Systems design architecture is the essential blueprint for any successful software application. It dictates how the application will handle data, how its different parts will talk to each other, and most importantly, how it will scale to meet user demand. In short, it’s the foundational plan that determines whether an app can delight millions or will crumble under pressure. Integrating AI into your custom software is becoming a must-have, and a well-thought-out architecture makes it possible. To streamline this process, many developers and entrepreneurs are turning to administrative tools like a prompt management system to modernize their apps for AI integration. If you're looking to see how such a tool can plug into your existing software, we can show you a demo.
Building Your Application's Unbreakable Foundation
Think of building a new application like constructing a skyscraper. You wouldn't just start stacking bricks and hope for the best, right? You’d start with a detailed architectural plan—a blueprint outlining the foundation, structural supports, plumbing, and electrical systems. This plan is what makes the building stable, functional, and able to accommodate everyone inside without collapsing.
Systems design architecture is that exact same blueprint, but for your software.
It’s the high-level strategy that defines how all the individual pieces of your application—from the user interface right down to the database—work together as a cohesive whole. A solid architecture is what makes an application feel fast, reliable, and secure, even when thousands of people are using it all at once. Without it, you’re just asking for a system that’s slow, prone to crashing, and impossible to update.
Why Architecture Matters More Than Ever
In today's market, a well-designed system isn't just a technical detail; it's a critical business advantage. The right architecture directly impacts your ability to grow, innovate, and respond to what your customers need. This is especially true now, as more businesses integrate modern capabilities like Artificial Intelligence into their operations.
This growing importance is clearly reflected in market trends. The architecture design software market was valued at USD 3.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow with a compound annual growth rate of over 12% from 2024 to 2032. This surge is being driven by a massive industry shift, with tools for AI-driven design and cloud collaboration completely reshaping how businesses build scalable systems. You can find more insights on this architectural software market trend on gminsights.com.
For business leaders, focusing on architecture is a direct investment in the long-term health of your software. The key benefits are impossible to ignore:
- Scalability: The power to handle growth without having to start over from scratch.
- Reliability: Making sure your application is always available when your users need it.
- Maintainability: Making it easier and cheaper to fix bugs or roll out new features.
- Security: Building a resilient foundation that protects user data from threats.
This kind of strategic planning is what separates an app that thrives from one that becomes a costly liability. For teams looking to fast-track AI integration, specialized tools like a prompt management system can provide a ready-made administrative layer. This helps manage AI models, control costs, and version prompts, accelerating your journey to a smarter, more resilient application.
To build a robust and future-proof application, it's crucial to grasp the core pillars that underpin modern systems design. These concepts form the bedrock of any successful digital product.
Core Pillars of Modern Systems Design Architecture
| Pillar | Description | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | The ability to handle increased load. This includes horizontal (adding more machines) and vertical (adding more power) scaling. | Ensures smooth performance as your user base grows, preventing crashes during peak traffic and supporting business expansion. |
| Reliability | The probability that a system will perform its intended function without failure for a specified period. | Builds user trust and loyalty by providing a consistently available and dependable service, which is critical for revenue and reputation. |
| Availability | The percentage of time a system is operational. Often expressed in "nines" (e.g., 99.99% availability). | Directly impacts user experience and revenue. High availability means your service is accessible when customers need it, minimizing lost sales. |
| Performance | The speed and responsiveness of the application. Measured by latency (delay) and throughput (data processed over time). | A fast, responsive application leads to higher user engagement, better conversion rates, and improved customer satisfaction. |
| Security | Protecting the system and its data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. | Safeguards sensitive user data, protects against financial loss, and preserves brand reputation by preventing security breaches. |
Understanding these pillars isn't just for developers; it's essential for anyone involved in building and managing a digital product. They are the fundamental trade-offs you'll navigate to create an application that is not only functional but truly successful.
Choosing the Right Architectural Pattern
Not all applications are built the same, and that’s a good thing. The architectural pattern you choose is the blueprint for how your system’s components fit together and talk to each other. This one decision has a ripple effect on everything, from how fast your team can build to how well the system holds up under pressure down the road.
Think about it like this: are you building a single, massive department store where every section is under one roof? Or are you designing a modern shopping mall filled with independent, specialized boutiques? The first approach is a Monolithic architecture—a classic, all-in-one build. The second is a Microservices architecture, where your application is a collection of smaller, independent services working in harmony.
