Healthcare is undergoing a radical transformation, driven by a convergence of AI, data science, and patient-centric design. These aren't just incremental updates; they are foundational shifts changing how we diagnose illnesses, manage chronic conditions, and deliver care. For business leaders and innovators in this space, staying ahead of the curve means understanding not just the 'what' but the 'how'—how to build scalable, intelligent applications that meet the moment. The key challenge is no longer if AI can be integrated, but how to manage it effectively. A robust AI integration strategy requires more than just connecting to an API; it demands sophisticated tools for managing prompts, controlling costs, versioning models, and ensuring clinical relevance.
At Wonderment Apps, we've built a powerful prompt management system specifically to solve this problem, helping developers and entrepreneurs modernize their applications for this new era. This article will explore the 10 most impactful healthcare tech trends and provide actionable insights on how to harness them to build software that lasts. We'll show you how to move from concept to a successful, scalable, and AI-powered reality. Understanding these technological shifts is crucial, but so is maintaining the ethical and governance structures that build trust. For insights into foundational ethical frameworks and governance within digital health, including comprehensive conflict of interest policies in healthcare, consider exploring established examples. Our guide will focus on the practical application of these trends, from AI-powered diagnostics and telehealth platforms to cybersecurity and the rise of digital therapeutics.
1. AI-Powered Diagnostic Imaging and Clinical Decision Support
One of the most impactful healthcare tech trends is the integration of artificial intelligence into medical imaging and clinical workflows. AI-powered diagnostic tools leverage sophisticated machine learning models, trained on vast datasets of X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to identify anomalies that might be missed by the human eye. This technology acts as a "second set of eyes" for radiologists, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and dramatically reducing the time from scan to diagnosis.
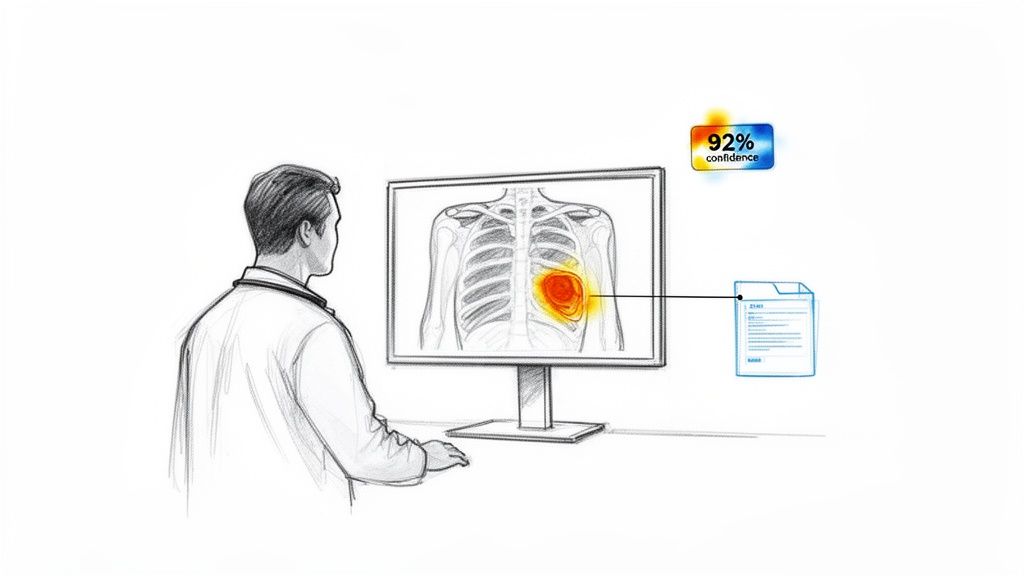
These systems go beyond simple image analysis. Modern platforms provide comprehensive clinical decision support by cross-referencing patient data with a massive knowledge base of medical literature and case histories. For example, systems like IBM Watson for Oncology can suggest personalized treatment plans based on a patient's specific genetic markers and tumor characteristics. The result is a more consistent, data-driven standard of care, helping to scale top-tier expertise across entire healthcare networks.
Practical Implementation Steps
For organizations looking to integrate this technology, the key is a phased, clinician-centric approach.
