Software engineering has become the central nervous system of modern medicine. It’s no longer just about digital record-keeping; it’s the engine driving diagnostics, creating personalized treatment plans, and fundamentally changing how patients engage with their own care. It's truly mission-critical for delivering better outcomes, especially when modernizing applications with AI.
But let's be honest, integrating AI into healthcare software can feel daunting. How do you harness its power without introducing new risks? The secret is having the right administrative tools from day one. For instance, a robust prompt management system acts as a central command center for all AI interactions, ensuring developers can build amazing, scalable app experiences while maintaining strict control over compliance, security, and costs. This is the key to building AI-powered software that lasts.
Building the Future of Patient Care
Think of building a modern healthcare application like constructing a state-of-the-art hospital. You wouldn’t start laying bricks without a detailed blueprint. The same principle applies here. A successful project requires so much more than code—it demands a deep, practical understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities inside the medical world.
A hospital needs specialized departments that all work together seamlessly, and healthtech software is no different. It depends on interoperability—the ability for different systems to communicate. It also requires an almost fanatical adherence to safety codes, which in our world means ironclad compliance with regulations like HIPAA. And, of course, the entire structure has to be scalable to handle ever-growing patient loads and data volumes.
The Foundation of Modern Healthtech
Building great software for this sector is a balancing act between technical excellence and genuine empathy for clinicians and patients. You have to nail a few key things:
- Robust Architecture: Your system has to be secure, reliable, and capable of growing without buckling under pressure.
- Strict Compliance: Every line of code and every single data transaction must adhere to legal and ethical standards for protecting patient information. No exceptions.
- Seamless Interoperability: This means using standards like FHIR and HL7 so that different electronic health records and apps can securely share data.
So many innovative healthtech solutions come from tailoring technology to very specific clinical needs, which really shows the value of transforming your business with custom software development. A custom approach ensures the final product actually works in the real, complex world of medicine.
The Role of AI in Healthcare Software
These days, artificial intelligence is a game-changer for modernizing healthcare applications. AI can help predict disease, automate mind-numbing administrative tasks, and personalize patient care in ways we could only dream of a decade ago. But integrating AI responsibly adds a whole new layer of complexity.
To manage AI effectively, you need strong governance. This is where a dedicated prompt management system becomes an indispensable tool. It acts as the administrative backbone, letting developers control, version, and monitor all AI interactions. This ensures every AI-driven feature is safe, compliant, and cost-effective, smoothing the path to adoption.
This market is exploding. The healthcare SaaS market was valued at USD 34.84 billion in 2024 and is projected to shoot past USD 94.56 billion by 2034.
If you're just getting started, our founder's guide to custom healthcare application development is a great place to build some foundational knowledge.
Understanding Healthtech's Non-Negotiable Rules
In the world of healthtech, software engineering carries a weight unlike almost any other industry. If a retail app has a bug, maybe a customer gets annoyed. But a flaw in a healthcare application? That could compromise patient safety or expose incredibly sensitive personal data. This is exactly why the field is governed by a set of non-negotiable rules that put trust, privacy, and security above everything else.
These rules aren't just red tape; they're the essential blueprints for building systems people can depend on with their lives. Regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and Europe's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) form the bedrock of patient data privacy. They dictate everything from how data is stored and encrypted to who is allowed to access it and why.
This all circles back to a single, central mission: patient care. Every technical decision, from architecture to AI integration, has to serve this primary goal.
