At the heart of modern AI, there are two fundamental ways a model learns to solve problems: supervised learning and unsupervised learning. For any business leader looking to modernize their software with custom AI integration, understanding the difference is the first step toward a successful strategy. Think of them as two distinct teaching philosophies for your AI.
So what's the core difference? It really boils down to one thing: supervised learning uses labeled data (like photos tagged 'cat' or 'dog') to make predictions, while unsupervised learning sifts through unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns on its own. It’s the difference between studying with an answer key versus figuring out the solutions from scratch. But integrating either requires more than just picking a model; it demands a solid system to manage it all. That's why we built a powerful prompt management system at Wonderment Apps—an administrative tool that lets developers and entrepreneurs plug AI into existing software with full control. We'll touch on this more later, but it’s the key to making AI work for you, not the other way around.
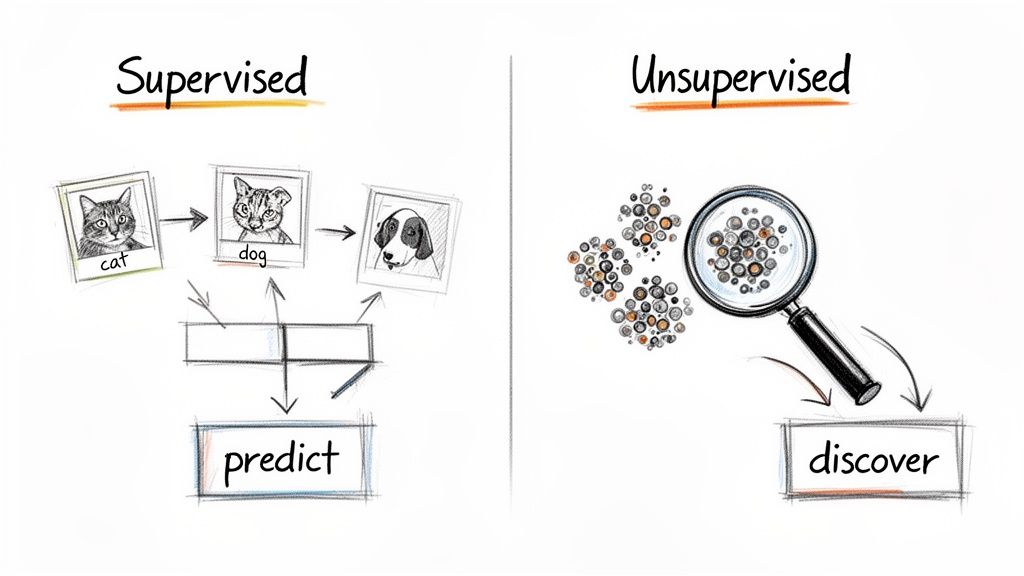
Supervised Learning: Learning by Example
Supervised learning is a lot like teaching a student with flashcards. Each flashcard has a question (the input data) and a correct answer (the label). For instance, you could feed a model thousands of customer emails, each one meticulously labeled as either "spam" or "not spam."
Over time, the model learns to recognize the patterns tied to spam and gets remarkably good at classifying new, unseen emails. This method is perfect for tasks where you have a clear, defined goal and historical data to learn from.
Unsupervised Learning: Discovering the Unknown
Unsupervised learning is a completely different beast. It's like giving that same student a massive, unorganized library and asking them to find common themes without any guidance. The data has no labels or predefined answers.
The AI's job is to dive into that raw information and identify inherent structures all on its own. It might analyze customer purchase histories to automatically group them into distinct personas, revealing market segments you never knew existed.
Comparing the Core Approaches
The path you choose—supervised or unsupervised—will directly shape your project's scope, budget, and ultimate success. To make the decision clearer, let's break down their key differences.
| Characteristic | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirement | Requires clean, accurately labeled data. | Works with raw, unlabeled data. |
| Primary Goal | To predict a specific, known outcome. | To discover hidden patterns or structures. |
| Common Tasks | Classification (e.g., spam filtering) and Regression (e.g., price prediction). | Clustering (e.g., customer segmentation) and Anomaly Detection. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Learns by comparing its predictions to the correct labels and minimizing errors. | Finds patterns based on the data's inherent properties, without external correction. |
Modernizing an application with AI involves more than just picking a model; it requires a solid system to manage it all. To simplify this journey, Wonderment Apps developed a prompt management system that acts as a central control panel for your AI integrations.