- Prioritize High-Impact Use Cases: Start with well-defined problems where AI has a proven track record, such as detecting diabetic retinopathy or flagging potential malignancies in mammograms.
- Establish Data Governance: Ensure all patient data used for model training and validation is anonymized and handled in strict compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Engage Clinicians Early: Involve radiologists and oncologists from the beginning to validate the AI's findings and ensure the tool integrates seamlessly into their existing diagnostic workflow, rather than disrupting it.
- Create Feedback Loops: Implement a system where clinicians can correct or validate the AI's suggestions. This real-world feedback is crucial for continuously training and improving the model's performance and trustworthiness over time.
For a deeper look into specific use cases, explore these advanced AI solutions for healthcare that are transforming patient outcomes.
2. Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring Platforms
The rapid expansion of telehealth and remote patient monitoring (RPM) platforms represents one of the most transformative healthcare tech trends, fundamentally changing how care is delivered and accessed. These digital solutions enable real-time video consultations and asynchronous communication, effectively breaking down geographical barriers between patients and providers. More than just virtual visits, integrated RPM systems continuously collect vital signs and health metrics from patients at home, allowing for proactive management of chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension, thereby improving outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions.
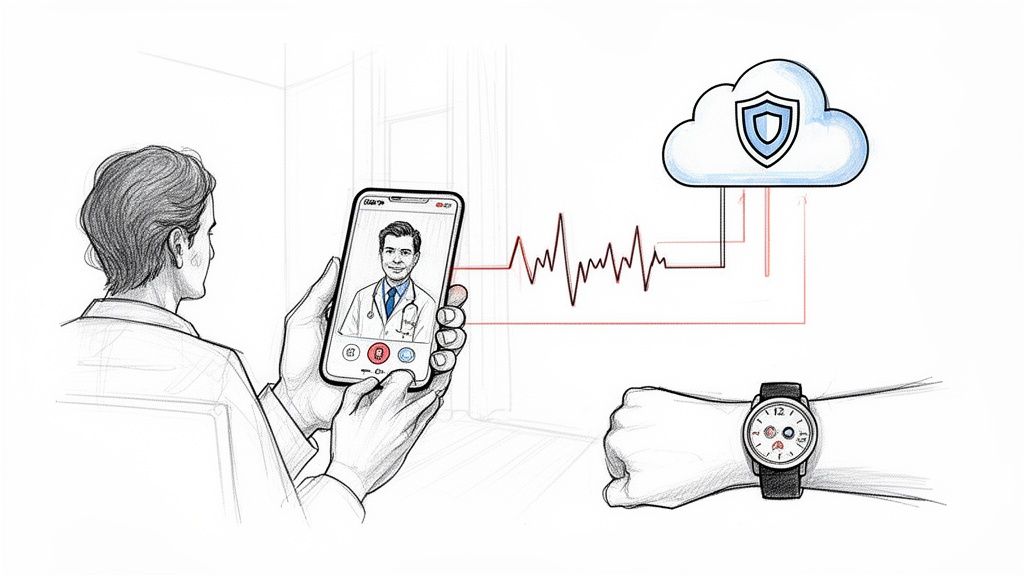
This trend has moved beyond a crisis-response tool to a core component of modern healthcare strategy. Companies like Teladoc Health have demonstrated the power of integrated platforms that combine virtual urgent care with chronic disease management, using data from connected devices to provide personalized, timely interventions. This approach fosters continuous engagement, shifting the care model from episodic to preventative and empowering patients to take a more active role in managing their health from the comfort of their homes.
Practical Implementation Steps
Successfully launching or scaling telehealth and RPM services requires a focus on seamless integration and user experience.
- Integrate with EHR Systems: Ensure the platform seamlessly integrates with existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. This provides clinicians with a complete view of the patient's history during virtual consults and allows for automated logging of RPM data, streamlining clinical workflows.
- Prioritize User-Friendly Design: Design simple, intuitive interfaces with clear accessibility features for all user demographics, including elderly patients or those with low technical literacy. Multi-device support for mobile, tablet, and desktop is essential for equitable access.
