Building a software application that scales to millions of users, especially one powered by AI, is like constructing a skyscraper. You wouldn't build it on a shaky foundation, and in software, that foundation is Quality Assurance. But how do you move beyond just 'checking for bugs' to implementing a world-class QA strategy? This is especially critical when modernizing applications with AI, where unpredictable model outputs and complex data pipelines introduce new layers of risk.
Traditional QA often struggles to keep up, leading to costly delays, security vulnerabilities, and brittle software. That's why forward-thinking teams are turning to administrative tools that streamline AI integration and testing from the very beginning. For example, a robust prompt management system, like the one we've developed at Wonderment Apps, allows you to version, test, and manage AI interactions with the same rigor you apply to your codebase. This proactive approach is a cornerstone of modern quality assurance testing best practices.
This guide dives into 10 essential best practices that will help you de-risk your projects, accelerate delivery, and build excellent, scalable app experiences. We will cover a range of critical topics, from automated testing and continuous integration to security, compliance, and user acceptance. For those looking to first solidify their understanding of the fundamentals, exploring A Guide To The Quality Assurance Testing Process offers a comprehensive overview of the foundational steps. Let's lay the groundwork for software that not only launches successfully but thrives for years to come.
1. Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Test-Driven Development (TDD) flips the traditional development sequence on its head. Instead of writing code and then testing it, TDD requires you to write a failing automated test before you write the production code to satisfy that test. This "red-green-refactor" cycle ensures that every piece of code is written with a specific, testable requirement in mind, embedding quality directly into the development process from the very first line.
This approach is one of the most effective quality assurance testing best practices because it builds a comprehensive safety net of unit tests. This net allows engineering teams to refactor and add new features with confidence, knowing that any regressions will be caught immediately. For organizations like those in fintech or healthcare, where security and compliance are non-negotiable, TDD provides a verifiable trail of requirements and their corresponding code implementations.
How to Implement TDD Effectively
To successfully adopt TDD, integrate it into your core development loop and culture. Start by applying it to the most critical components of your application, such as payment processing logic or user authentication flows.
- Establish a Clear "Definition of Done": Your team's definition of a completed user story should explicitly include passing TDD tests and meeting a specified code coverage percentage. This makes quality a shared responsibility.
- Integrate with CI/CD: Ensure your TDD test suite runs automatically with every commit. This provides immediate feedback, preventing broken code from ever reaching the main branch.
- Pair TDD with AI Modernization: When integrating AI, use TDD to validate the inputs and outputs of your models. For instance, you could write a test to ensure a prompt sent to an AI via a tool like Wonderment’s prompt management system returns a response in the correct format and without errors. This practice is crucial for building reliable, predictable AI-powered features.
2. Automated Testing (Unit, Integration, E2E)
Automated testing is the practice of using specialized software tools to run tests and compare actual outcomes against predicted outcomes. By automating tests at multiple levels, such as unit, integration, and end-to-end (E2E), teams can eliminate repetitive manual effort, accelerate feedback loops, and enable the continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines necessary for modern software development.
This strategic automation is a cornerstone of quality assurance testing best practices because it provides a scalable and repeatable way to validate application stability. For organizations that rely on high-performance, scalable applications, from Shopify ensuring ecommerce platform reliability to Stripe executing comprehensive API tests for fintech compliance, automation is non-negotiable. To master your overall quality assurance, a robust strategy for automated testing for web applications is essential, encompassing various types of tests.
