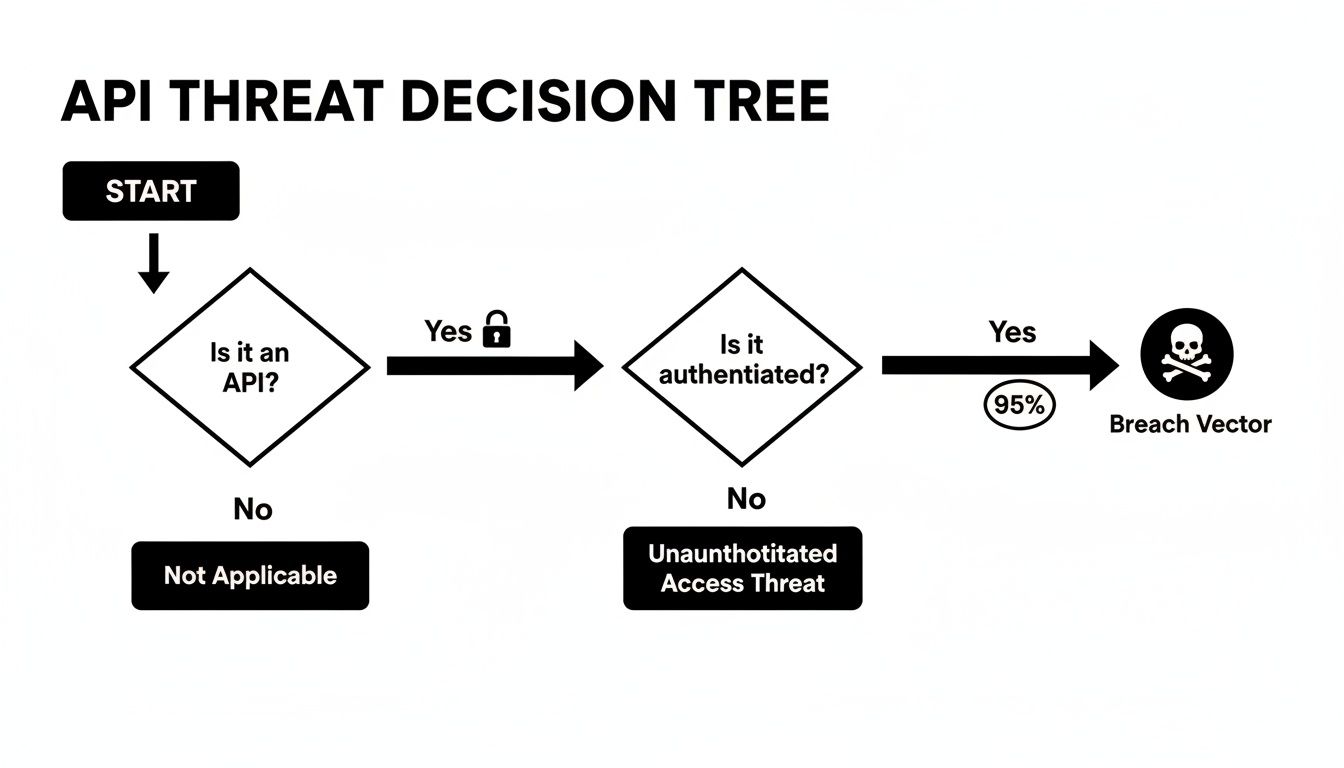
This visual drives home a critical point: since the vast majority of attacks target authenticated sessions, the strength of your chosen scheme is absolutely paramount.
To help you navigate this, let's break down the four most common authentication schemes you'll encounter. Each has its own strengths and is built for different scenarios.
OAuth 2.1: The Delegated Access Standard
OAuth 2.1 is the modern gold standard for authorization, especially when you need to grant a third-party application limited access to a user's data without sharing their credentials. Think of it like a modern hotel key card. When you check in, the front desk (the authorization server) verifies your identity and gives you a key card (an access token). That card only opens your room (a specific resource) for a limited time.