This administrative tool empowers developers and entrepreneurs to seamlessly plug AI into existing software, featuring a prompt vault with versioning, a parameter manager for database access, comprehensive logging, and a cost manager to track cumulative spend.
This system is built to streamline the management of both supervised and unsupervised models, making your software modernization initiative faster, more efficient, and easier to control.
The Critical Divide: Labeled vs. Unlabeled Data
The real split between supervised and unsupervised learning doesn’t start with complex algorithms or abstract theory—it begins with the data. Your most important decision is whether to use labeled data, which essentially acts as a teacher, or unlabeled data, which is more like a landscape to be explored. This single choice will shape your project's cost, timeline, and what it can ultimately achieve.
Think of supervised learning as a student studying with a detailed answer key. For the model to learn anything, it needs a dataset where every single piece of information is meticulously tagged with the correct outcome. This is what we call labeled data.
Let’s say you want to build an AI feature that automatically spots defective products on an assembly line. To do this, you’d have to feed the model thousands of images, each one explicitly marked as either "defective" or "not defective." The model learns the visual patterns tied to each label, becoming an expert through this guided repetition.
The High Cost of a Knowledgeable Teacher
This labeling process, often called data annotation, is incredibly effective but comes at a steep price. It's a manual, time-consuming effort requiring human experts to review and tag every single data point. The accuracy of your model is directly linked to how good those labels are.
This critical step is often the most expensive part of an AI initiative. In fact, studies have shown that data annotation expenses for supervised models can consume up to 80% of total project budgets.
With costs anywhere from $0.50 to $5 per label, a project needing hundreds of thousands of data points can quickly turn into a massive financial investment. This is a crucial factor for business leaders to weigh when planning an AI modernization project. You can find out more by exploring the costs associated with different learning models.
The Freedom and Frugality of Unlabeled Data
Unsupervised learning completely flips this script. It thrives on raw, messy, and totally unlabeled data—the kind businesses generate in enormous quantities every day. The approach is more like handing an anthropologist a trove of ancient artifacts and asking them to find cultural groupings without any prior context.
The model gets no answer key. Instead, its job is to analyze the inherent structure of the data and discover meaningful patterns or clusters on its own. For example, it could sift through millions of customer transactions to identify natural purchasing segments without anyone telling it what to look for.
This method drastically cuts down upfront costs. By getting rid of the need for manual tagging, unsupervised learning can slash data preparation expenses by 70-90%. It’s the perfect choice when your goal is exploratory—to understand your customers, find anomalies in your network, or organize huge content libraries without a predefined outcome.
The trade-off is clear. Supervised learning delivers high precision for specific, well-defined tasks but requires a significant up-front investment in data labeling. Unsupervised learning gives you a cost-effective way to uncover hidden insights from raw data, making it a powerful tool for discovery and strategic analysis. Your choice directly connects your data strategy to your business goals, balancing the need for predictive accuracy with the power of open-ended exploration.
A Practical Comparison of Learning Models
Beyond the high-level theory, supervised and unsupervised learning models differ in their real-world objectives, the methods they use, and how we measure their success. Choosing between them isn't just about the data you have—it’s about the problem you’re actually trying to solve. This breakdown gets into the core operational differences, giving you a clear framework for your projects.
At its heart, a supervised model is all about prediction. It learns a specific map from inputs to known outputs, with the goal of accurately forecasting outcomes for new, unseen data. On the flip side, an unsupervised model is geared toward discovery. It dives into data without any predefined targets, looking to uncover hidden structures, groupings, or anomalies that you didn't even know were there.
Comparing Core Objectives
The primary goal drives everything else, from which algorithm you pick to how you define a "win."
- Supervised Learning's Objective: The goal here is laser-focused: predict a specific outcome. The model is trained to be as accurate as possible in tasks like classifying an email as spam or forecasting next quarter's sales. Success is quantifiable because you're measuring it against a known ground truth.