- Establish Robust Security Protocols: Implement end-to-end encryption and stringent access controls to protect sensitive patient information. Adherence to HIPAA and other privacy regulations is non-negotiable and builds crucial patient trust in the platform.
- Provide Comprehensive Clinician Training: Equip healthcare providers with training on virtual care best practices, or "webside manner," as well as the technical skills to use the platform effectively. This ensures a high-quality, consistent patient experience and maximizes clinician adoption.
Building a platform that meets these criteria often requires deep technical expertise. For insights into creating secure and scalable platforms, explore the essentials of custom healthcare application development that can support modern telehealth initiatives.
3. Wearable Health Technology and Continuous Health Monitoring
Another transformative healthcare tech trend is the proliferation of consumer-grade wearables and medical-grade sensors that enable continuous health monitoring. Devices like the Apple Watch, Oura Ring, and Dexcom continuous glucose monitors have moved beyond simple step counting. They now track sophisticated biometric data, including heart rate variability (HRV), blood oxygen levels, sleep stages, and even on-demand ECGs. This constant stream of data provides a longitudinal view of a person's health that was previously impossible to capture outside of a clinical setting.
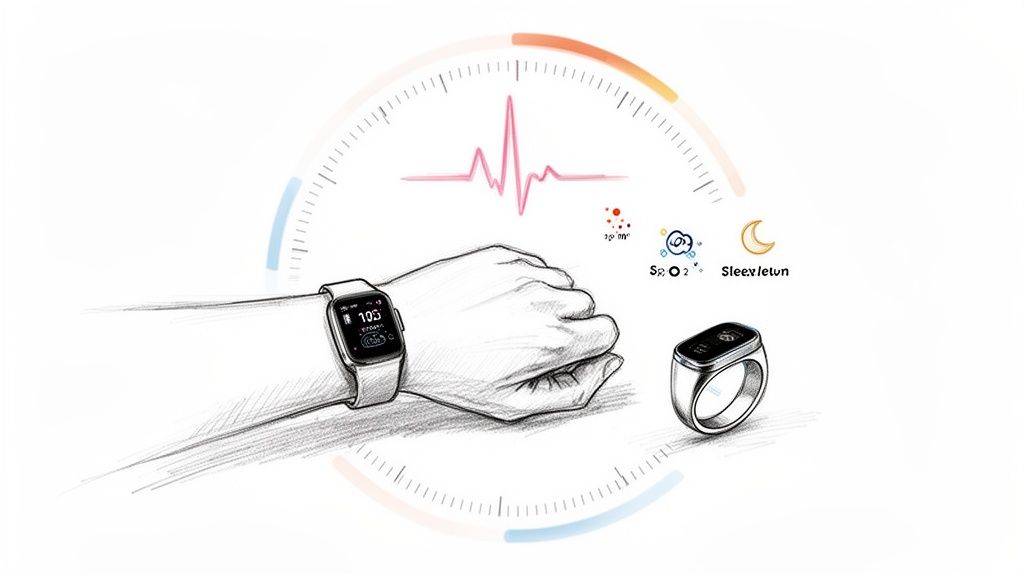

This technology is a cornerstone of proactive and preventive care. By syncing data to companion apps and provider platforms, these devices allow for the early detection of trends that may indicate a developing health issue, such as atrial fibrillation or sleep apnea. For patients with chronic conditions like diabetes, platforms like Livongo use smart devices to offer real-time feedback and coaching, empowering users to manage their health more effectively and reducing the likelihood of acute events.
Practical Implementation Steps
Healthcare organizations aiming to leverage wearable data must focus on integration, validation, and patient engagement.
- Prioritize Interoperability: Use modern data standards like FHIR to ensure wearable data can be seamlessly and securely integrated into the Electronic Health Record (EHR). This creates a unified patient view for clinicians.
- Establish Clinical Validation Protocols: Not all consumer data is clinical-grade. Develop protocols to validate the accuracy of metrics from different devices before incorporating them into care plans.
- Design Actionable Companion Apps: The companion app is the primary user interface. Design it to present complex health data through clear, understandable visualizations and provide actionable insights, not just raw numbers.