You never give the valet your master key; you delegate specific, temporary access. This is the magic behind features like "Log in with Google" or allowing a financial planning app to read your bank transactions without it ever seeing your actual banking password.
OAuth 2.1 is designed for delegated authorization, not just authentication. It's the ideal choice for user-facing applications where you need to manage permissions for third-party services securely and with granular control.
This method expertly separates the roles of the resource owner (the user), the client (the application), and the authorization server, creating a secure workflow that prevents credential exposure.
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs): The Digital Passport
While often used alongside OAuth, JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are a powerful mechanism on their own. A JWT is a compact, self-contained "digital passport" that carries information about a user's identity and permissions. When a user logs in, the server issues a JWT that is cryptographically signed.
For every subsequent API request, the client simply sends this JWT in the header. The server can then verify the token's signature to confirm its authenticity without needing to look up the user in a database for every single call. This stateless approach makes JWTs incredibly scalable and efficient for modern microservices architectures.
The key benefits of using JWTs include:
- Statelessness: Each token contains all the information needed for verification, reducing server load.
- Portability: JWTs can be easily passed between different services in a distributed system.
- Security: A digital signature ensures that the token's contents haven't been tampered with.
API Keys: The Simple Gatekeeper
Classic API keys are the simplest form of authentication. An API key is just a long, unique string that a server generates and assigns to a client. The client then includes this key in its requests to identify itself.
While they are dead simple to implement, API keys are essentially static, long-lived passwords. If an API key is leaked, an attacker can use it indefinitely until it's manually revoked. Because of this, API keys are best suited for simpler, lower-risk scenarios like:
- Server-to-server communication within a trusted network.
- Tracking API usage for billing or analytics purposes.
- Providing public data access with basic rate limiting.
For anything involving sensitive data or user permissions, you should absolutely reach for a more robust, token-based method.
Mutual TLS (mTLS): The Ultimate Security Handshake
For the highest level of security, particularly in machine-to-machine communication, Mutual TLS (mTLS) is the ultimate solution. Standard TLS (the "S" in HTTPS) only involves the client verifying the server's identity. It's a one-way street.
With mTLS, the process goes both ways: the client verifies the server, and the server verifies the client. Both parties present a cryptographic certificate to prove their identity before any communication even begins. This creates a highly secure, encrypted channel where you can be certain that both ends of the connection are exactly who they claim to be.
It’s the digital equivalent of a secret handshake between two trusted machines, making it ideal for protecting internal microservices or high-stakes financial and healthcare APIs.
Comparing Popular API Authentication Schemes
Choosing the right scheme is all about matching the tool to the job. The table below offers a side-by-side look at these methods to help you decide which armor fits your API best.
| Scheme | Primary Use Case | Security Level | Complexity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OAuth 2.1 | Third-party delegated access | High | High | User-facing apps that need to integrate with other services (e.g., "Log in with Google"). |
| JWTs | Stateless authentication | High | Medium | Microservices architectures and single-page applications where scalability is key. |
| API Keys | Simple service identification | Low | Low | Public APIs, internal services with low-risk data, and usage tracking. |
| mTLS | Machine-to-machine authentication | Very High | High | Zero-trust networks, fintech/healthcare APIs, and securing internal microservice traffic. |
Ultimately, the best choice depends entirely on your specific threat model, the sensitivity of the data you're protecting, and the types of clients that will be consuming your API. For many modern applications, a combination of these methods (like using JWTs within an OAuth 2.1 flow) often provides the most comprehensive security.
The Principle of Least Privilege Securing Your Digital Kingdom
Giving an API key unlimited access is like handing a valet the keys to your house, your car, and your safe deposit box when all they need to do is park your car. It’s a massive, unnecessary risk. If that one master key falls into the wrong hands, the damage could be catastrophic.
This is where one of the most fundamental concepts in all of security comes into play: the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP).
The idea is simple but incredibly powerful. It states that any user, application, or process should only have the absolute minimum permissions required to do its job. Nothing more. By aggressively limiting access rights, you shrink your application's attack surface and contain the fallout from any potential security breach.