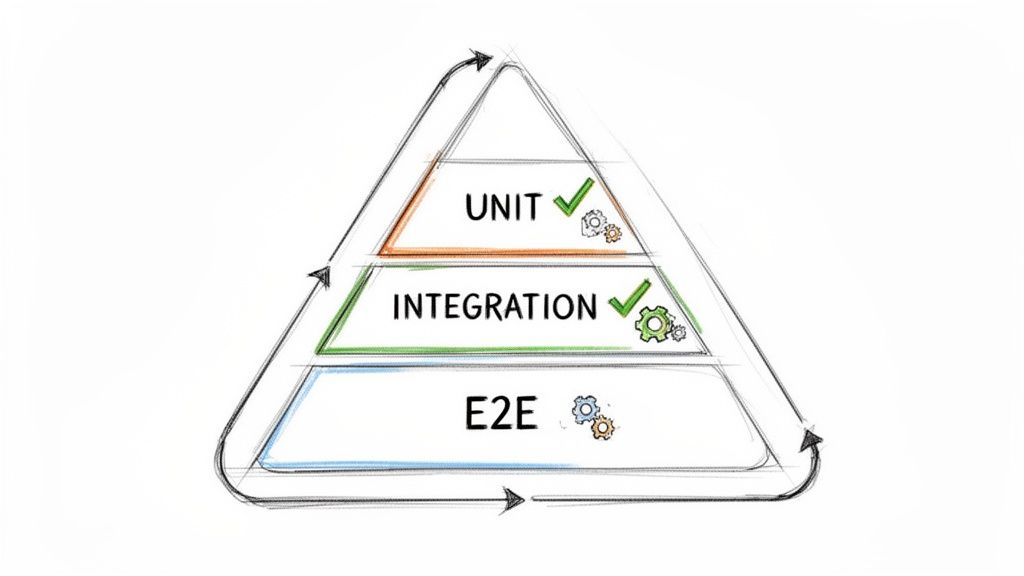
How to Implement Automated Testing Effectively
A successful automation strategy requires a balanced approach, often visualized as the testing pyramid. Focus on building a large base of fast, isolated unit tests, a smaller layer of integration tests, and a very select number of comprehensive but slower E2E tests.
- Follow the 70/20/10 Rule: As a guideline, aim for a test distribution of roughly 70% unit tests, 20% integration tests, and 10% E2E tests. This structure optimizes for speed and stability, making your test suite more efficient and less brittle.
- Prioritize Critical User Journeys: Begin your E2E automation efforts by scripting the most critical paths in your application. For an ecommerce site, this would be user login, product search, and the checkout process.
- Automate AI Model Validation: For AI-powered applications, automate the validation of model outputs. Use scripts to check that data pipelines are functioning correctly and that responses from AI services, managed through a tool like Wonderment’s prompt management system, adhere to expected formats and business rules. This ensures your AI features remain reliable and predictable.
- Implement Parallel Execution: Configure your CI/CD pipeline to run tests in parallel. This dramatically reduces the time it takes to get feedback, allowing developers to merge code faster and with greater confidence.
3. Risk-Based Testing Strategy
A Risk-Based Testing (RBT) strategy moves away from the idea that all parts of an application must be tested with equal intensity. Instead, it prioritizes testing efforts based on the probability and potential business impact of failures. Teams systematically identify high-risk areas, such as critical business functions or historically buggy modules, and allocate a greater share of QA resources to them, ensuring that the most important functionality receives the most rigorous validation.
This approach is one of the most efficient quality assurance testing best practices because it optimizes resource allocation and aligns QA directly with business priorities. For organizations in high-stakes industries, like fintech or healthcare, RBT is crucial. It ensures that intensive testing is focused on areas like payment processing, patient data security, or HIPAA compliance, where a failure would have catastrophic consequences for the business and its users.
How to Implement a Risk-Based Testing Strategy Effectively
To adopt RBT, you must make risk assessment a collaborative, ongoing process involving stakeholders from product, engineering, and business teams. This ensures your testing focus remains aligned with both technical complexity and business value.
- Create and Maintain a Risk Register: Develop a living document that identifies potential risks, rating each one on probability and business impact. Use this register to guide the creation and prioritization of your test cases, focusing automated testing on the highest-scoring risks.
- Involve Cross-Functional Teams: Risk identification shouldn't happen in a silo. Involve product managers, business analysts, and developers in workshops to gain a holistic view of risks, from business logic flaws to security vulnerabilities and performance bottlenecks.