- Focus on Patient Education: Create resources to improve health literacy, helping patients understand what their data means and when to contact a healthcare provider. This prevents unnecessary anxiety and ensures the data is used constructively.
4. Electronic Health Records (EHR) Modernization and Health Information Exchange
Another critical healthcare tech trend is the fundamental overhaul of Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems. Traditional, siloed EHRs are being replaced by cloud-native platforms designed with an API-first approach. This modernization focuses on interoperability, using standards like Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) to enable the seamless flow of patient data between different providers, labs, and health systems.
This shift moves beyond simple digital record-keeping. Modern EHRs, such as those from Epic Systems and Cerner, act as a central hub for patient care, integrating data from various sources to provide a single, comprehensive view of a patient's health journey. This connected ecosystem improves clinical workflows, reduces duplicate tests, and empowers clinicians with the complete information needed for accurate, timely decision-making. The result is a more collaborative and efficient care model that directly benefits patient safety and outcomes.
Practical Implementation Steps
For healthcare organizations aiming to upgrade their EHR infrastructure, a strategic and phased approach is essential for success.
- Prioritize FHIR Compliance: When selecting a new EHR system or upgrading an existing one, ensure it is built on FHIR standards. This is non-negotiable for future-proofing your organization's ability to exchange data and integrate with third-party applications.
- Engage Clinical Staff Early: Involve doctors, nurses, and administrative staff from the very beginning of the selection and implementation process. Their buy-in and feedback are crucial for configuring workflows that enhance, rather than hinder, their daily tasks.
- Implement Staged Migrations: A "big bang" switchover is risky and disruptive. Plan a staged migration, moving one department or function at a time to the new system. This minimizes downtime, allows for iterative problem-solving, and reduces stress on staff.
- Establish Robust Data Governance: Create clear policies for data quality, access controls, and security before going live. A strong governance framework ensures the integrity and privacy of patient information as it becomes more accessible across the network.
This evolution is a core component of the broader digital transformation in the healthcare industry, moving from isolated data repositories to a connected, intelligent health ecosystem.
5. AI-Powered Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Clinical Documentation
One of the most significant operational healthcare tech trends addresses a major source of clinician burnout: documentation. AI-powered Natural Language Processing (NLP) is transforming this burden by automatically extracting structured clinical information from unstructured sources like physician dictations, progress notes, and discharge summaries. These algorithms can understand medical terminology and context, converting conversational language into accurate, coded data for electronic health records (EHRs).
This technology goes far beyond simple transcription. Advanced solutions like Nuance's Dragon Ambient eXperience (DAX) act as a clinical documentation assistant, listening to patient-physician conversations and autonomously generating compliant clinical notes in real-time. This not only frees clinicians to focus on patient interaction but also improves the accuracy and timeliness of medical coding and billing. The result is a dramatic reduction in administrative tasks, leading to better physician satisfaction and more efficient revenue cycle management.
Practical Implementation Steps
For healthcare organizations aiming to reduce the documentation burden with NLP, a focus on workflow integration and quality assurance is paramount.
- Implement Privacy-Preserving NLP: Prioritize solutions that can be deployed on-premise or in a private cloud to maintain control over sensitive patient data, ensuring strict HIPAA compliance.
- Establish Human-in-the-Loop QA: Create a quality assurance process where trained medical coders or clinicians review and validate AI-generated documentation. This is critical for accuracy and for providing the feedback needed to refine the models.
- Train Models on Specialty-Specific Data: Ensure the NLP models are trained on documentation patterns specific to different medical specialties, such as cardiology or oncology, to understand their unique terminologies and abbreviations.
- Integrate Seamlessly with EHR Workflows: The NLP tool must integrate directly into the existing EHR system. A tool that requires clinicians to switch between applications will hinder adoption and negate the efficiency gains.
6. Healthcare Cybersecurity and Zero Trust Architecture
As healthcare becomes more digitized and interconnected, the attack surface for cyber threats has expanded exponentially. One of the most critical healthcare tech trends is the industry-wide shift from traditional perimeter security to a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). This advanced framework operates on a simple but powerful principle: never trust, always verify. It assumes that threats can originate from anywhere, both inside and outside the network, and therefore requires continuous verification for every user, device, and application attempting to access resources.