This isn’t just a good idea; it’s a cornerstone of modern API authentication best practices. It’s about shifting from a reactive "what happened?" mindset to a proactive security posture.
Defining Granular Scopes and Permissions
In the world of APIs, you apply the Principle of Least Privilege through scopes and permissions. Instead of issuing a single, all-powerful key, you break down access into granular permissions tied to specific actions. This turns your authorization model from a blunt on/off switch into a sophisticated control panel.
Let’s say you're building an e-commerce platform that integrates with a third-party shipping app. What does that app really need to do?
- It needs to read order information to know what to ship and where.
- It needs to write a tracking number back to that order record once it's shipped.
That’s it. That app has no business modifying product prices, viewing customer credit card details, or deleting user accounts. Granting it the ability to do any of those things is a glaring security hole waiting to be exploited.
By defining clear, task-oriented scopes, you ensure that even if a third-party application's token is compromised, the blast radius is tiny. An attacker could only perform the limited actions of reading orders and writing tracking data—a far less catastrophic scenario than having full control.
This is where you’d define specific scopes like orders:read and shipments:write. When the shipping app authenticates, it can only request these specific permissions. Your system, likely at the API gateway, then enforces these rules, flatly rejecting any call trying to hit an endpoint outside this limited authorization.
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Defining individual scopes is the first step. The next is organizing them so you don't go crazy managing them. This is where Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a lifesaver. RBAC simplifies permission management by bundling individual permissions into logical roles that map directly to user types or job functions.
Instead of trying to assign dozens of specific scopes to every single service or user, you just assign them a role. For example:
- Shipping Clerk Role: Gets
orders:readandshipments:writescopes. - Customer Service Rep Role: Gets
orders:readandcustomer_address:updatescopes. - Store Admin Role: Gets
products:create,products:update, andproducts:deletescopes.
This approach doesn’t just make administration cleaner; it makes security audits infinitely easier. Need to know what a user can do? Just check their role, instead of trying to decipher a long list of cryptic permissions. It’s a clean, scalable way to enforce least privilege across your entire ecosystem.
Following this principle is also critical for data privacy. It's a foundational concept for building GDPR compliant software and integration practices because it protects user data by design.
Ultimately, a well-structured RBAC system is one of the most effective security layers you can build. To see how this fits into the bigger picture, you can explore other key data security concepts that complement a strong API strategy. By combining granular scopes with logical roles, you build a digital kingdom where every key opens only the necessary doors, keeping your most valuable assets safe and sound.
Mastering Token Lifecycle: Rotation, Storage, and Transmission
Once an authentication token is issued, it becomes a powerful key to your kingdom. If that key gets lost, stolen, or copied, your entire system is at risk. That’s why managing the full lifecycle of a token—from its birth to its expiration—is a non-negotiable part of modern API authentication.
Effective management isn't a one-and-done deal. It's a continuous cycle of rotation, secure storage, and safe transmission. The best way to think about a token is as a temporary pass, not a permanent key. Your goal is to keep its lifespan and exposure to an absolute minimum, so if it ever falls into the wrong hands, the window of opportunity for an attacker is incredibly small.
