In today's fast-paced digital environment, enterprise application integration (EAI) is no longer about simply making your CRM talk to your ERP. It's the strategic foundation for scalability, security, and groundbreaking innovation, especially when modernizing your software with AI. Poor integration leads to data silos, brittle connections, and security vulnerabilities, crippling your ability to adapt. Getting it right means creating a resilient, high-performance ecosystem that can seamlessly incorporate intelligent features, from personalized user experiences to sophisticated fraud detection.
The challenge, however, is the increasing complexity. Managing the connections between legacy systems, modern microservices, and multiple AI models is a significant hurdle. How do you version control the prompts sent to different AIs? How do you track token costs across various services? At Wonderment Apps, we've seen this challenge firsthand, which is why we built a prompt management system. This administrative toolkit is designed for developers and entrepreneurs to plug directly into existing software, offering a prompt vault with versioning, a parameter manager for secure database access, comprehensive logging, and a cost manager to keep AI spend in check. It's a key tool for any business leader looking to make their software initiatives successful and build applications that last.
This guide will walk you through the 10 essential enterprise application integration best practices that form the backbone of such modern, AI-enabled systems. These principles are not just theoretical; they are the actionable tips and tricks needed to ensure your next project is scalable, secure, and built to last in an AI-driven future. We will explore everything from microservices and event-driven patterns to zero-trust security and AI model governance, providing the framework for building a truly cohesive digital ecosystem.
1. Microservices Architecture with API-First Design
Adopting a microservices architecture with an API-first design is a cornerstone of modern enterprise application integration best practices. This approach decomposes large, monolithic applications into a collection of smaller, independently deployable services. Each service is built around a specific business capability and communicates with others through well-defined, language-agnostic APIs.
This pattern provides immense flexibility, allowing teams to develop, deploy, and scale services independently. For instance, Amazon's retail platform leverages microservices to manage everything from the shopping cart to personalized recommendations, enabling rapid innovation without disrupting the entire system. Similarly, Netflix's content delivery network relies on this architecture to handle massive-scale streaming and optimize user experiences across countless devices.
Why This Approach Works
Microservices excel in complex environments where agility and scalability are critical. By isolating functions, you can update a single service (like a payment processor) without redeploying the entire application. This modularity also simplifies the integration of new technologies, including AI models, as they can be encapsulated within their own dedicated services. Modern AI integration often requires managing complex prompts and parameters, and a microservices approach allows you to build specialized services for this. A dedicated prompt management service, for example, can handle versioning, logging, and cost tracking for AI interactions, modernizing your application without a complete overhaul.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this strategy, focus on incremental adoption and robust tooling from the start.
- Start Small: Decompose 3-5 critical, high-impact services first rather than attempting a "big bang" migration of your entire monolith.
- Prioritize Resilience: Implement patterns like circuit breakers (to prevent a failing service from cascading failures) and retry logic within your API gateways.
- Establish Clear Ownership: Assign dedicated, cross-functional teams to own the full lifecycle of each microservice, fostering accountability.
- Invest in Observability: Use distributed tracing and centralized logging tools from day one to monitor performance and troubleshoot issues across service boundaries. For a deeper dive into architectural patterns, you can learn more about software architecture best practices on wondermentapps.com.