This approach replaces the outdated "castle-and-moat" model, where once a user was inside the network, they had broad access. With ZTA, access is granted on a least-privilege basis through micro-segmentation, strong identity management, and multi-factor authentication for every single request. For example, a clinician accessing an EHR from a hospital workstation would still need to verify their identity to view a specific patient's file. This granular control is essential for safeguarding sensitive protected health information (PHI) and ensuring operational continuity. Implementations by the Department of Veterans Affairs and healthcare leaders like the Mayo Clinic showcase its effectiveness in protecting vast, complex digital ecosystems.
Practical Implementation Steps
Transitioning to a Zero Trust model is a strategic journey, not a single product deployment. Organizations should focus on an incremental and risk-based rollout.
- Conduct Comprehensive Risk Assessments: Identify your most critical assets and data flows, such as EHR systems, connected medical devices, and patient portals. This will help prioritize your ZTA implementation efforts.
- Implement Graduated Deployment: Start by applying Zero Trust principles to high-risk areas first. For instance, secure remote access for telehealth providers or protect internet-of-medical-things (IoMT) devices, which are often vulnerable entry points.
- Establish Robust Incident Response Protocols: A core tenet of Zero Trust is assuming a breach is inevitable. Develop and regularly test clear incident response and communication plans to minimize damage and ensure a swift recovery.
- Prioritize Continuous Staff Training: Technology alone is not enough. All staff, from clinicians to administrators, must receive regular training on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing awareness and secure password hygiene, to fortify the human element of your defense.
For a deeper dive into modernizing security frameworks, explore how custom enterprise applications are being built with security and compliance at their core.
7. Personalization and Recommendation Engines in Healthcare Apps
The "one-size-fits-all" approach to patient engagement is rapidly becoming obsolete, replaced by one of the most consumer-centric healthcare tech trends: hyper-personalization. Drawing inspiration from platforms like Netflix and Spotify, healthcare apps are now using sophisticated machine learning algorithms to deliver tailored experiences. These recommendation engines analyze individual health profiles, behavioral patterns, and personal preferences to suggest relevant content, wellness activities, and even care pathways, transforming passive patient portals into dynamic, engaging health partners.
This technology powers a new generation of digital health tools that proactively support patient wellness. For instance, a patient with Type 2 diabetes might receive personalized meal suggestions, reminders for blood sugar checks timed to their daily routine, and articles about managing their specific symptoms. Companies like Livongo (now part of Teladoc) have pioneered this with adaptive interventions that become more attuned to a user's needs over time. The result is a significant boost in patient adherence, improved chronic disease management, and better long-term health outcomes.
Practical Implementation Steps
To successfully build personalization into a healthcare application, product teams must focus on trust, relevance, and ethical algorithm design.
- Build Transparent Recommendations: Clearly explain why a particular piece of content or action is being recommended. This transparency is key to building patient trust and encouraging them to follow the guidance.
- Ensure HIPAA-Compliant Analytics: Use a robust, secure data infrastructure to track user interactions and health data. All personalization algorithms must operate within a strict, HIPAA-compliant framework to protect patient privacy.
- Implement A/B Testing for Relevance: Continuously test different recommendation models and content types to see what resonates most with different patient segments. This iterative process ensures the engine's suggestions remain effective and valuable.
- Monitor for Algorithmic Bias: Actively audit your algorithms to ensure they provide fair and equitable recommendations across all demographic groups. Proactively address any biases to prevent an unequal standard of digital care.
8. Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology for Healthcare Data Integrity
While often associated with cryptocurrency, blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) are emerging as a powerful force for ensuring data integrity and security in healthcare. This trend involves creating an immutable, decentralized, and transparent record of transactions, which is crucial for sensitive health information. By distributing records across a network of computers, blockchain makes it virtually impossible to alter or tamper with data once it's been recorded, providing an unprecedented level of trust and security.