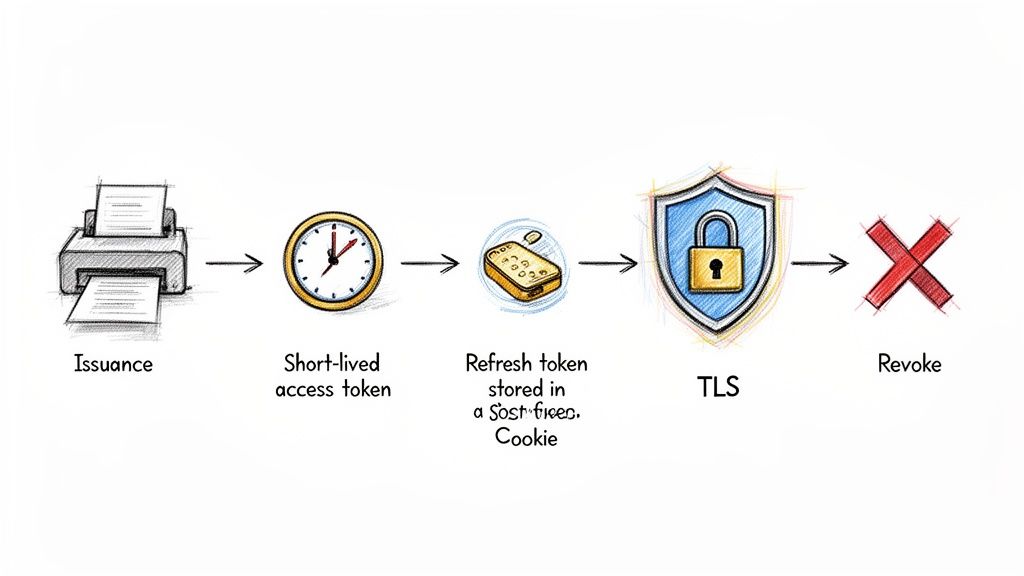
This operational knowledge is crucial for building resilient systems, especially as you scale. In fact, solid token management is fundamental to creating secure, independent services—a topic we explore further in our guide to microservices architecture best practices.
The Short-Lived Access Token and Long-Lived Refresh Token Strategy
One of the most effective strategies for balancing tight security with a smooth user experience is pairing short-lived access tokens with long-lived refresh tokens. This is the standard approach used in OAuth 2.1, and it’s a game-changer for token lifecycle management.
Here’s the breakdown:
- Access Token: This is the token sent with every API request to access protected resources. It's designed to have a very short lifespan, typically just 15 to 60 minutes. If it leaks, it becomes useless almost immediately.
- Refresh Token: This token has a much longer life, from hours to even months. Its only job is to request a new access token when the old one expires. It’s stored securely on the client and is only sent to a special, highly protected endpoint.
This two-token system means the powerful, long-lived refresh token is exposed far less often, drastically cutting its risk of being intercepted. Meanwhile, the short-lived access token can be transmitted more freely, since its value evaporates so quickly.
This strategy effectively shrinks your attack surface. A compromised access token grants only a few minutes of access, while the more valuable refresh token remains securely stored and is used infrequently, providing an excellent balance of usability and security.
Secure Token Storage Best Practices
Where you store tokens on the client-side is just as important as how you create them. Storing them improperly is like leaving your house keys under the welcome mat—it’s the first place an attacker will look.
For web applications, the debate often comes down to HTTP-Only Cookies vs. Local Storage. The clear winner here is secure, HTTP-only cookies. Here’s why:
- HTTP-Only Cookies: These cookies are inaccessible to client-side JavaScript. This gives you built-in protection against Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks, where an attacker injects malicious scripts to steal sensitive data.
- Local Storage: Tokens stored here are completely exposed to any JavaScript running on the page. A single XSS vulnerability could allow an attacker to easily snatch the token and impersonate the user.
For mobile apps, tokens should always be stored in the platform’s native secure storage, like the Android Keystore or iOS Keychain. These are encrypted, hardware-backed containers designed specifically for this kind of sensitive information.
Enforcing Secure Transmission with TLS
Finally, a token is only as secure as the channel it travels through. Transmitting tokens over an unencrypted connection is a catastrophic mistake, opening the door for attackers to easily intercept them in a "man-in-the-middle" attack.
It is absolutely mandatory to enforce Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 or higher for all API communication. TLS encrypts the entire data stream between the client and the server, making it unreadable to anyone snooping on the network. There are no exceptions to this rule.
By mastering these three pillars—a smart rotation strategy, secure storage, and encrypted transmission—you can build a robust token management system that protects your data, your users, and your reputation.
Building Your API Security Watchtower
Even the most fortified castle needs guards on the walls. In the same way, the strongest API authentication needs a vigilant monitoring system—a digital watchtower—to spot threats in real time. Nailing your authentication schemes is a critical first step, but a proactive security posture demands continuous observation. Without it, you're flying blind, unable to tell the difference between normal traffic and a brewing attack.