2. Event-Driven Architecture and Message Queuing
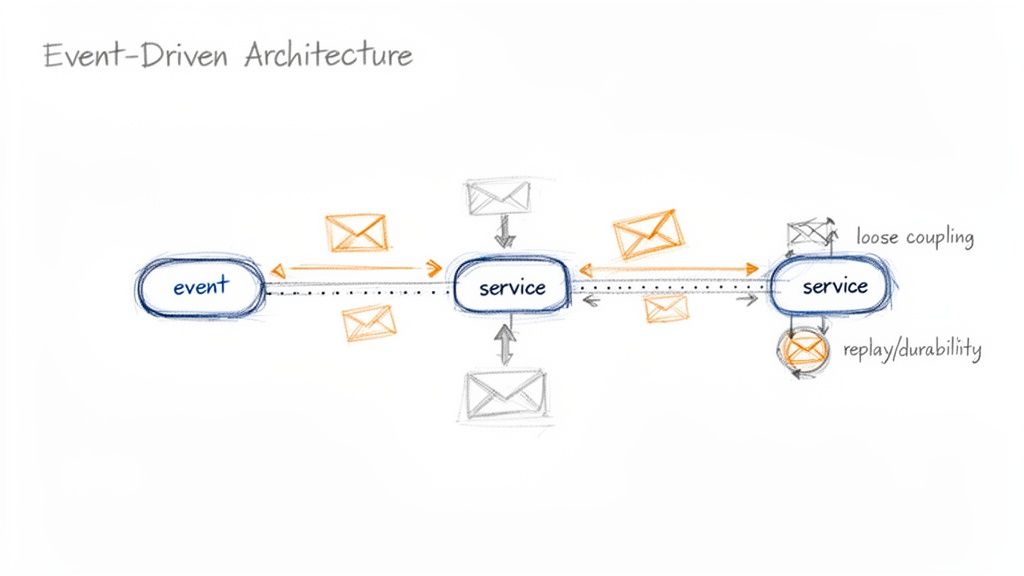
Embracing an event-driven architecture (EDA) with message queuing is a powerful strategy among enterprise application integration best practices. This pattern decouples applications by having them communicate asynchronously. Instead of making direct requests, a service publishes an "event" (a record of a significant change) to a central message broker or event stream. Other interested services subscribe to these events and react accordingly, without the producer needing to know who or what is listening.
This temporal and logical decoupling creates highly resilient and scalable systems. For example, Shopify uses an event-driven model to process millions of orders. When a customer makes a purchase, an OrderCreated event is published. Separate services for inventory management, shipping, and notifications can then consume this event independently and in parallel, ensuring the system remains responsive even under peak load. Similarly, financial institutions leverage Apache Kafka to stream transaction events for real-time fraud detection without slowing down the core payment processing.
Why This Approach Works
Event-driven architecture excels at building responsive, scalable, and resilient systems. Since services are not directly linked, the failure of one consumer does not impact the producer or other consumers. This asynchronous communication allows applications to absorb spikes in traffic and process workloads efficiently, making it ideal for high-volume ecommerce, IoT data ingestion, and real-time analytics. Furthermore, this pattern simplifies adding new functionality; a new service can simply subscribe to existing event streams without requiring changes to legacy systems.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To succeed with an event-driven approach, focus on the integrity of your events and the resilience of your consumer services.
- Choose the Right Broker: Use Apache Kafka for high-throughput, persistent event streaming scenarios like analytics pipelines. Opt for RabbitMQ when you need complex routing logic and per-message guarantees.
- Ensure Idempotent Consumers: Design your services to safely process the same message multiple times without unintended side effects, as message brokers can sometimes deliver duplicates.
- Establish a Schema Registry: Use a tool like Confluent Schema Registry to enforce a consistent data structure for your events, preventing integration failures from schema changes.
- Plan for Failures: Implement dead-letter queues (DLQs) from the start to capture and analyze messages that fail processing, preventing data loss and providing insight into system errors.
3. API Management and Gateway Pattern
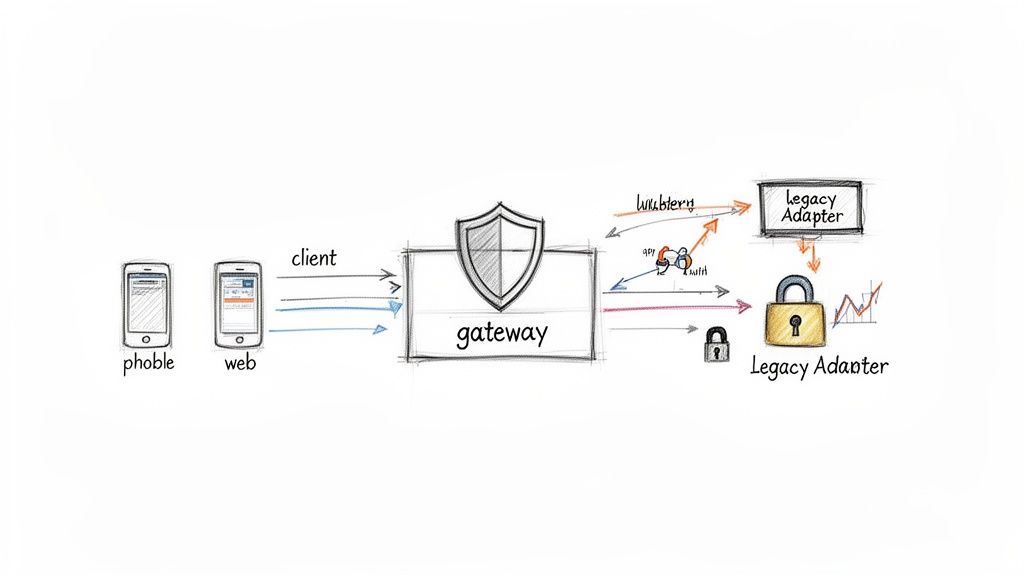
Implementing an API Management and Gateway pattern is a critical component of successful enterprise application integration best practices. This approach establishes a centralized, unified entry point that intercepts all incoming API requests. The gateway acts as a reverse proxy, routing requests to the appropriate backend services while abstracting the underlying complexity from the client applications. It's the gatekeeper that enforces policies, secures endpoints, and provides invaluable insights into your integration ecosystem.