This technology directly addresses critical challenges like data fragmentation, fraud, and interoperability. For instance, a patient's medical history can be stored as a series of encrypted blocks, accessible only to authorized providers with the patient's consent. Companies like Medicalchain are building platforms for patient-controlled electronic health records, while projects like the IBM Hyperledger Health networks are creating secure ecosystems for sharing claims and payment information. This ensures that every interaction, from a prescription fill to a clinical trial entry, is securely logged and verifiable.
Practical Implementation Steps
For organizations exploring blockchain, the focus should be on targeted, high-value applications where trust and immutability are paramount.
- Target Specific, High-Impact Use Cases: Don't try to solve every problem at once. Start with well-defined areas like pharmaceutical supply chain traceability (to combat counterfeit drugs), credential verification for medical professionals, or managing patient consent for clinical trials.
- Opt for Permissioned Blockchains: Unlike public blockchains (e.g., Bitcoin), a permissioned or private blockchain is essential for healthcare. This ensures only authorized participants (hospitals, labs, insurers) can join the network, maintaining strict privacy and control in compliance with HIPAA.
- Establish Clear Governance Models: Before implementation, all stakeholders must agree on the rules of the network. This includes data ownership, access protocols, and how consensus is achieved. A strong governance framework is the foundation of a successful healthcare blockchain.
- Plan for Legacy System Integration: Blockchain solutions must work with existing healthcare IT infrastructure like EHRs and billing systems. Use APIs and middleware to create a seamless bridge between the new DLT network and legacy platforms, ensuring data can flow securely without disrupting established workflows.
9. Predictive Analytics, Risk Stratification, and Healthcare Data Analytics
Another of the most transformative healthcare tech trends is the use of predictive analytics to forecast patient outcomes and stratify populations by risk. This approach combines machine learning with comprehensive business intelligence, aggregating vast datasets from EHRs, insurance claims, and wearable devices. By analyzing these inputs, models can predict the likelihood of events like hospital readmissions, sepsis onset, or the progression of chronic diseases, allowing providers to intervene proactively.
These systems translate raw data into actionable clinical and operational intelligence. For instance, integrated analytics platforms like those from Optum or those built using Tableau and Power BI can create dashboards that help hospital administrators optimize resource allocation. Clinically, algorithms used by Epic and Cerner can flag high-risk patients directly within the EHR, enabling care teams to implement preventive measures before a crisis occurs. This shift from reactive to preemptive care improves patient outcomes and significantly reduces costs.
Practical Implementation Steps
For healthcare organizations aiming to leverage predictive analytics, a focus on governance, transparency, and integration is paramount.
- Target High-Impact Predictions: Begin with clinically validated models that address pressing needs, such as predicting acute kidney injury or identifying patients at high risk for sepsis. These use cases have clear ROI and established protocols.
- Establish Strong Data Governance: Implement rigorous standards for data quality and integrity. Ensure that all data sources are reliable and that the analytics pipeline is secure and compliant with all privacy regulations.
- Prioritize Explainable AI (XAI): Use techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) or LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) to make model predictions understandable to clinicians. Transparency is crucial for building trust and ensuring physician oversight.
- Integrate Insights into Workflows: Develop dashboards and alerts that align with the specific needs of different stakeholders, from front-line nurses to C-suite executives. Be mindful to design systems that minimize alert fatigue and present information in a clear, actionable format.
10. Digital Therapeutics (DTx) and App-Based Clinical Interventions
One of the most transformative healthcare tech trends is the rise of Digital Therapeutics (DTx), which deliver clinical-grade, software-based treatments directly to patients. These app-based interventions use evidence-backed cognitive behavioral therapy, data tracking, and personalized feedback to manage chronic conditions, improve mental health, and drive positive lifestyle changes. Unlike generic wellness apps, DTx products undergo rigorous clinical trials and often require a prescription, positioning them as legitimate medical interventions.
This approach makes treatment more accessible, scalable, and discreet than traditional methods. For instance, platforms like Big Health’s Sleepio provide a structured program for insomnia, while Pear Therapeutics' reSET offers a digital curriculum for substance use disorder. These tools empower patients to manage their health proactively, bridging gaps in care and providing continuous support outside of a clinical setting. The result is a more integrated, patient-centric model that can complement or even replace conventional therapies.
Practical Implementation Steps
For organizations aiming to develop or implement DTx solutions, the focus must be on clinical rigor and user engagement.