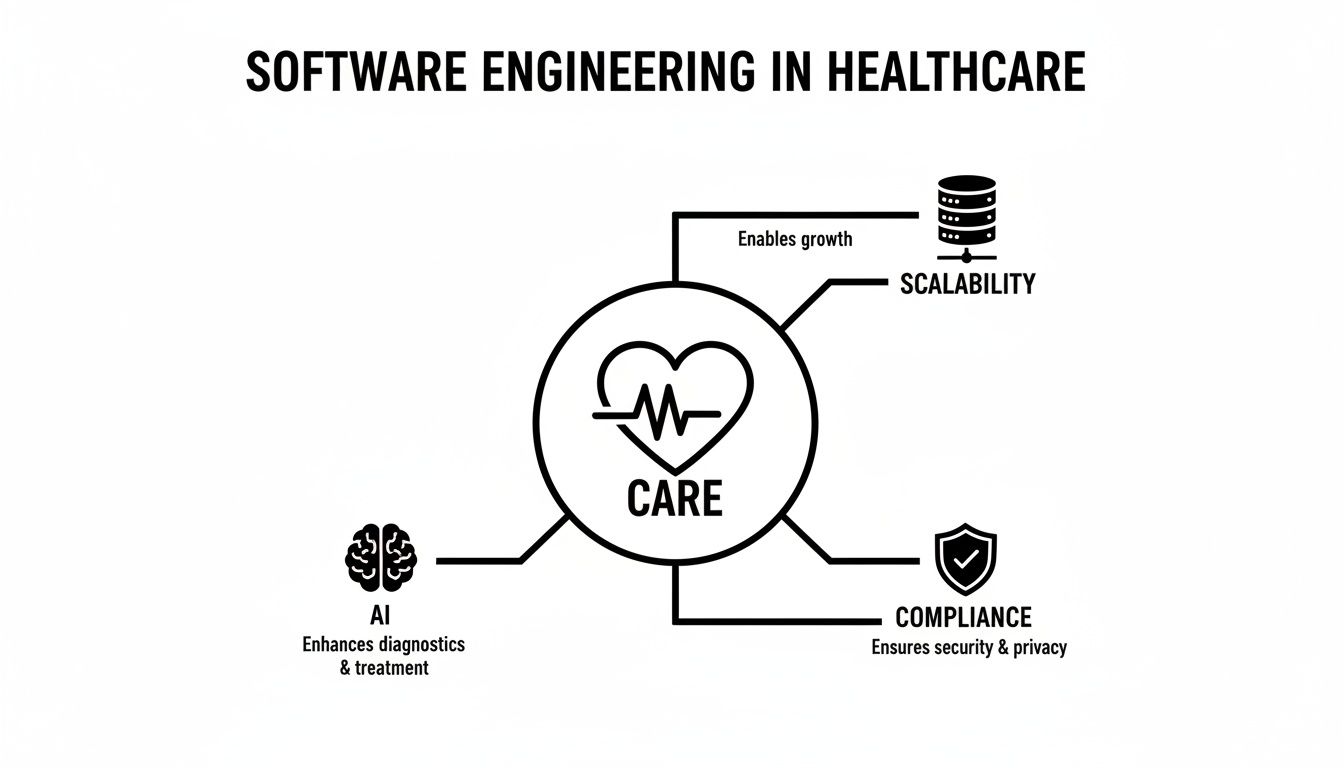
As the diagram shows, while technology and growth are vital, they must always support the core purpose of improving and protecting patient outcomes.
Getting Health Data to Speak the Same Language
Beyond the legal guardrails, there’s a massive technical challenge: communication. A single patient's medical history is often fragmented across different hospitals, clinics, and labs, with each one using its own proprietary software. For a doctor to get a complete, accurate picture, all these disconnected systems need to speak the same language.
This is where data interoperability standards are indispensable.
- HL7 (Health Level Seven): This is the old guard, the foundational standard for swapping clinical and administrative data between the software applications used by healthcare providers for decades.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): FHIR is the modern, web-based answer to HL7's complexity. It uses APIs to make sharing electronic health records faster, simpler, and more flexible—perfectly suited for today's world of mobile apps and cloud computing.
Building with these standards isn't optional. It’s a fundamental requirement for any software project that needs to plug into the wider healthcare ecosystem, ensuring critical information can follow a patient securely and efficiently, no matter where they get care.