For example, Salesforce's API Management platform allows thousands of partners to securely integrate with its ecosystem, while Twilio's gateway handles billions of API calls for its communication services. Similarly, retail platforms like Shopify use gateways to control and monitor third-party app access to merchant data, ensuring stability and security. This pattern is essential for managing integrations with legacy systems, controlling third-party access, and even managing access to internal AI models.
Why This Approach Works
An API Gateway provides a crucial layer of control and abstraction in a distributed architecture. It decouples clients from services, allowing you to modify backend systems without impacting the end-user experience. This centralization simplifies the implementation of cross-cutting concerns like authentication, rate limiting, and logging, preventing redundant code across multiple services. When modernizing with AI, a gateway can manage access to different model endpoints, enforce usage quotas, and transform requests, making it easier to integrate and swap out AI providers without re-architecting client applications.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To deploy an effective API Gateway, focus on robust security, clear versioning, and comprehensive monitoring from the outset.
- Implement a Clear Versioning Strategy: Use URL path versioning (e.g.,
/api/v2/users) or custom request headers from the beginning to manage API evolution without breaking existing client integrations. - Secure Endpoints with OAuth 2.0: Standardize on robust security protocols like OAuth 2.0 and JSON Web Tokens (JWT) to ensure secure, scalable authentication and authorization for all services.
- Establish Tiered Rate Limiting: Configure different usage quotas and throttling limits for various consumer segments (e.g., internal, partner, public) to protect backend services from overuse and ensure fair resource allocation.
- Monitor Key Performance Metrics: Actively track API latency, error rates, and usage patterns to identify performance bottlenecks and understand how your APIs are being consumed.
- Define a Deprecation Policy: Create and communicate a clear policy for retiring old API versions to manage technical debt and encourage consumers to migrate to newer, more efficient endpoints.
4. Data Integration with ETL/ELT Patterns
Effective data integration using Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) or Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) patterns is a fundamental component of enterprise application integration best practices. These processes are designed to consolidate data from numerous disparate sources, standardize it into a usable format, and move it to a centralized system like a data warehouse or data lake for analysis, reporting, or to feed machine learning models.
This practice is essential across industries. For example, a global retailer like Stitch might use a cloud-based ELT pipeline to pull sales data from thousands of stores, web traffic from its e-commerce site, and inventory levels from its ERP into a single data warehouse. This consolidated view enables real-time analytics on customer behavior and supply chain efficiency. Similarly, fintech companies rely on robust ETL processes managed by tools like Talend to ensure PCI-compliant data handling for regulatory reporting.
Why This Approach Works
ETL and ELT patterns are crucial for creating a single source of truth, which is necessary for reliable business intelligence and operational efficiency. By centralizing clean, high-quality data, organizations can power everything from executive dashboards to sophisticated AI-driven recommendation engines. Integrating and transforming data is also a prerequisite for modernizing applications with AI, as high-quality, structured training data is the lifeblood of accurate and effective models. A well-designed data pipeline ensures AI systems are fed consistent, reliable information, preventing skewed outcomes.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To build resilient and scalable data pipelines, focus on modern architectural choices and rigorous data governance from the outset.