- Prioritize Clinical Validation: Base the intervention on proven therapeutic principles and invest in robust, randomized controlled trials to demonstrate efficacy and safety. This evidence is crucial for gaining clinician trust and regulatory approval.
- Design for Sustained Engagement: Combat high user drop-off rates by incorporating gamification, personalized feedback, and a seamless user experience. The app must be intuitive and motivating to ensure patients complete their treatment programs.
- Integrate Clinician Oversight: Develop a dashboard or portal that allows healthcare providers to monitor patient progress, adherence, and outcomes. This keeps clinicians in the loop and ensures the DTx is used as part of a coordinated care plan.
- Navigate the Regulatory and Reimbursement Pathway: Engage with regulatory bodies like the FDA early in the development process to understand clearance requirements. Simultaneously, build partnerships with insurers and employers to establish clear pathways for reimbursement.
For a deeper dive into creating user-centric medical applications, explore these strategies for custom healthcare software development that prioritize both compliance and patient experience.
Top 10 Healthcare Tech Trends: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Item | Implementation complexity | Resource requirements | Expected outcomes | Ideal use cases | Key advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI‑Powered Diagnostic Imaging & Clinical Decision Support | High — model training, validation, regulatory review | Large labeled imaging datasets, GPU/cloud compute, EHR integration, radiologist input | Faster, more accurate detection; reduced reading time | Cancer screening, emergency radiology, multi‑site standardization | Scales specialist expertise; standardized reads; confidence scoring |
| Telehealth & Remote Patient Monitoring Platforms | Medium — real‑time apps, device integrations, compliance | Responsive web/mobile apps, secure backend, device APIs, reliable connectivity | Improved access, reduced readmissions, increased engagement | Chronic care follow‑up, rural access, triage and follow‑up visits | Increases accessibility; lowers travel/costs; continuous monitoring |
| Wearable Health Technology & Continuous Monitoring | Medium — device HW/SW and integration; validation needed | Sensors/devices, mobile apps, cloud pipelines, analytics | Continuous biometric trends; early detection; personalized prevention | Chronic condition monitoring, clinical trials, wellness programs | 24/7 data capture; preventive insights; patient engagement |
| EHR Modernization & Health Information Exchange | High — migration, interoperability, workflow redesign | Cloud infrastructure, FHIR/HL7 APIs, vendor licensing, staff training | Coordinated care, fewer duplicates, better clinician efficiency | Large health systems, value‑based care, networked providers | Seamless data exchange; workflow optimization; compliance support |
| AI‑Powered NLP for Clinical Documentation | Medium‑High — domain models, accuracy, privacy controls | Medical speech/text datasets, NLP pipelines, EHR connectors, QA workflows | Reduced documentation time; better coding and data quality | High‑documentation clinics, hospitals, revenue cycle ops | Cuts admin burden; improves coding accuracy; richer structured data |
| Healthcare Cybersecurity & Zero Trust Architecture | High — architecture overhaul, continuous ops | MFA, EDR/XDR, encryption, skilled security teams, monitoring | Lower breach risk, faster incident response, regulatory compliance | Hospitals, large networks, organizations with sensitive data | Strong protection; compliance readiness; minimized downtime |
| Personalization & Recommendation Engines in Healthcare Apps | Medium — ML pipelines, experimentation, privacy design | Historical user data, ML infrastructure, A/B testing, privacy controls | Higher engagement and adherence; targeted interventions | Patient portals, chronic disease apps, wellness platforms | Improves relevance and retention; enables timely interventions |
| Blockchain & Distributed Ledger for Data Integrity | High — governance, integration, consensus choices | Permissioned ledger tech, governance frameworks, integration middleware | Immutable audit trails; improved traceability and trust | Supply chain, credentialing, clinical trial provenance | Tamper‑evident records; transparent sharing; patient data control |
| Predictive Analytics & Risk Stratification | High — data engineering, model governance, clinical validation | Data warehouse, cross‑source integration, ML teams, monitoring | Early identification of high‑risk patients; optimized resources | Population health, readmission reduction, sepsis prediction | Proactive care targeting; resource optimization; measurable impact |
| Digital Therapeutics (DTx) & App‑Based Interventions | Medium‑High — clinical trials, regulatory clearance, UX | Clinical evidence generation, app development, clinician dashboards | Scalable behavioral treatments; improved adherence and outcomes | Mental health, diabetes management, sleep and habit change | Evidence‑based scalable care; lower cost than traditional therapy |
From Trends to Transformation: Building Your AI-Powered Future
The journey through today's most pivotal healthcare tech trends reveals a powerful, unifying narrative. We are moving decisively away from reactive, episodic care and into an era of proactive, continuous, and deeply personalized health management. From AI enhancing diagnostic imaging and NLP streamlining clinical notes, to telehealth platforms and wearables extending care beyond the hospital walls, the message is clear: the future of healthcare is intelligent, interconnected, and built on data.