- Unsupervised Learning's Objective: This is all about understanding the inherent structure of the data. The model identifies patterns, like segmenting customers into distinct behavioral groups, without being told what those groups should be ahead of time. Success is often measured by the quality of the insights it generates.
The visual below illustrates how data costs—a huge factor in any ML project—stack up. You'll notice supervised learning often comes with a significant upfront investment.
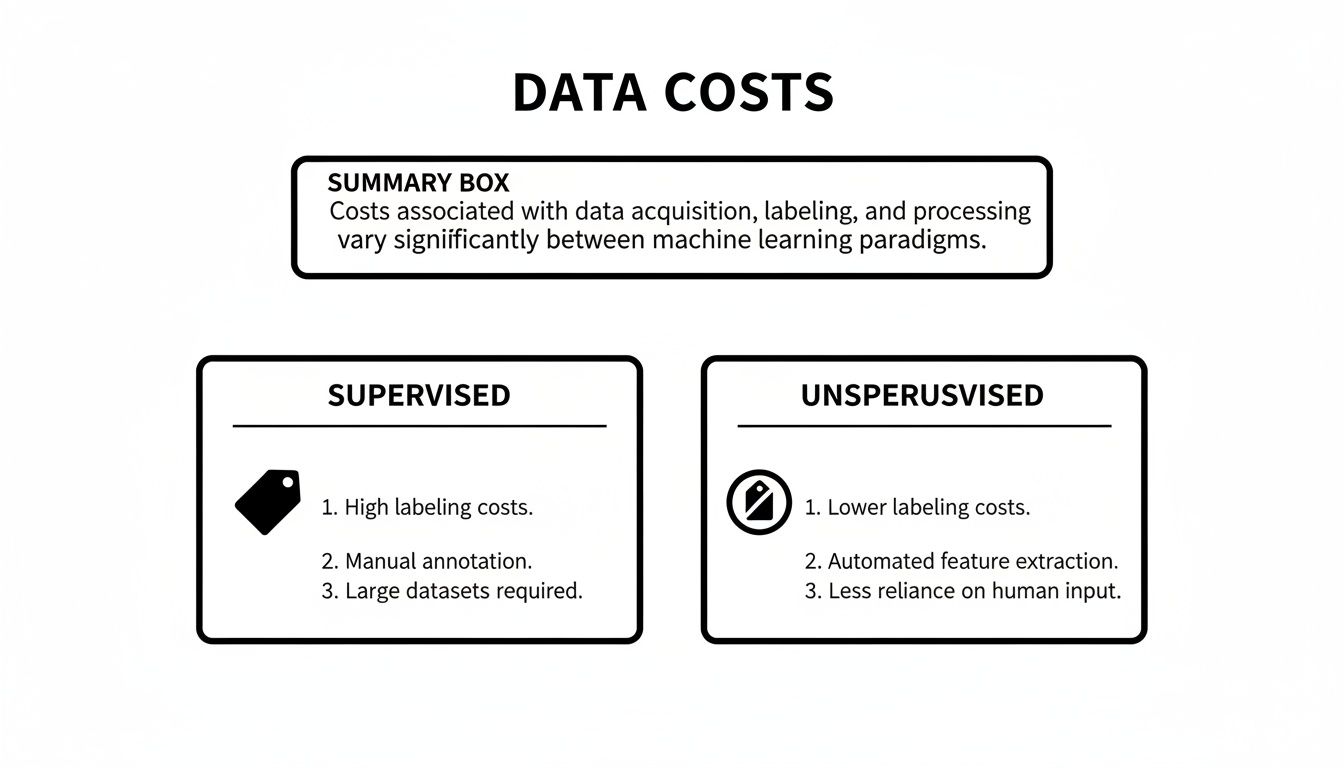
This really brings home a critical point: the high cost of data labeling for supervised models is a major consideration. Unsupervised models sidestep this expense entirely, which makes them perfect for exploratory analysis, especially when you're on a budget.
Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning at a Glance
For a quick side-by-side view, this table breaks down the key characteristics that define supervised and unsupervised machine learning models, from data requirements to typical business goals.
| Characteristic | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Input | Labeled data (features + correct outputs) | Unlabeled data (features only) |
| Primary Goal | Prediction and classification | Discovery and pattern identification |
| Evaluation Metrics | Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1 Score | Silhouette Score, Davies-Bouldin Index |
| Human Feedback | Provided upfront through data labeling | Applied after to interpret and validate results |
As you can see, the differences are fundamental. Supervised learning relies on having the "answers" upfront, while unsupervised learning is about finding interesting questions within the data itself.