- Prefer ELT for Cloud Architectures: For modern data stacks, favor the ELT pattern. Load raw data directly into a cloud data warehouse like Snowflake or BigQuery and use its powerful compute capabilities to perform transformations in-place, increasing flexibility.
- Implement Robust Data Quality Checks: Institute automated validation checks at both the source (before extraction) and in the target warehouse (post-transformation) to catch anomalies, duplicates, and formatting errors early.
- Use Version Control for Transformations: Treat your transformation logic (e.g., SQL scripts or dbt models) as code. Store it in a Git repository to enable versioning, peer reviews, and automated CI/CD deployments.
- Build Idempotent Pipelines: Design your transformations to be idempotent, meaning they can be re-run multiple times on the same input data without creating duplicate records or causing unintended side effects. This makes failure recovery much safer and simpler.
5. Zero Trust Security Architecture
Implementing a Zero Trust security architecture is a critical component of modern enterprise application integration best practices. This security model operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," assuming no implicit trust for any user or device. Every access request is rigorously authenticated, authorized, and encrypted, regardless of whether it originates from inside or outside the corporate network.
This approach is essential for protecting distributed systems and sensitive data. For example, financial institutions use Zero Trust to secure trading platforms and customer data, ensuring every transaction and data request is validated. Similarly, healthcare providers rely on this model for HIPAA-compliant electronic health record (EHR) integrations, protecting patient information from unauthorized access across interconnected systems.
Why This Approach Works
Zero Trust excels in today's complex, perimeter-less IT environments where applications and data are accessed from anywhere. By enforcing strict identity verification and least-privilege access, it drastically reduces the attack surface and contains potential breaches. This is particularly vital when integrating AI models, as it allows you to control access to sensitive training data and prevent unauthorized use of AI services, thereby securing your intelligent automation workflows from internal and external threats.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Adopting a Zero Trust framework requires a layered, identity-centric approach to security.
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Make MFA the baseline requirement for accessing all integrated applications, APIs, and data sources.
- Implement Microsegmentation: Use tools like a service mesh (e.g., Istio) to create granular security perimeters around individual services and enforce encrypted mTLS communication between them.
- Deploy Strict IAM: Utilize a robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution to enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring users and services have only the minimum access required.
- Monitor for Anomalies: Implement real-time anomaly detection to identify and respond to unusual access patterns or suspicious behavior across the integration landscape. For a comprehensive overview, you can explore more about application security best practices on wondermentapps.com.
6. Observability and Distributed Tracing
Implementing comprehensive observability with distributed tracing is a critical enterprise application integration best practice for modern, complex systems. This approach goes beyond traditional monitoring by combining metrics, logs, and traces to provide a holistic, end-to-end view of how requests flow across multiple applications and services. It allows you to understand not just that a problem occurred, but why it happened by tracking a single request's journey through a distributed architecture.
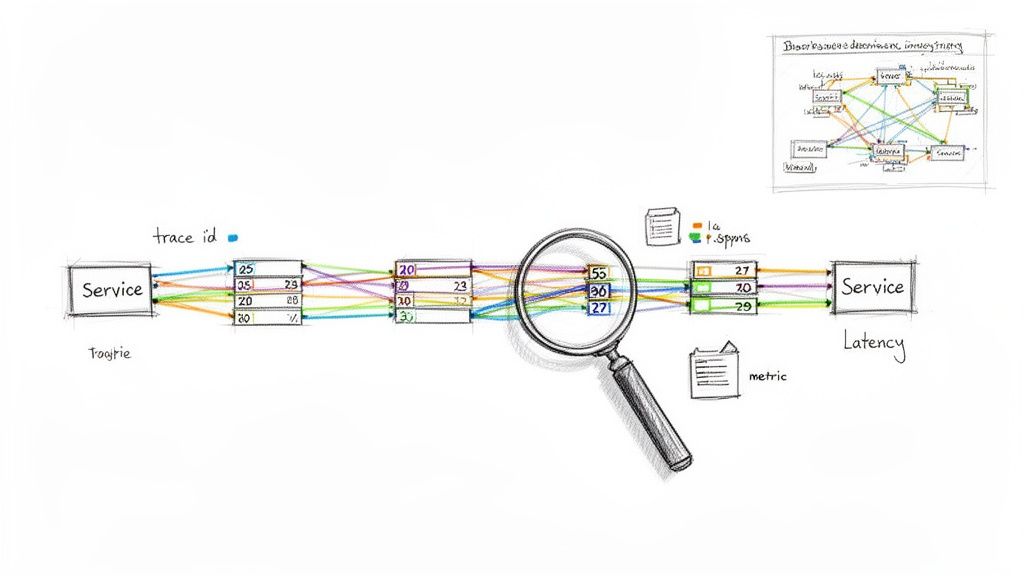
This level of insight is essential in high-stakes environments. For example, Uber utilizes Jaeger to trace transactions across its vast microservices landscape, pinpointing performance bottlenecks in real time. Similarly, fintech institutions track transaction flows to ensure compliance and identify failures, while healthcare platforms monitor complex FHIR data pipelines to guarantee low latency and data integrity.