Each has its place, and getting this choice right from the start is a game-changer for your entire project. This decision tree can help you start thinking through which path makes the most sense for what you're trying to build.
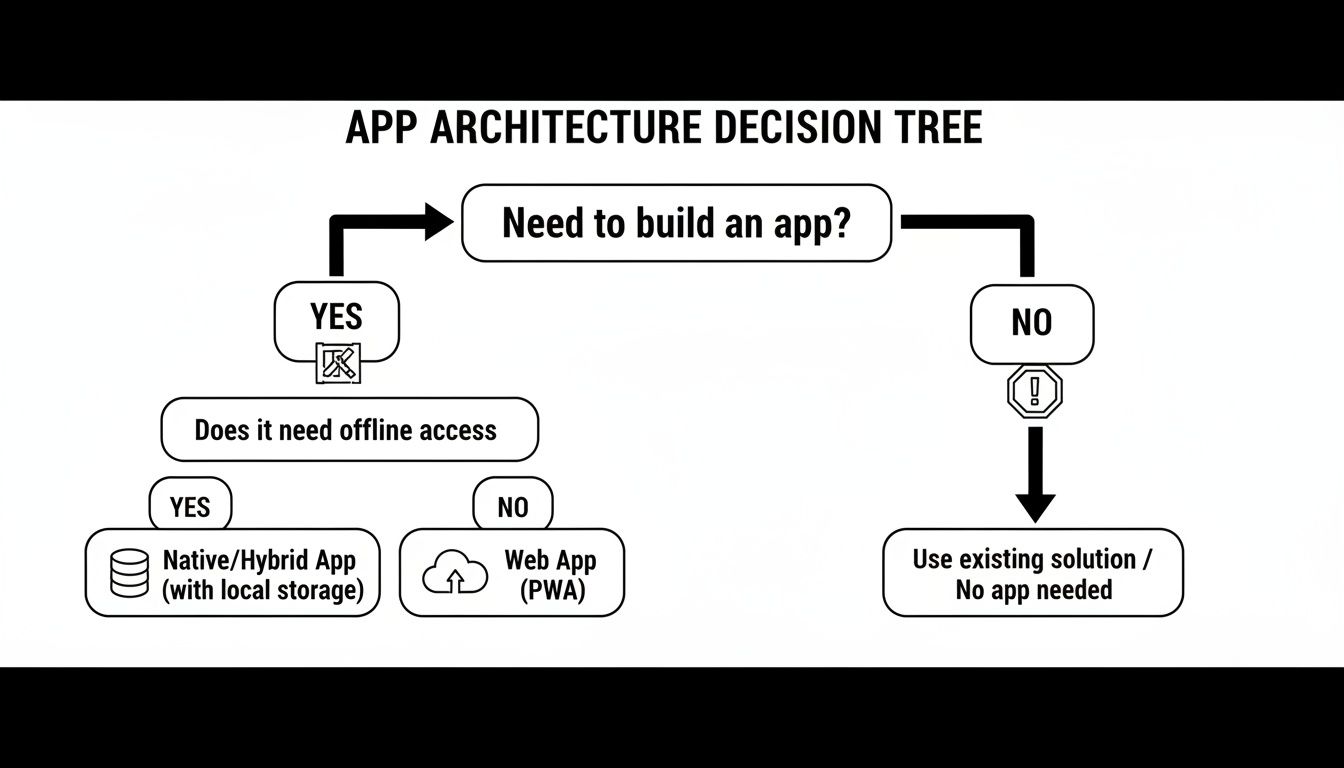
This visual helps frame those initial, crucial questions. It guides you from the fundamental need for an application right into the blueprinting phase of your software journey.
Monolithic Architecture
The monolithic pattern is the old-school, traditional way of building applications. In this model, every feature, function, and piece of business logic is bundled into a single, tightly-coupled codebase. For good reason, it’s often the go-to for new projects.
For small teams or startups aiming to launch a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a monolith is often the fastest way to get an idea into the hands of users. The simplicity of a single codebase means less operational complexity right out of the gate. But be warned: as the application grows, that initial simplicity can turn into a major bottleneck, making every update slow, risky, and complicated.