A Completely Different Engineering Mindset
The unique demands of healthcare require a fundamentally different approach to building software. A "best practice" in e-commerce could easily be a major compliance disaster in healthtech.
To illustrate just how different the playing field is, let's compare the two side-by-side.
Key Differences Between Standard and Healthcare Software Engineering
| Aspect | Standard Software Engineering | Software Engineering in Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Driver | User engagement, revenue, speed | Patient safety, data privacy, clinical outcomes |
| Data Sensitivity | Low to high (e.g., user preferences) | Extremely high (Protected Health Information – PHI) |
| Regulatory Oversight | Varies by industry, often minimal | Strict and mandatory (HIPAA, GDPR, FDA) |
| Core Principle | Move fast and break things | Do no harm; privacy by design |
| Interoperability | Nice-to-have (e.g., social logins) | Mission-critical (HL7, FHIR standards) |
| Testing Focus | Functionality, performance, usability | Security, compliance, clinical workflow validation |
| Consequence of Failure | Lost revenue, brand damage | Patient harm, legal liability, massive fines |
This table makes it clear: the stakes are simply higher in healthcare, demanding a more rigorous, security-first mindset from day one.
For a great deep dive into what it takes to meet these high standards, check out this technical guide on how to get SOC 2 certification. While not exclusively for healthcare, SOC 2 is a critical framework for demonstrating your commitment to securely managing user data.
Understanding these strict requirements from the outset is crucial. If you want to dig deeper into the specifics of building secure applications in this space, our guide on HIPAA compliant app development offers practical insights. It helps frame these regulations not as obstacles, but as a roadmap for creating technology that patients and providers can truly trust.
How AI Is Revolutionizing Patient Outcomes
Artificial intelligence is causing a fundamental shift in healthcare, moving it from a reactive discipline to a predictive one. Instead of just treating illnesses after they show up, software powered by AI can now help clinicians see health events coming, personalize treatments, and automate the mundane tasks that eat up their day. This isn't some far-off sci-fi concept; it's the real-world application of software engineering in healthcare, and it's delivering measurable improvements to patient care right now.

This shift isn't just a slow creep, either. The adoption of AI and AI-enabled software in healthcare is accelerating, completely changing engineering priorities. According to a comprehensive report on the state of AI in healthcare from Menlo Ventures, 22% of healthcare organizations had put domain-specific AI tools into practice by 2025—a huge jump from the previous year.
We see the same trend in medical devices. The Stanford HAI AI Index points out a massive spike in regulatory approvals for AI-enabled medical devices, going from just 6 in 2015 to 223 in 2023. This data is a clear signal: engineered AI products are breaking out of the research lab and into clinical use, all under the watchful eye of regulators.
Practical AI Use Cases in Modern Healthcare
The true potential of AI really clicks when you look at the specific, real-world tools that software engineering teams are building today. These aren't just hypotheticals; they're applications that are directly changing how care is delivered.
-
AI-Powered Diagnostic Tools: Machine learning models are becoming incredibly good at spotting subtle patterns in medical images that the human eye might miss. For example, an AI algorithm can scan a chest X-ray and flag potential signs of pneumonia or find early-stage cancerous growths in mammograms, often with remarkable accuracy. This doesn't replace radiologists but acts as a second set of eyes, letting them focus their expertise on the most complex cases.
-
Personalized Treatment Algorithms: Every patient is different, and AI is helping medicine finally move beyond one-size-fits-all treatments. By crunching a patient's genetic data, lifestyle factors, and medical history, AI models can predict which treatment plan is most likely to work for that specific person. This is a game-changer in fields like oncology, where AI can help match patients to targeted therapies based on their tumor's unique genetic profile.
-
Administrative and Operational Automation: A huge chunk of a clinician's day is swallowed by paperwork and admin tasks. AI-driven software can automate a lot of this grunt work, like transcribing a doctor's spoken notes, managing appointment schedules, and handling billing codes. This frees up doctors and nurses to spend more time on what actually matters—talking to and caring for their patients.