Why This Approach Works
Observability is indispensable in distributed systems where a single business process, like an e-commerce checkout, might involve dozens of independent services. Without it, debugging becomes a frustrating exercise in guesswork. Distributed tracing provides the necessary context to correlate events, identify root causes of latency, and understand service dependencies. This is especially vital when integrating modern AI services, where a single API call can trigger a complex chain of internal processes. A dedicated logging system for AI interactions can track prompts, responses, and costs, tying them back to the original user request and providing full visibility into the AI's impact on performance.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To build an effective observability practice, focus on standardization and linking technical data to business outcomes.
- Implement Structured Logging: Use a consistent format (like JSON) and embed a unique correlation ID in every log entry and service call to trace a request's entire lifecycle.
- Adopt OpenTelemetry: Start with OpenTelemetry as a vendor-neutral standard for collecting traces, metrics, and logs, ensuring future flexibility.
- Use Tail-Based Sampling: For high-throughput systems, collect data for 100% of requests but only store traces for those that are slow or result in an error, managing costs without losing critical insights.
- Create Business-Centric Dashboards: Monitor key business metrics (e.g., checkout completion rate, transaction success percentage) alongside technical metrics like CPU usage and latency.
7. Contract Testing and API Specification
Adopting contract testing and a specification-first approach is a pivotal step in modern enterprise application integration best practices. This methodology requires you to define how services will communicate using a formal contract, such as an OpenAPI (formerly Swagger) specification, before any code is written. Each service is then tested independently against this contract, ensuring that the provider (producer) and the consumer of the API remain compatible without requiring slow, brittle end-to-end integration tests.
This strategy decouples development teams, allowing them to work in parallel with confidence. For example, retail platforms like Shopify use OpenAPI to define their partner app ecosystem, allowing thousands of third-party developers to build integrations that are guaranteed to work. Similarly, financial institutions leverage BIAN (Banking Industry Architecture Network) contracts to ensure interoperability between disparate banking systems, while healthcare organizations use FHIR specifications to define strict API boundaries for exchanging patient data securely.
Why This Approach Works
Contract testing excels at preventing integration failures early in the development lifecycle, especially in complex microservices or partner ecosystems. It provides a single source of truth for how an API should behave, reducing ambiguity and miscommunication between teams. This is particularly valuable when integrating third-party services or specialized AI models. A well-defined contract can specify the exact inputs a prompt-based AI service expects and the structure of its response, allowing you to build and test your consuming application against a reliable mock generated directly from the contract.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To implement contract testing effectively, you must embed it into your development culture and automated pipelines.
- Define Contracts First: Use a specification language like OpenAPI 3.0 to define your API endpoints, request/response schemas, and error codes before development begins.
- Use Consumer-Driven Contracts: For microservices, use tools like Pact to let the consumer service define its expectations. The provider service is then tested to ensure it meets those specific needs.
- Automate Everything: Automatically generate API documentation, server stubs, and client SDKs directly from the contract file to ensure consistency.
- Integrate into CI/CD: Add contract testing as a mandatory step in your CI/CD pipeline to catch breaking changes before they are deployed to any environment.