Microservices Architecture
On the other side of the coin, a microservices architecture breaks an application down into a suite of small, independent services. Each service is built around a distinct business function and can be developed, deployed, and scaled entirely on its own.
This approach delivers incredible flexibility and scalability. Imagine an e-commerce platform with separate services for user accounts, product catalogs, and the shopping cart. If a flash sale causes a massive spike in traffic to the shopping cart, you can scale just that service without touching the rest of the application. Many teams find that diving into software architecture best practices helps clarify the right moment to make the jump from a monolith to microservices.
A key takeaway is that microservices are not just a technical choice; they are an organizational one. They thrive in environments where small, autonomous teams can take full ownership of individual services, fostering faster innovation and greater resilience.
Other Important Patterns
Beyond the big two, a few other patterns have emerged to solve different kinds of problems. Knowing about them gives you a richer toolkit for your systems design architecture.
- Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA): Often seen as the forerunner to microservices, SOA also organizes an application into distinct services. The key difference is that SOA typically relies on a central "enterprise service bus" (ESB) to manage communication and focuses heavily on reusing services across an entire organization.
- Event-Driven Architecture (EDA): This pattern is built around producing, detecting, and reacting to "events"—like a user adding an item to a cart or a sensor reporting a new reading. It's perfect for applications that need to respond to changes in real-time. Think fraud detection in fintech or processing data from thousands of IoT devices. Components communicate asynchronously, which can make your system feel incredibly responsive.
When you're weighing your options, getting a handle on foundational concepts—like the difference between an application server vs web server—is also crucial. This knowledge helps you see the real-world trade-offs between different architectural patterns more clearly.
Comparing Common Architectural Patterns
To make the choice a bit easier, here’s a head-to-head comparison of monolithic, microservices, and event-driven architectures. This table breaks down what each pattern is best for, its main advantage, and its biggest headache.
| Architectural Pattern | Best For | Key Advantage | Biggest Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic | MVPs, small projects, simple applications | Simplicity in development and initial deployment | Becomes complex and slow to update as it scales |
| Microservices | Large, complex applications, large development teams | Independent scaling and deployment of services | High operational complexity and distributed systems management |
| Event-Driven | Real-time systems, IoT, asynchronous workflows | High responsiveness and loose coupling between components | Difficult to debug and maintain a clear, linear logic |
Ultimately, there's no single "best" pattern. The right choice is the one that best fits your specific business needs, your team's structure, and your goals for the future.
Designing for Scale, Reliability, and Security
So you’ve built a beautiful application. It works perfectly for ten users. But what happens when ten thousand show up? Or ten million? An application that can’t grow with its audience is, unfortunately, doomed to fail. This is where we shift our focus from just building features to mastering the non-functional requirements that truly define a great user experience: scalability, reliability, and security.
These three pillars aren't just technical afterthoughts; they are the fundamental promises you make to your users. They promise that your app will be fast, always available, and a safe place for their data. Neglecting them is like building a skyscraper on a foundation of sand—it’s only a matter of time before things start to crumble under the weight.
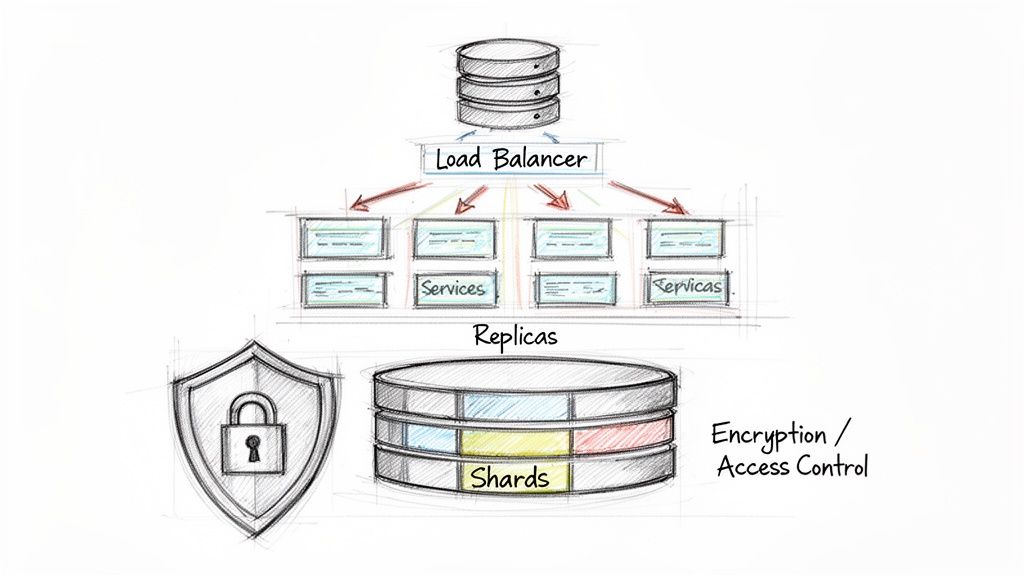
Planning for Millions With Smart Scaling
Scalability is all about your application's ability to handle a growing amount of work without breaking a sweat. When traffic surges, you basically have two ways to meet the demand:
Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up): Think of your single server as a weightlifter. Vertical scaling is like giving that weightlifter more protein and better gym equipment—you upgrade the server with more RAM, a faster CPU, or bigger storage. It’s simple, but eventually, you hit a physical limit. There's only so much you can beef up a single machine.
Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out): Instead of making your one weightlifter stronger, you hire an entire team of them. Horizontal scaling means adding more machines (servers) to your pool. For handling massive, internet-scale traffic, this is the far more powerful approach.
For most modern applications, horizontal scaling is the name of the game. It’s what allows giants like Netflix and Amazon to serve millions of users at the exact same time. But just throwing more servers at the problem isn't enough; you need smart strategies to spread the work around.
- Load Balancing: A load balancer is like a traffic cop standing in front of your servers. It takes all the incoming user requests and distributes them evenly across the team. This prevents any one server from getting swamped, ensuring a smooth, responsive experience for everyone.
- Database Sharding: As your data grows, a single database can become a serious bottleneck. Sharding is the process of splitting that massive database into smaller, faster, more manageable pieces called "shards." Each shard holds a portion of the data, so queries get spread across multiple machines, which drastically improves performance.
Building an Always-On Application With Reliability
Reliability is about one thing: making sure your application is always available and working correctly for your users. The goal is to build a system that can take a punch—it can withstand failures without going dark. Think of it as having a backup plan for every single component.
The key metric here is availability, often measured in "nines." For example, 99.99% availability (or "four nines") means your application is down for less than an hour per year. Getting to that level requires designing for fault tolerance from the ground up.
The core principle of reliability is to assume that components will fail. A reliable system isn't one where nothing ever breaks; it's one that is designed to keep working even when things do break.
Techniques like redundancy (having duplicate components) and failover (automatically switching to a standby system if the main one fails) are your best friends here. For instance, if a server crashes, a load balancer can instantly redirect its traffic to healthy servers, making the failure completely invisible to your users.
Protecting Your Users With Rock-Solid Security
In a world of constant digital threats, security is non-negotiable. It’s a foundational requirement, especially for applications in fintech, healthcare, and government, where a data breach can have devastating consequences. A truly secure architecture bakes protection into every single layer of the application.
Here are a few key practices that should be second nature:
- Data Encryption: This means protecting data both "in transit" (as it moves across the network) and "at rest" (when it's stored in a database). This ensures that even if someone manages to intercept your data, it's completely unreadable.
- Access Control: You need to implement strict rules about who can access what. This "principle of least privilege" ensures that users and services only have the permissions they absolutely need to do their jobs, and nothing more.
- Threat Detection: This involves actively monitoring your system for common attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks and defending against them in real-time.
By thoughtfully weaving scalability, reliability, and security into your system's DNA from day one, you build more than just a functional app. You build a robust, resilient, and trustworthy platform that can grow with your business and earn the lasting loyalty of your users.
Systems Design Architecture in the Real World
Theory is great, but the real test for any systems design architecture is how it holds up under pressure. Let's move past the diagrams and see how top industries are actually using these concepts to solve tough problems, build resilient platforms, and give users an experience they’ll remember. Each one of these use cases is a blueprint, showing how smart architectural choices create real business value.
As we look at these examples, you’ll notice a pattern. The right architecture is never just a technical footnote; it’s a direct answer to a business problem, whether that’s handling millions of users at once, locking down financial data, or ensuring a system is life-or-death reliable.