By automating routine administrative work, AI can help reduce clinician burnout, a critical issue in the healthcare industry. When engineers build tools that give clinicians back their time, they are directly contributing to a more sustainable and effective healthcare system.
Engineering Challenges in Healthcare AI
As exciting as all this is, building and deploying AI in a clinical setting comes with its own unique set of engineering challenges. It demands a disciplined approach that puts safety, accuracy, and governance first. The stakes are simply too high for a "move fast and break things" mindset.
Here are some of the key hurdles engineers have to clear:
-
Ensuring Model Accuracy and Fairness: An AI model is only as good as the data you train it on. Engineers have to work tirelessly to root out biases in datasets that could lead to worse outcomes for certain groups of patients. A model's accuracy must be rigorously tested and validated against clinical benchmarks before it ever gets near a real patient workflow.
-
Managing Massive Datasets Securely: To be effective, AI models need to be trained on enormous amounts of data, much of which is highly sensitive Protected Health Information (PHI). The software architecture has to be designed from the ground up for security, ensuring HIPAA compliance is baked into every stage of the MLOps lifecycle, not just bolted on at the end.
-
Building a Scalable MLOps Foundation: Launching an AI model isn't a one-and-done event. It requires a solid Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) foundation for continuous monitoring, governance, and improvement. Engineers need to build systems that can track model performance in real time, retrain models as new data flows in, and keep detailed audit trails for regulators. This is what ensures the AI remains effective and safe long after its initial deployment.
Modernizing Legacy Systems Without Disruption
Many healthcare organizations are running on software built decades ago. These legacy systems, while once reliable, often act like anchors, holding back innovation and preventing the adoption of modern tools that could improve patient care. The thought of replacing them can be terrifying, conjuring images of massive disruptions to critical clinical workflows.
But here’s the good news: modern software engineering offers a strategic roadmap for upgrading these platforms without bringing daily operations to a halt.
The core idea isn't a "rip and replace" approach. Instead, it’s a gradual, carefully managed evolution. Think of it like renovating a historic building while people are still living inside. You don't tear down the whole structure at once; you cordon off one section, modernize it, and then move on to the next, ensuring the residents are never without a place to stay. This phased migration strategy is key.
Breaking Down the Monolith
The first step is often shifting from a monolithic architecture—where the entire application is one massive, interconnected unit—to a microservices architecture. In this model, the application gets broken down into a collection of smaller, independent services. Each service handles a specific function, like patient scheduling or billing, and can be updated or replaced individually without affecting the others.
This approach brings some huge advantages to the table:
- Targeted Upgrades: Teams can focus on modernizing the most critical or outdated parts of the system first.
- Improved Scalability: High-demand services can be scaled independently, which optimizes resource use and performance.
- Technology Flexibility: New services can be built using modern programming languages and tools, allowing for gradual innovation.
Adopting an API-first development approach is crucial here. By creating well-documented Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), new applications can securely talk to the legacy system, pulling data and functionality as needed. This creates a bridge between the old and the new, enabling a seamless coexistence during the transition. To learn more, check out our guide on how to modernize legacy systems for actionable strategies.
Using AI to Bridge the Old and New
Artificial intelligence can play a powerful role here, acting as a smart intermediary that extracts value from old data while new systems are being built. For example, AI models can be trained on historical data trapped within a legacy Electronic Health Record (EHR) to identify at-risk patients or predict operational bottlenecks. These insights deliver immediate value, long before the full system replacement is complete.
By applying AI to legacy data, organizations can unlock hidden patterns and improve decision-making long before the old system is fully decommissioned. This turns the modernization process from a pure cost center into a value-generating initiative from day one.
This focus on digital transformation is a top priority across the industry. A recent Deloitte outlook on global healthcare found that about 70% of surveyed executives considered investing in digital tool platforms important. What’s more, nearly 90% expect digital technology use to accelerate in the coming year.