8. Comprehensive Data Governance and Compliance Framework
Establishing a comprehensive data governance and compliance framework is a non-negotiable component of modern enterprise application integration best practices. This systematic approach involves managing data quality, lineage, privacy, and regulatory adherence across all integrated systems. It ensures that data is consistent, trustworthy, and handled in accordance with legal standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
This practice is critical for organizations handling sensitive information. For example, financial institutions use platforms like Informatica to enforce data governance for PCI compliance, ensuring payment data is secure. Similarly, healthcare organizations implement Collibra to maintain HIPAA-compliant data lineage, tracking every touchpoint of patient health information. These frameworks are not just about avoiding fines; they build customer trust and data-driven confidence.
Why This Approach Works
In a connected enterprise, data flows between dozens of applications, creating significant risk if not properly managed. A strong governance framework provides the rules of the road for your data, defining who can access it, how it can be used, and how its quality is maintained. This is essential for regulatory compliance and for making reliable business decisions. It also supports secure AI integration by ensuring that models are trained on high-quality, compliant data, preventing biased or legally problematic outcomes.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To build a successful data governance program, start with high-risk assets and create clear, automated processes.
- Prioritize High-Risk Data: Begin by identifying and classifying your most sensitive data assets, such as personal health information (PHI) or payment card information (PCI).
- Automate PII Detection: Implement automated tools within your integration pipelines to detect, mask, or redact personally identifiable information (PII) in real time.
- Establish Data Ownership: Assign clear data owners and stewards within business units to take responsibility for specific data domains, ensuring accountability.
- Create Accessible Glossaries: Develop and maintain a central data dictionary and business glossary that are easily accessible to both technical and non-technical teams. For practical steps and a comprehensive resource to simplify evidence gathering for your framework, refer to this detailed SOC 2 compliance checklist.
9. Resilience Patterns and Chaos Engineering
Implementing resilience patterns and chaos engineering is a crucial step in modern enterprise application integration best practices. This strategy moves beyond reactive problem-solving to proactively build systems that anticipate and gracefully handle failures. It involves using established patterns like circuit breakers and bulkheads to isolate issues, combined with the deliberate injection of failures into a system to test its resilience.
This proactive approach ensures that the failure of one integrated component does not cause a catastrophic system-wide outage. For example, Netflix famously pioneered chaos engineering with its Chaos Monkey tool, which randomly disables production instances to verify that engineers implement services resiliently. Similarly, financial trading platforms implement circuit breakers that automatically halt trading during extreme market volatility, preventing cascading failures and protecting both the system and its users.
Why This Approach Works
In a distributed integration landscape, failures are not a possibility; they are an an inevitability. Resilience patterns work by creating defensive layers that contain the blast radius of a failure. A circuit breaker, for instance, can stop an application from repeatedly calling a failing service, preventing resource exhaustion. Chaos engineering validates that these patterns work as expected under real-world stress. This methodology is essential for maintaining high availability in critical systems where downtime in one area, such as a third-party payment gateway, cannot be allowed to bring down an entire e-commerce platform.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To build a truly resilient integration architecture, you must codify fault tolerance into your design and continuously validate it.
- Implement the Circuit Breaker Pattern: Use libraries like Hystrix or Resilience4j to implement circuit breakers with three states: closed (normal operation), open (requests are blocked), and half-open (a limited number of requests are allowed to test recovery).
- Isolate Dependencies with Bulkheads: Use the bulkhead pattern to partition system resources, such as connection pools or thread pools, for each integration point. This prevents a slow or failing dependency from consuming all available resources.
- Establish Aggressive Timeouts: Define and enforce strict timeout policies for all remote calls, aligning them with your Service Level Objectives (SLOs) to prevent cascading delays.
- Start Chaos Engineering in Staging: Begin by running controlled "game day" experiments in a pre-production environment. Intentionally disrupt services, increase latency, or block network access to identify weaknesses.
- Measure and Monitor Resilience: Track metrics like Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR) and service availability. Use dashboards to visualize the impact of your resilience patterns during chaos experiments and real incidents.
10. AI/ML Model Integration and Governance
Integrating AI and machine learning models directly into business processes is a critical evolution of enterprise application integration best practices. This involves more than just connecting an AI service; it requires a structured approach to manage the entire model lifecycle, from development and deployment to continuous monitoring and governance. This ensures that models deliver accurate, reliable, and fair outcomes.