The Ecommerce Titan Handling the Holiday Rush
Picture a massive ecommerce site on Black Friday. Millions of users are hammering the site, all trying to grab the best deals at the same time. Without a solid architecture, the whole thing would buckle, leading to a huge loss in sales and a ton of angry customers. So, how do they keep the lights on?
- The Problem: Unpredictable, massive traffic spikes and the need for personalized product recommendations in real-time.
- The Architectural Solution: A microservices architecture is the undisputed champion here. Functions like the product catalog, user login, shopping cart, and payment processing are all split into separate, independent services. For a deeper dive, check out our guide to microservice architecture examples.
- The Outcome: When the shopping cart service gets slammed, the system uses horizontal autoscaling to spin up more instances of just that service. This elasticity keeps the site snappy and responsive. Meanwhile, a separate AI service handles personalized recommendations, and it can be updated or scaled independently without ever touching the core checkout flow.
The Fintech App Protecting Every Transaction
In the world of fintech, security and compliance aren't just features—they're the entire foundation of trust. The architecture has to be built from the ground up to guard sensitive financial data and meet tough regulatory rules.
The core architectural principle in fintech is "defense in depth." This means building multiple layers of security so that if one layer is compromised, others are still in place to protect critical data and systems.
This layered defense is non-negotiable. Here’s how it plays out:
- The Problem: Guaranteeing absolute data security, staying compliant with standards like PCI DSS, and ensuring every single transaction is sound.
- The Architectural Solution: You’ll often see a hybrid approach. A stable, well-structured monolith might handle core banking functions, while secure microservices are used for newer features. Every API call is obsessively authenticated, all data is encrypted (both at rest and in transit), and event-driven patterns are used to spot fraud in real-time.
- The Outcome: Users feel safe trusting the platform with their financial lives. This architecture also makes audits much smoother and simplifies adapting to new regulations, helping the business stay secure and compliant as it grows.
The Healthcare Platform Prioritizing Privacy
When you're dealing with healthcare, the stakes couldn't be higher. A systems design architecture for a healthcare app has to be built around HIPAA compliance and the absolute privacy of patient data. Reliability is just as critical, since doctors and nurses might be relying on the app for life-saving information.
- The Problem: Navigating strict HIPAA compliance, securing Protected Health Information (PHI), and guaranteeing high availability for medical professionals.
- The Architectural Solution: A service-oriented architecture (SOA) or microservices are common choices because they help isolate sensitive data. Every service has strict access controls and detailed logging built-in. Data is stored in databases that support powerful encryption and are hosted in a compliant cloud environment.
- The Outcome: The architecture ensures patient data is protected by design, not as an afterthought, which drastically reduces the risk of a breach. This builds trust with both patients and providers and protects the organization from massive legal and financial fallout.
These industry examples point to a much larger economic reality. The architectural services market, which is tied directly to systems design, was valued at USD 411.67 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit USD 605.62 billion by 2033. This surge is fueled by a worldwide need for well-engineered digital platforms. Projects that effectively blend advisory and engineering services often speed up processing times by 25-50%, which in turn boosts user retention through better performance and personalization. You can learn more about the growth of the architectural services market on grandviewresearch.com.
Integrating AI to Modernize Your Application
These days, a modern application is an intelligent one. Weaving AI into your systems design architecture isn't some far-off idea anymore; it's a practical way to build smarter, more engaging experiences for your users. The goal is to move beyond static features and create systems that can learn, predict, and interact in a much more human way.
This journey starts by finding the right places to add that intelligence. You don't have to tear down your whole system and start over. Instead, you can surgically inject AI where it delivers the most bang for your buck, like adding a recommendation engine to personalize content or a chatbot to handle customer questions 24/7.