You can explore more about these trends in the full 2025 global health care executive outlook. This data underscores the urgency of modernizing legacy platforms to build a more resilient and efficient future for healthcare. The goal is to create a tech stack that is not only scalable and secure but also capable of unlocking the wealth of data that has been siloed for years.
Assembling Your Healthtech Development Team
Building great healthcare software is more of a human challenge than a technical one. In this high-stakes field, the success of any project comes down to the mix of skills and experience on your team. Just hiring talented coders won't cut it. You need to build a collaborative unit that can confidently handle the tricky intersection of technology, clinical reality, and dense regulations.
Think of it like putting together a surgical team. You wouldn’t just staff a room with surgeons. You need anesthesiologists, nurses, and technicians, each bringing a critical and unique skill to the operating table. It’s the exact same principle for a healthtech team—developers alone can't get the job done right.
The Core Roles Your Healthtech Team Needs
While a solid engineering group is your foundation, a team that truly delivers integrates specialized knowledge from across the healthcare world. Each of these roles offers a unique perspective that helps you sidestep costly mistakes and ensures the final product is not only compliant but genuinely useful in a clinic or hospital.
A well-rounded team for a software engineering in healthcare project includes:
- Clinical Informatics Specialists: These folks are the essential translators between your engineers and the clinical staff. They live and breathe clinical workflows and medical terminology, and they know firsthand how technology can either empower or frustrate a care team. Their insight is what makes software something a doctor or nurse will actually embrace.
- UX Designers with Healthcare Experience: Standard UX principles often fall flat in a hospital. A designer who gets the high-stress, fast-paced nature of clinical work can build interfaces that are intuitive, fast, and minimize user error—which is non-negotiable when a patient’s well-being is on the line.
- Regulatory and Compliance Experts: You simply cannot build without this role. These experts make sure every single feature, data transfer, and architectural choice is buttoned up and compliant with regulations like HIPAA. Getting them involved from day one saves you from disastrous, expensive redesigns down the road.
- Data Security Engineers: With Protected Health Information (PHI) in play, a dedicated security expert is a must-have. They are laser-focused on threat modeling, penetration testing, and locking down the system to prevent data breaches.
Key Qualities to Look for When Hiring
Beyond the job titles, every person on your healthtech team needs to share a certain mindset. You can always teach new technical skills, but finding people with a deep-rooted respect for the industry's unique demands is much more challenging.
The best healthtech teams operate with a 'do no harm' philosophy. Every decision, from a database schema to a UI element, is weighed against patient safety, data privacy, and clinical effectiveness.
When you’re interviewing candidates, make sure you prioritize people who show these traits:
- A Deep Understanding of Data Privacy: Look for candidates who can talk fluently about HIPAA, data encryption, and secure data handling. They should see compliance not just as a box to check, but as a fundamental design principle.
- Experience with Clinical Workflows: Ask them about their experiences observing or working in a clinical setting. Can they tell you about the real-world pressures of a chaotic ER or a busy primary care office? That kind of ground-level knowledge is priceless.
- A Collaborative and Empathetic Mindset: The real breakthroughs happen when different experts put their heads together. Find team players who are genuinely curious to learn from clinicians and are driven by a desire to make things better for patients, not just to solve a cool technical puzzle.
Your Partner in AI-Powered Healthcare Innovation
Building software for the healthcare space, especially when you bring AI into the mix, can feel like walking a tightrope. It demands a delicate balance of deep technical know-how, a real understanding of clinical settings, and an unwavering commitment to regulatory compliance. Ultimately, success isn't just about what you build, but how you build it—with patient safety and positive outcomes as your north star.
This is where having the right set of tools can make all the difference. As we've seen, AI offers incredible potential, but it also opens a Pandora's box of new risks around governance, unpredictable costs, and security. It's this extra layer of complexity that causes so many promising projects to grind to a halt.