These are not isolated advancements. They are converging to create a new healthcare ecosystem. The modernization of EHRs provides the foundational data layer, while advancements in cybersecurity and Zero Trust architecture ensure that this sensitive information remains secure. Meanwhile, predictive analytics and digital therapeutics leverage this data to forecast health risks and deliver targeted interventions directly to patients, transforming smartphones into powerful clinical tools.
The Unifying Force: Strategic AI Integration
The common denominator driving this transformation is Artificial Intelligence. AI is the engine that powers predictive models, personalizes patient engagement, and uncovers insights from vast datasets that would be impossible for humans to discern alone. However, simply "adding AI" to a healthcare application is not a strategy. True transformation requires a deliberate, well-architected approach.
Success hinges on building scalable, compliant, and user-centric applications that can handle the immense complexity of AI integration. This is where many initiatives falter. The challenges are significant: managing multiple AI models, ensuring data privacy, controlling spiraling operational costs, and maintaining a clear audit trail for regulatory compliance.
Your Actionable Roadmap for Modernization
Translating these healthcare tech trends from concept to reality requires a focused, step-by-step plan. Here is a practical roadmap for your organization or product team:
- Conduct a Strategic Gap Analysis: Before chasing the newest trend, evaluate your current capabilities. Where are your biggest operational bottlenecks or opportunities for patient engagement? Map specific trends, like predictive analytics or NLP for documentation, to your most pressing business problems.
- Prioritize Interoperability and Data Hygiene: Your AI is only as good as your data. Focus on modernizing your data infrastructure. Adopt FHIR standards and invest in data cleansing and governance to create a reliable foundation for any future AI initiatives.
- Implement a Robust AI Governance Framework: The "black box" nature of AI is a non-starter in healthcare. This is where a dedicated management layer becomes critical. A system that offers a prompt vault for versioning, a parameter manager for secure database access, comprehensive logging, and cost management tools is no longer a luxury; it is a necessity for de-risking AI deployment and ensuring you can build with confidence and control.
- Adopt a Pilot-to-Scale Methodology: Don't try to boil the ocean. Identify a high-impact, low-risk use case for a pilot project. For example, start with an internal AI tool to help clinicians summarize patient histories before attempting a patient-facing diagnostic AI. Learn from the pilot, refine your process, and then scale.
- Understand the Regulatory Landscape: Building a great product is only half the battle. To move beyond conceptual trends and truly build an AI-powered future, a deep understanding of the medical device product development process is essential for transforming innovative ideas into deployable, compliant solutions.
The ultimate goal is to build software that not only incorporates these trends but lasts for years to come. This requires a partner who understands both the intricacies of AI modernization and the principles of creating exceptional, scalable user experiences. Choosing the right development team is arguably the single most important decision in your technology journey.
The path forward is clear: embrace these trends not as a checklist, but as integrated components of a cohesive digital health strategy. By focusing on a strong data foundation, implementing rigorous AI governance, and choosing the right expert partner, you can move from simply observing trends to actively shaping the future of healthcare.
Ready to modernize your healthcare application with AI but need the tools to control its complexity? Wonderment Apps has developed a powerful prompt management system that gives your team the administrative layer needed to manage, log, and scale your AI integrations with confidence. Schedule a demo today and see how we can help you turn healthcare tech trends into your competitive advantage.