Common Algorithms in Action
Each learning model has its own toolkit of algorithms tailored to its specific job.
For Supervised Learning:
- Linear Regression: A classic for a reason. It's used to predict a continuous value, like the price of a house based on its square footage and location.
- Logistic Regression: Don't let the name fool you; this is a classification algorithm. It predicts a binary outcome, such as whether a credit card transaction is fraudulent (Yes/No).
- Decision Trees: These models are great because they're easy to interpret. They use a series of if-then-else rules to classify data, like a tree that decides whether to approve or deny a loan application.
For Unsupervised Learning:
- K-Means Clustering: This algorithm is a workhorse for grouping data points into a predefined number of clusters (k). A retail company might use it to segment its customer base into five distinct personas for more targeted marketing campaigns.
- Hierarchical Clustering: Instead of telling the model how many clusters to find, this method builds a tree of clusters. It's incredibly useful when you don’t know how many natural groupings exist in your data.
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA): This is a dimensionality reduction technique. It simplifies complex datasets by identifying the most important features, making the data easier to visualize and analyze without losing critical information.
The difference between supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms is like a detective following specific clues to solve a case (supervised) versus one who sorts through a pile of evidence to find any possible pattern (unsupervised).
Distinct Metrics for Success
So how do you know if a model is any good? The answer depends entirely on the approach. Since supervised models learn from a correct answer key, their performance is measured directly against that ground truth. But unsupervised models don't have an answer key, so they're evaluated on the quality and usefulness of the patterns they uncover.
Ultimately, a supervised model's success is a direct measure of its predictive power. An unsupervised model's success, however, is determined by the value of the insights it surfaces—and that often requires a human expert to interpret those findings and translate them into a solid business strategy.
Real-World Use Cases in Modern Business
Knowing the theory is one thing, but seeing how these learning models actually drive business outcomes is where it all clicks. The real difference between supervised and unsupervised learning becomes clear when you see them in the wild, solving tangible problems and creating new opportunities. Each approach shines in different scenarios, impacting everything from your bottom line to your security protocols.
Let's dive into how modern businesses are putting these powerful AI techniques to work.
Supervised Learning in Action
Supervised learning is your go-to when you have a specific question to answer and the historical data to find that answer. It's the workhorse behind optimizing processes, predicting concrete outcomes, and automating decisions that demand a high degree of accuracy.
Here are a few prime examples of where it excels:
- Fintech Fraud Detection: Financial institutions lean heavily on supervised models to protect their customers. A model is trained on millions of past transactions—each one clearly labeled as either "fraudulent" or "legitimate"—so the AI learns to spot the subtle red flags of theft. When a new transaction comes through, the model instantly classifies it, blocking shady activity in real-time and saving millions.
- E-commerce Personalization Engines: Ever wonder how an online store recommends a product you actually want to buy? That's supervised learning. These systems are trained on massive datasets of user behavior, like past purchases and viewed items, all labeled with the final outcome (purchase or no purchase). This teaches the model to predict what a new user is most likely to buy, creating a tailored experience that drives sales.
- Healthcare Diagnostic Imaging: In the medical field, supervised models are trained to analyze images like X-rays and MRIs. Radiologists label thousands of scans, identifying tumors, fractures, or other issues. The AI learns these visual patterns and becomes a powerful assistant, helping doctors detect diseases earlier and more accurately than ever before.
Supervised learning is all about using historical answers to guide future predictions. For example, 70% of spam filters use supervised logistic regression to keep your inbox clean, while Amazon credits its labeled purchase prediction models with a 35% sales uplift.
Unsupervised Learning in Action
Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, is the explorer. It ventures into raw, unlabeled data to discover valuable insights you didn't even know were there. It's perfect for understanding complex systems, identifying hidden structures, and finding anomalies without any preconceived notions.