For example, Shopify's recommendation engine integrates ML models to personalize shopping experiences, boosting conversion rates and average order value. Similarly, Stripe leverages sophisticated fraud detection models to protect merchants and consumers in real-time, showcasing how deeply integrated AI can become a core business function. These integrations are not static connections but dynamic systems that require constant oversight.
Why This Approach Works
AI/ML integration excels at automating complex decision-making and uncovering insights that drive significant business value. Unlike traditional integrations that move data between static rule-based systems, AI integrations introduce dynamic, learning components into the application landscape. This allows enterprises to adapt to changing data patterns, such as shifting consumer behavior or emerging security threats, without manual intervention.
A key aspect of modernizing with AI is managing the inputs, or prompts, that feed these models. A dedicated prompt management system can be crucial, providing version control, parameter management, and cost tracking for all AI interactions. This turns a potentially chaotic process into a governed, scalable, and auditable part of your integration strategy. For a deeper look into how this technology can transform your operations, you can learn more about applying machine learning for businesses.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To successfully integrate and govern AI/ML models, establish a robust MLOps foundation from the outset.
- Use a Feature Store: Implement a feature store (like Tecton or Feast) to ensure consistency between the data used for model training and real-time inference.
- Adopt Model Lifecycle Management: Utilize tools like MLflow or AWS SageMaker to track experiments, version models, and automate deployment pipelines.
- Monitor for Drift: Continuously monitor for model prediction drift and data drift to detect when a model’s performance is degrading and needs retraining.
- Implement Explainability: Use explainability tools (SHAP, LIME) to make model decisions interpretable and transparent for stakeholders and compliance audits. For further insights into the responsible development and deployment of AI, an article on Artificial Intelligence Governance provides valuable guidance.
Top 10 Enterprise Integration Best Practices Comparison
| Pattern / Solution | Implementation complexity | Resource requirements | Expected outcomes | Ideal use cases | Key advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microservices Architecture with API-First Design | High — distributed services, advanced DevOps | Containers/Kubernetes, CI/CD, service mesh, observability, cross-functional teams | Independent deploys, scalable services, faster feature delivery | Large ecommerce, media, fintech, healthcare modernization | Rapid iteration, fault isolation, tech diversity, scalable personalization |
| Event-Driven Architecture and Message Queuing | Medium–High — async coordination, consistency challenges | Message brokers (Kafka/RabbitMQ), schema registry, idempotent consumers, replay storage | High-throughput processing, loose coupling, real-time flows | Order processing, fraud detection, real-time personalization, analytics | Scalability under load, resilience, audit trails, easy extensibility |
| API Management and Gateway Pattern | Medium — central control and governance | API gateway (Apigee/Kong/AWS), IAM/OAuth, analytics, HA setup | Consistent security, centralized routing, usage visibility | Partner integrations, legacy adapters, controlled AI access | Centralized auth/policy, rate limiting, versioning, developer onboarding |
| Data Integration with ETL/ELT Patterns | Medium — transformation logic and orchestration | ETL/ELT tools (Airflow, dbt, Fivetran), data warehouse, data engineers | Consolidated analytics, historical datasets, feeding ML models | BI, reporting, model training in ecommerce/fintech/healthcare | Single source of truth, data quality, historical context for ML |
| Zero Trust Security Architecture | High — pervasive auth and segmentation | Modern IAM (Okta/Azure AD), mTLS/service mesh, encryption, monitoring | Reduced breach impact, regulatory compliance, secure distributed access | Sensitive data systems in fintech, healthcare, hybrid/multi-cloud | Continuous verification, least privilege, strong auditability |
| Observability and Distributed Tracing | Medium — instrumentation and storage planning | OpenTelemetry/Jaeger, metrics/logs platforms, alerting, storage | Faster MTTR, performance insight, end-to-end visibility | Microservices, high‑availability systems, model performance monitoring | Root-cause analysis, SLOs/error budgets, performance optimization |
| Contract Testing and API Specification | Low–Medium — discipline and CI integration | OpenAPI/Pact, mock servers, CI pipelines, spec governance | Fewer integration failures, faster parallel development | Microservices ecosystems, third-party APIs, partner platforms | Early compatibility checks, autogenerated clients, living docs |
| Comprehensive Data Governance and Compliance Framework | High — policy, tooling and cross-functional process | Governance tools (Collibra/Informatica), data stewards, legal/compliance | Regulatory compliance, data lineage, privacy-by-design | Fintech, healthcare, GDPR/PCI-sensitive organizations | Auditability, risk reduction, consistent data stewardship |