De-Risk Your AI Initiatives with the Right Tools
To confidently weave AI capabilities into your healthcare software, you need an administrative toolkit that gives you complete control and visibility. Think of it as the flight control system for your AI, making sure every single operation is tracked, secure, and running efficiently. This is the exact reason we built Wonderment's prompt management system.
It’s an administrative tool your developers can plug straight into new or existing software to get it ready for AI. Once you do, you immediately gain a whole suite of essential governance features:
- A Centralized Prompt Vault: Get total control over your AI prompts with built-in versioning and clear audit trails. This keeps everything consistent and lets you track every change over time—something that's absolutely critical for regulatory paperwork.
- A Parameter Manager: This feature acts as a secure gatekeeper, allowing you to connect your AI to internal databases without ever exposing sensitive information or PHI. It carefully manages how AI accesses and uses your protected health data.
- Unified Logging and Cost Management: Get a transparent, single-pane-of-glass view of all AI activity across every model you've integrated. The built-in cost manager keeps a running tab on your spending, preventing nasty surprise bills and helping you fine-tune your AI usage.
Integrating a dedicated administrative tool like this doesn't just bolt on a few features; it lays the foundational governance you need to responsibly scale AI. It turns AI from a high-stakes experiment into a manageable, secure, and fully auditable part of your healthcare application.
Build the Next Generation of Healthcare Software
The future of healthcare is being written in code, and AI is its next chapter. But innovation without solid guardrails is a liability waiting to happen. By giving your development team a robust prompt management system, you empower them to build with confidence. They'll know they have the tools in place to protect patient data, keep costs in check, and nail compliance standards.
Ready to see how you can de-risk your AI projects and get to market faster? Schedule a demo of our prompt management tool and see for yourself how to build the next generation of AI-powered healthcare software with complete confidence.
Got Questions? We Have Answers
Diving into healthtech software can feel like learning a new language. It's totally normal to have questions, whether you're a business leader trying to see the big picture or a developer getting into the weeds. Here are some of the most common ones we hear.
What Is the Biggest Challenge in Healthcare Software Development?
Without a doubt, the biggest hurdle is the sheer complexity of regulatory compliance and data security. This isn't like other industries where a bug might cause an inconvenience. In healthcare, a software flaw could have life-or-death consequences.
That means you can't just talk about security; you have to live it. Following standards like HIPAA in the US or GDPR in Europe is the absolute baseline, not a feature. It goes beyond secure coding—we're talking about exhaustive testing, bulletproof audit trails, and airtight access controls to guard sensitive patient data. The real trick is building something that’s both fortress-secure and genuinely easy for a busy clinician to use. It’s a constant balancing act.
How Does AI Integration Differ in Healthcare Compared to Other Sectors?
When you bring AI into healthcare, the stakes are infinitely higher. An e-commerce site recommending the wrong product is no big deal. An AI model getting a diagnosis wrong could cause serious patient harm. Because of this, the burden of proof for safety, effectiveness, and fairness is immense.
This is where the concept of explainability becomes critical. You can't just have a "black box" model; you need to understand why the AI made a specific decision. Every model needs rigorous clinical validation and has to be monitored constantly once it's live. You also have to be hyper-aware of biases in the data you train it on to make sure it delivers fair outcomes for everyone. The entire process, from finding data to flipping the switch on the model, has to be documented meticulously for regulators.
What Are FHIR and HL7 and Why Are They Important?
Think of FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and HL7 (Health Level Seven) as the universal translators for medical data. They're data exchange standards that let different, disconnected healthcare systems finally talk to each other. HL7 is the older, more established standard, while FHIR is the modern, web-friendly version built on APIs.
You really can't overstate how important this is. Without these standards, a patient's medical history is fragmented and locked away in different digital silos. This makes it impossible to get a complete picture of their health. For engineers, building with FHIR APIs is non-negotiable if you want to create apps that can pull and push information securely across the entire healthcare landscape.
Ready to build the future of healthcare with confidence? Wonderment Apps provides the tools and expertise to de-risk your AI initiatives and accelerate development.