This is where logging, monitoring, and alerting come together. A well-designed security watchtower doesn't just record events; it gives you the intelligence to detect suspicious activity, respond to incidents swiftly, and harden your defenses over time. It transforms your security from a static set of rules into a dynamic, living system that adapts to new threats.
What to Log and What to Leave Out
Effective logging is a balancing act. You need enough detail to reconstruct security events without blowing up user privacy or creating a new security risk. If you log too much sensitive data, your logs suddenly become a treasure trove for attackers.
Here’s a practical guide on what should—and shouldn't—be in your authentication logs:
Log These Events:
- Successful and Failed Authentication Attempts: This is the absolute baseline. Always log the timestamp, source IP address, and user ID (if applicable).
- Token Validation Failures: When a token gets rejected, log the reason. Was it expired, invalid, or did its signature not match?
- Changes to Permissions or Roles: Track any event where a user's or service's permissions are elevated or modified.
- API Key Rotation Events: Note when keys are created, revoked, or rotated to maintain a clear audit trail.
Never Log These:
- Raw Tokens or API Keys: Storing these credentials in logs is a massive security risk. If the logs are breached, every single key is compromised.
- Passwords or Password Hashes: This is non-negotiable. This kind of sensitive information should never, ever appear in application logs.
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Avoid logging full names, addresses, or other sensitive user data unless it's absolutely required for compliance—and even then, it should be heavily protected.
Setting Up Automated Alerts
Logs are only useful if someone is actually watching them. Automated alerts turn your passive log data into an active threat detection system, pinging your team the moment something smells fishy. Your goal here is to catch anomalies before they escalate into full-blown breaches.
An effective alerting system acts as your digital tripwire. By defining specific, high-risk patterns, you can move from finding out about breaches after the fact to stopping them as they happen.
Think about setting up alerts for these critical security indicators:
- Multiple Failed Logins from a Single IP: A classic sign of a brute-force attack. An alert after five failed attempts in a minute can give you time to block the IP.
- A Token Used Outside Its Defined Scope: If a token with
orders:readpermission suddenly tries to hit an endpoint for deleting products, that's a major red flag. - An Impossible Travel Scenario: A user logs in from New York. Five minutes later, the same user logs in from Tokyo. One of those sessions is almost certainly compromised.
- Sudden Spike in API Usage: A massive, out-of-the-blue increase in requests from a single client could indicate a compromised key or an attempt to overwhelm your system.
A key part of building a robust API security watchtower is conducting comprehensive cybersecurity risk assessments to figure out which threats are most relevant to your specific application.
Your High-Level Incident Response Checklist
When an alarm does go off, a clear, practiced plan is your best defense against chaos. An incident response plan makes sure your team acts quickly and effectively to minimize the damage. While a full plan is extensive, every team should start with this high-level checklist:
- Contain the Breach: The first priority is to stop the bleeding. This might mean revoking a compromised API key, blocking a suspicious IP address, or temporarily disabling an affected service.
- Assess the Damage: Once it's contained, investigate the scope. What data was accessed? Which systems were affected? This step is crucial for understanding the true impact.
- Eradicate the Threat: Identify the root cause of the breach—was it a leaked key, a software vulnerability, or something else entirely?—and make sure the attacker is fully removed from your systems.
- Recover and Restore: Bring the affected systems back online safely. This may involve restoring from backups or deploying patched software.
- Learn and Improve: Conduct a post-mortem to understand what went wrong and how you can prevent it from happening again. This final step is vital for improving your overall security posture.
Building a security watchtower is a core piece of a holistic defense strategy. For more insights on this topic, check out our complete guide on https://www.wondermentapps.com/blog/application-security-best-practices/.
Modernize and Secure Your App with Wonderment
Juggling robust API authentication best practices while pushing forward with AI innovation can feel like walking a tightrope. The principles we’ve covered—from least privilege to diligent monitoring—aren’t just items on a checklist. They're the very foundation of any modern, scalable, and secure application that real people will trust and use.
This is where Wonderment Apps comes in. We don't just build software; we engineer digital products where security is baked into the architecture from day one, not bolted on as an afterthought. Our team thrives on navigating these complexities for you, ensuring that every application we deliver is both cutting-edge and built on a zero-trust foundation.