Here’s where it really shines:
- SaaS Customer Segmentation: A software company has tons of user engagement data but might not know how to group its customers. An unsupervised clustering algorithm can sift through this unlabeled data—login frequency, feature usage, support tickets—and automatically segment users into distinct personas like "power users," "at-risk customers," or "new explorers." This insight allows for incredibly targeted marketing and product development. For more on this, check out our guide on applying machine learning for businesses.
- Retail Market Basket Analysis: The reason stores place certain items next to each other often comes from market basket analysis, a classic unsupervised technique. By analyzing transaction data, an algorithm can discover association rules—like "customers who buy diapers also tend to buy beer"—without anyone telling it to look for that connection. These discoveries directly inform product placement and promotional strategies.
- Cybersecurity Anomaly Detection: In cybersecurity, the biggest threats are often the ones you’ve never seen. Unsupervised models learn the "normal" rhythm of network traffic. When something unusual happens—a sudden spike in data transfer or an access request from a strange location—the system flags it as a potential threat, even if it doesn't match a known attack signature. This proactive approach is critical for stopping novel breaches before they do real damage.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Application
Now that you have a solid handle on how supervised and unsupervised models work, the real question is: which one is right for your project? The answer isn't about picking a "better" model. It’s about choosing the one that syncs up with your business problem, your data, your budget, and what you’re trying to achieve.
The core difference between supervised and unsupervised learning naturally leads them to different use cases. Making the right call is a strategic move that sets the tone for your entire project.
Start by asking one simple question: Do I have a specific, known outcome I want to predict? If the answer is a firm "yes," you’re almost certainly looking at supervised learning. This approach shines when you have a clear target, like forecasting sales, flagging customer churn, or automatically sorting support tickets.
But if your question is more open-ended, something like "What hidden patterns are hiding in my data?", then unsupervised learning is your tool. It’s built for discovery, helping you find natural customer segments, spot unusual network activity, or group similar products without any preconceived ideas.
Key Decision Factors to Consider
Your business goals are the jumping-off point, but the practical realities will shape your final choice. Before you commit, weigh your project against these factors.
- Data Availability and Quality: Do you already have a large, accurate, and well-labeled dataset? If not, you need to be ready for the significant time and money it takes to annotate data. The high cost of labeling can be a non-starter for supervised learning if you don't have a data pipeline already in place.
- Business Problem Definition: Is your goal to automate a known process (supervised) or to uncover new strategic insights (unsupervised)? The clarity of your objective is a huge clue. You can learn more about how to implement AI in business to help sharpen your goals.
- Desired Accuracy and Interpretability: Supervised models, since they're trained on "ground truth" data, can usually hit higher accuracy on predictive tasks. On the other hand, the insights from an unsupervised model might be less precise but can reveal game-changing business intelligence that a predictive model would completely miss.
Ultimately, the choice between supervised and unsupervised learning is a trade-off between predictive accuracy and exploratory discovery. Supervised learning gives you answers to questions you already know how to ask, while unsupervised learning helps you discover the questions you didn't know you needed to ask.
Making a Pragmatic Choice
Let’s make this real. Imagine an e-commerce company that wants to improve customer retention.
- A supervised approach would mean training a model on past customer data, all neatly labeled with who churned and who didn’t. The endgame is a highly accurate prediction model that flags at-risk customers so the company can step in with targeted offers.
- An unsupervised approach would involve feeding raw customer behavior data into a clustering algorithm. The model might discover three distinct personas: "Bargain Hunters," "Loyal Brand Advocates," and "Occasional Big Spenders." This kind of insight lets the company build tailored retention strategies for each group, creating a more nuanced and effective plan.
Neither path is inherently better—they just solve different parts of the same business problem. Often, the smartest move is to start with unsupervised learning to get the lay of the land. Then, you can use those fresh insights to build a more focused and powerful supervised learning project down the road.
Modernize Your App with Smart AI Integration
Bringing AI into your application is a big move, but picking between supervised and unsupervised learning is really just the first step. The real work—and the biggest opportunity—is in building a scalable system to support your models long-term. A successful AI project needs a solid foundation that lets you experiment, monitor, and manage the whole implementation without derailing your core development roadmap.