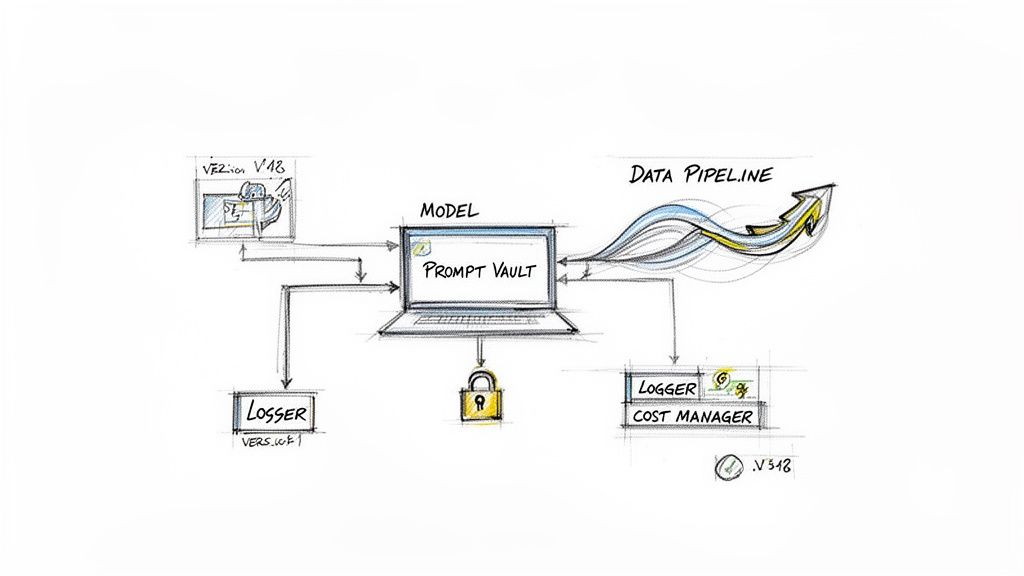
Architectural Shifts for AI Integration
Bringing AI into your application does require a few key architectural shifts. For starters, you'll need solid data pipelines to feed your models clean, relevant information. You also have to decide where these models will live and run—on your own servers, or will you call an API from a provider like OpenAI or Anthropic?
This is exactly where the idea of a central control panel for your AI work becomes so important. Without a proper management layer, bolting on AI can get chaotic and expensive, fast.
A dedicated prompt management system is a cornerstone of modern AI architecture. It acts as the command center, allowing you to build, test, and deploy AI-powered features in a controlled, scalable, and cost-effective manner.
A tool like this lets you modernize a legacy system without a complete, costly overhaul. It’s a strategic move that helps you build an intelligent, data-powered environment that is truly built to last. For a deeper look, check out our guide on how to leverage artificial intelligence in your software.
Key Components of an AI Management Layer
To really nail AI integration, your systems design needs a toolkit that gives you full control and visibility. This administrative layer is what separates a successful AI project from a costly science experiment. At Wonderment Apps, our prompt management system is designed to plug directly into your existing software, providing a suite of tools to manage and scale your AI initiatives effectively.
A well-designed system should offer:
- A Prompt Vault with Versioning: Think of this as a secure, central library for all your AI prompts. Version control is crucial here—it lets you track changes, test out different phrasing, and roll back to a previous version if a new prompt isn't performing well.
- A Parameter Manager: This piece is the bridge connecting your AI models to your internal databases. It lets you securely pass relevant business data into your prompts, which is how the AI can generate highly contextual and personalized responses.
- Comprehensive Logging: Every single interaction with your AI models should be logged. Our system logs activity across all integrated AI models, creating an invaluable audit trail for debugging, monitoring performance, and understanding how people are actually using your new AI features.
- A Cost Manager: AI models use up resources, and token spend can add up quickly. A cost manager gives you a real-time dashboard to see your cumulative spend across all integrated models. This helps you prevent surprise bills and find ways to be more efficient.
This kind of structured approach is becoming more and more critical as the market for intelligent software explodes. The numbers tell a conflicting but interesting story. One analysis from marketresearch.com puts the global architecture design software market at USD 4,936 million in 2025 with a 7.20% CAGR, while another projects it will hit a massive USD 21,597.49 million by 2035.
These figures just highlight how dynamic systems design has become in the age of AI—a trend Wonderment Apps helps fintech and SaaS teams master.
How to Find the Right Development Partner
Let’s be honest: your systems design architecture is only as good as the team that brings it to life. A brilliant blueprint is just a piece of paper without the right craftspeople to turn it into reality. This makes choosing a development partner one of the most critical business decisions you’ll make, and it will directly shape your project's success and long-term health.
Finding the right team is about more than just checking off a list of technical skills. You need a partner who truly gets your vision, speaks the language of your industry, and has a proven track record of building applications that are scalable, reliable, and secure. Their expertise in systems design architecture should be obvious in every project they’ve touched.