Bridge the Gap Between Security and AI Innovation
Bringing AI into your existing software stack adds a whole new layer of complexity, especially around data access and security. How do you let a large language model access your internal database without opening the floodgates to sensitive information? How do you manage and protect the valuable AI prompts that form your competitive advantage?
We built our proprietary AI administrative toolkit—the Wonderment Prompt Management System—to solve these exact problems. It’s designed to help you modernize your application with AI without having to compromise on security.
Our toolkit is a secure bridge to the future. It lets you integrate powerful AI capabilities while maintaining ironclad control over your data, costs, and intellectual property. It’s all about enabling innovation—securely.
A Security-First AI Management System
This toolkit is far more than a simple connector. It's a comprehensive management system built on the very security principles we've discussed in this guide. It gives entrepreneurs and developers the controls to implement best practices without the hassle of building them from scratch.
Here’s how its core features create a powerful security posture:
- Prompt Vault with Versioning: Your prompts are incredibly valuable IP. Our vault secures them, tracks every change, and ensures only authorized services can ever access them. This protects you from prompt injection attacks and outright theft.
- Parameter Manager for Database Access: This feature is all about enforcing the principle of least privilege at the data level. You can define exactly which internal database parameters an AI model can touch, preventing broad, unauthorized data exposure.
- Logging System Across All Integrated AIs: Our toolkit provides the visibility you need for your security watchtower. It logs every single interaction across your integrated AI models, giving you a crystal-clear audit trail to spot anomalies.
- Cost Manager: Get full transparency into your cumulative spend. By tracking token usage and costs across all integrated AI platforms, you can instantly detect unusual spikes in activity that might signal misuse or a compromised service.
All these pieces work in concert to ensure your application is not only intelligent but also resilient and built to last for many years to come.
If you’re ready to modernize your software with AI securely and efficiently, let's talk. Schedule a demo of our AI administrative toolkit and see firsthand how we can help you build your next great application the right way.
Frequently Asked Questions About API Authentication
Even with a rock-solid plan, questions are bound to pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common things that come up when putting API authentication best practices into action.
What Is the Single Biggest Mistake in API Authentication?
Hands down, the most dangerous mistake is relying on long-lived, static API keys that have way too many permissions. Teams often treat these as a "set it and forget it" solution. But if one of these keys gets leaked—whether from a public code repository or a compromised developer's laptop—it’s like handing an attacker a permanent, all-access pass to your systems.
The right way to think about this is to use short-lived tokens, like JWTs issued through OAuth 2.1, that expire quickly. When you pair that approach with the principle of least privilege, you drastically shrink both the window of opportunity and the potential damage from a breach.
How Often Should I Rotate Keys and Tokens?
The rotation schedule really depends on what kind of credential you're talking about.
- Short-Lived Access Tokens (JWTs): These should have a very brief life, usually somewhere between 15 and 60 minutes. They get renewed using a securely stored, long-lived refresh token.
- Static API Keys: When you absolutely need them for server-to-server communication, a rotation policy of every 90 days is a good security baseline. More importantly, you must have an automated process ready to rotate them instantly if you even suspect a compromise.
Is OAuth 2.1 Overkill for an Internal API?
Not always. While OAuth 2.1 can feel like a heavy lift for simple internal services, its security benefits are huge in a zero-trust world where you can't automatically trust any service, internal or not.
For very simple, low-risk internal machine-to-machine communication, a securely managed API key combined with mTLS can work just fine. However, if that internal service might one day be exposed to third parties or if it handles any sensitive data, starting with an OAuth 2.1 framework is a much smarter, more scalable long-term strategy.
Implementing these security principles while modernizing your app with AI can get complex. The team at Wonderment Apps specializes in building secure, scalable applications with integrated AI capabilities, founded on these best practices. Our proprietary AI toolkit provides the controls you need to innovate safely.
Ready to build an application that's both intelligent and secure? Schedule a demo with Wonderment Apps today.