This is exactly why a dedicated administrative toolkit is so important. Just plugging in an AI model without the right controls is like driving a race car with no dashboard. You've got the power, but no way to see your speed, fuel level, or engine status. To truly modernize your app and build it to last, you need a central command center. To get a better handle on creating and scaling intelligent applications, you can dive into the world of AI-powered software development.
Building a Future-Proof AI Foundation
At Wonderment Apps, we built our prompt management system to solve these exact operational headaches. It’s the foundational layer that makes sure your AI integration is a sustainable part of your business, not just another feature. Whether you’re deploying a predictive supervised model or an exploratory unsupervised one, our system provides the control you need to succeed.
Our toolkit handles four critical functions:
- Prompt Vault with Versioning: Your model’s instructions, or prompts, are valuable assets. Our vault helps you manage, test, and version them so you can fine-tune performance or roll back changes without breaking your app.
- Parameter Manager: This securely connects your AI models to internal databases. It gives your AI the right information to provide relevant, context-aware responses while maintaining strict data governance.
- Cross-AI Logging System: Get a single, unified view of all AI interactions. Our logging system gives you full visibility into model performance, user inputs, and outputs, making troubleshooting and optimization a breeze.
- Cost Manager: AI models often run on a pay-per-use basis, and costs can get out of hand quickly. Our cost manager lets you track your cumulative spend across all integrated AI services, giving you the financial oversight to manage your budget effectively.
This toolkit isn’t just about adding features; it’s about providing the essential infrastructure for any business serious about building intelligent, long-lasting software. It transforms AI from a complex black box into a transparent, manageable system.
Take Control of Your AI Integration
The difference between a successful AI project and a failed one often boils down to operational control. You can leverage artificial intelligence far more effectively when you have the right tools to manage it. By giving your team a centralized system for prompt management, data access, logging, and cost control, you’re not just integrating AI—you’re building a foundation for continuous improvement.
Ready to see how our administrative toolkit can de-risk your AI initiatives and help you build smarter, more powerful applications? Schedule a demo with our team today and discover how to modernize your app with confidence.
Common Questions, Answered
When you're digging into AI, a lot of questions pop up, especially when you're weighing foundational approaches like supervised and unsupervised learning. Let's tackle some of the most common ones that business leaders and developers run into.
Can I Use Both Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Together?
Absolutely. In fact, combining them is often a seriously powerful strategy.
A pretty common workflow is to kick things off with an unsupervised learning model to just explore a massive, unlabeled dataset. This is a great way to discover natural customer segments or spot key features hiding in your data that you didn't even know were there.
Once you have those initial insights, you can use them to create much more meaningful labels for a smaller, high-impact dataset. That newly labeled data is then perfect for training a supervised model for a specific predictive task. You're basically getting the best of both worlds—the exploratory power of one and the predictive accuracy of the other.
Which Model Is Generally More Expensive to Implement?
Supervised learning almost always carries a heavier upfront cost. The real budget-eater isn't the algorithm itself; it's the massive effort and expense that goes into data labeling. Building a high-quality, accurately labeled dataset can chew up as much as 80% of a project's budget and needs a ton of human oversight to get right.
Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, gets to work on raw, unlabeled data, which slashes those initial prep costs. The catch? You'll need to factor in the cost of expert analysis to actually interpret the results and turn those discovered patterns into something your business can act on.
The core difference in cost comes down to paying for data preparation (supervised) versus paying for expert interpretation (unsupervised). Your budget and the resources you have on hand will heavily influence which path makes more sense for you.
Does One Approach Require More Data Than the Other?
This is less about the sheer amount of data and more about its quality and type. Supervised learning models, particularly deep learning ones, are famously data-hungry. They need huge volumes of labeled examples to learn effectively and not get tripped up by overfitting. If you don't have enough labeled data, you can expect pretty poor predictive performance.
Unsupervised learning can also handle massive datasets, but its real strength is finding value in the raw, unlabeled information that most businesses already have sitting around in piles. The focus here isn't on pre-labeled answers but on having enough data to let statistically significant patterns reveal themselves. Both benefit from more data, but the nature of that data is what really separates them.
Ready to move beyond theory and start building intelligent software? The team at Wonderment Apps specializes in helping businesses like yours modernize their applications with the right AI models and a robust administrative toolkit to manage them. Schedule a demo today to see how we can accelerate your AI journey.