Evaluating a Potential Partner
When you start sizing up potential partners, their portfolio is your first stop. Don’t just get distracted by pretty designs; you need to dig deeper. Have they solved problems similar to yours? A team with deep experience in your specific industry—whether it’s ecommerce, fintech, or healthcare—will already have a handle on your unique challenges around compliance, user expectations, and security.
From there, start asking targeted questions that get to the heart of their process and philosophy.
- Communication and Methodology: How do they work? Do they lean into transparent, agile methodologies? How will they keep you in the loop about progress and potential roadblocks? Look for a partner who makes clear, consistent communication a top priority.
- Design Philosophy: What’s their approach to user experience (UX)? A great partner is obsessed with UX-driven design, making sure the final product isn’t just technically sound but also genuinely intuitive and engaging for the people using it.
- Long-Term Vision: Ask them about scalability, security, and ongoing support. The best partners don’t just think about launch day; they’re already planning for future growth and maintenance from the get-go.
A true development partner doesn't just build what you ask for. They challenge your assumptions, offer strategic insights, and act as a genuine extension of your team, committed to achieving your business goals.
Assembling Your Dream Team
Once you’ve vetted their experience, it’s time to think about how you’ll work together. The right team structure depends entirely on your needs, what resources you have in-house, and the scope of your project. Generally, you have two main ways to engage a partner.
- Managed Projects: This is the full-service approach. Your partner puts together and manages a complete team of engineers, designers, project managers, and QA experts. It’s the perfect fit for businesses that need a dedicated team to own the entire project, from initial concept to launch and beyond.
- Curated Staffing: Already have a team but need to fill a few specific skill gaps? Curated staffing is your answer. A good partner can bring in pre-vetted experts—like a senior React developer or a specialized QA analyst—to join your existing crew and help you move faster.
Picking the right partner and the right way to work with them is the final, crucial step. It’s what turns your architectural vision into a high-performing reality and ensures you have the exact mix of talent, experience, and leadership to build something that doesn't just meet expectations, but blows them away.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you're diving into system design, a lot of questions pop up. It's a complex world, especially if you're a business leader or a developer just getting your feet wet. Here are some straightforward answers to the questions we hear most often.
What Is the First Step in Systems Design Architecture?
The first move—and the most important one—is always gathering requirements. I'm not just talking about a feature list. This is about getting to the heart of the business goals and what users actually need the system to do for them.
You have to define the functional requirements (what the system does) and, just as critically, the non-functional requirements (how it performs). Think about things like expected user traffic, how much uptime is acceptable, and what security standards are non-negotiable. Skipping this foundational step is the number one reason projects need expensive rework or just plain fail.
How Do I Choose Between Monolithic and Microservices Architecture?
Picking between a monolith and microservices really boils down to your project's complexity, the size of your team, and where you see the product going long-term. There’s no magic answer; it’s all about trade-offs.
- Go with a Monolith if: You’re a small team building a fairly simple application or an MVP. Your main goal is to get something built and deployed quickly.
- Go with Microservices if: You're tackling a large, complex application with multiple teams that need to work on different parts at the same time. You know you'll need the flexibility to scale individual features down the road.
A monolith can get you to market faster, but a microservices approach is generally better for handling complexity and scale over the long run. The key is to choose the pattern that solves today's problems without creating bigger ones tomorrow.
How Does AI Impact Modern Systems Design Architecture?
AI isn't just another feature; it fundamentally changes the blueprint for an application. When you're building a systems design architecture with AI, you have to plan for a few new, resource-hungry components that weren't a big deal a few years ago.
For one, you need solid data pipelines to feed and retrain your machine learning models. Second, the architecture has to support APIs for model inference, which can be a heavy computational lift requiring specialized hardware or cloud services.
Finally, integrating AI means you absolutely need dedicated management tools. Things like prompt management systems, cost trackers for token usage, and detailed logging for every AI interaction aren't optional anymore. They are core parts of the architecture if you want to build intelligent apps that are maintainable and cost-effective.
At Wonderment Apps, we turn your architectural vision into a high-performance reality. Whether you need to modernize a legacy system with AI or build a scalable new application from the ground up, our expert teams are ready to help. Schedule a demo to see how we can build your software to last.