| Resilience Patterns and Chaos Engineering | Medium–High — design patterns and controlled testing | Resilience libraries, chaos tools (Gremlin), monitoring, runbooks | Fewer cascading failures, improved availability and recovery | Mission-critical services in retail, fintech, healthcare | Fault isolation, proactive failure discovery, safer rollouts |
| AI/ML Model Integration and Governance | High — ML lifecycle, monitoring and explainability | Model registry (MLflow), feature store, ML engineers, serving infra | Personalized experiences, monitored model performance, compliant AI | Personalization, fraud detection, predictive healthcare analytics | Model versioning, drift detection, governed responsible AI |
Bringing It All Together: Your Next Steps in AI Modernization
Navigating the landscape of enterprise application integration can feel like assembling a complex, high-stakes puzzle. The pieces we've explored, from Microservices Architecture with API-First Design to AI/ML Model Integration, are not just isolated components; they are interconnected elements of a cohesive, strategic framework. Mastering these enterprise application integration best practices is the critical step that elevates your organization from simply connecting systems to building a truly agile, resilient, and intelligent digital ecosystem.
We’ve seen how adopting an Event-Driven Architecture decouples your services, allowing them to scale independently and react to business events in real-time. We've highlighted the necessity of a robust API Management and Gateway Pattern to enforce policies, secure endpoints, and manage traffic effectively. This architectural discipline forms the bedrock of a modern enterprise.
But a solid foundation is only the beginning. The real transformative power lies in what you build upon it.
From Solid Integration to Strategic Intelligence
The true value of mastering these integration patterns in today's market is their ability to prepare your organization for the next technological leap: AI modernization. Integrating sophisticated AI and ML models is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day competitive necessity. However, this introduces a new layer of complexity that a traditional integration strategy alone cannot solve.
Consider the challenges:
- Prompt Volatility: The prompts that interact with large language models are not static code; they are dynamic assets that require constant refinement, testing, and versioning. How do you manage this "prompt-as-code" lifecycle across teams?
- Secure Data Access: How do you allow AI models to securely access and reason with your proprietary internal data without creating security vulnerabilities or data leaks?
- Operational Blind Spots: When you integrate multiple AI services from providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, how do you maintain a single, unified view of performance, usage, and logs?
- Unpredictable Costs: The token-based pricing models of AI services can lead to runaway costs if not meticulously monitored. How do you give your developers the freedom to innovate while maintaining strict budgetary control?
Addressing these specific challenges is the final, crucial piece of the integration puzzle. This is where a specialized management layer becomes not just a nice-to-have, but an essential component of your AI-powered application stack.
Your Actionable Path to AI-Powered Integration
The enterprise application integration best practices outlined in this article provide the "how" for building a robust architectural foundation. The next step is to equip that foundation with the right tools to manage the unique demands of AI. This is precisely why we developed the Wonderment Apps administrative toolkit. It serves as the command center for your AI integrations, built to address the exact challenges outlined above.
Our platform provides a centralized prompt vault with versioning, allowing your teams to collaborate, iterate, and roll back prompts with the same rigor they apply to source code. The parameter manager creates a secure, governed bridge to your internal databases, while the unified logging system gives you the observability needed to debug and optimize performance across all AI services. Most importantly, the integrated cost manager provides a real-time dashboard of your cumulative AI spend, turning unpredictable expenses into manageable operational costs.
By layering this specialized AI management toolkit on top of a well-architected integration strategy, you create a system that is not only connected but truly intelligent, secure, and cost-effective. You empower your teams to build next-generation features with confidence, knowing they have the guardrails and visibility needed to succeed. The journey from siloed applications to a fully integrated, AI-driven enterprise is a strategic imperative, and with the right practices and tools, it is well within your reach.
Ready to bridge the gap between your integration strategy and your AI ambitions? Wonderment Apps provides the essential administrative toolkit to manage, monitor, and scale your AI integrations securely and cost-effectively. Schedule a demo today to see how you can accelerate your AI modernization efforts and take full control of your intelligent applications.