- Apply RBT to AI Modernization: When integrating AI features, use a risk-based approach to test the model’s behavior. For instance, you could use a tool like Wonderment’s prompt management system to prioritize testing prompts that access sensitive user data or control critical application functions. This ensures that your most impactful AI interactions are also your most reliable.
4. Continuous Integration and Continuous Testing (CI/CT)
Continuous Integration and Continuous Testing (CI/CT) automates the process of merging code changes and immediately running a comprehensive suite of tests. Whenever a developer commits new code, the CI server automatically builds the application and triggers a test pipeline. This rapid feedback loop ensures that integration issues and bugs are identified minutes after they are introduced, not weeks later during a manual QA phase.
This practice is fundamental among modern quality assurance testing best practices because it establishes an automated quality gate that every change must pass before proceeding. For high-velocity teams at companies like Spotify or Airbnb, CI/CT is what enables them to deploy hundreds of changes per week with confidence. It transforms quality from a reactive, end-of-stage activity into a proactive, continuous process that safeguards the integrity of the main codebase and accelerates delivery.
How to Implement CI/CT Effectively
A successful CI/CT implementation hinges on creating fast, reliable, and comprehensive pipelines that provide immediate and actionable feedback to developers. Your goal is to make the pipeline an indispensable part of the daily workflow.
- Define Clear Quality Gates: Your pipeline should enforce minimum standards before code can be merged. This includes static code analysis, security vulnerability scans (SAST/DAST), unit test coverage thresholds, and passing critical integration tests.
- Implement a Fail-Fast Approach: Structure your pipeline to run the quickest tests first (e.g., unit tests) and more time-consuming tests (e.g., end-to-end tests) later, often in parallel. This provides developers with the fastest possible feedback if a simple error is detected.
- Integrate AI Model Validation: For teams modernizing with AI, your CI pipeline is the perfect place to test AI components. Using a prompt management tool like Wonderment’s platform, you can include automated tests that validate AI responses for structure, accuracy, and latency, ensuring AI features remain reliable with every code change. To dive deeper into pipeline optimization, explore these CI/CD pipeline best practices.
5. Performance and Load Testing
Performance and Load Testing validates that your application can handle expected and peak user loads without degrading the user experience. This practice involves simulating various traffic conditions, from normal daily usage to extreme stress scenarios like a Black Friday sale, to identify system bottlenecks, measure response times, and confirm that your infrastructure can scale effectively. By proactively finding these limits, you ensure stability and reliability when it matters most.
This methodology is one of the most critical quality assurance testing best practices because it directly impacts user retention and revenue. A slow or unavailable application, especially during high-traffic events, can lead to abandoned carts, frustrated users, and a damaged brand reputation. For fintech platforms processing high-volume trades or healthcare apps supporting telemedicine appointments, performance isn't just a feature; it's a core requirement for operational integrity and user trust.
How to Implement Performance and Load Testing Effectively
To get the most value, integrate performance testing into your development lifecycle, not just as a final pre-launch check. This allows you to catch and fix performance regressions early and often, making scalability an architectural principle.
- Establish Clear Performance Baselines: Before you begin, measure your application's current performance metrics in a production-like environment. This baseline gives you a clear benchmark to compare against and define acceptable thresholds for response times and resource usage (CPU, memory).
- Test Realistic User Scenarios: Go beyond simply hitting an API with a high volume of requests. Simulate real user journeys, such as searching for a product, adding it to the cart, and completing checkout. This provides a more accurate picture of how your system will behave under real-world stress.
- Monitor AI Performance Metrics: When modernizing with AI, performance testing must include the AI components. For Wonderment clients, this means testing AI inference times and data pipeline throughput. Use a prompt management system to analyze response latency from different AI models, ensuring your AI features enhance, rather than hinder, the user experience.
6. Security and Compliance Testing
Security and Compliance Testing is a non-negotiable process that validates whether an application can protect sensitive data and adhere to legal and industry-specific regulations. It goes beyond finding functional bugs by actively seeking out vulnerabilities, threats, and risks that could be exploited. This involves a suite of specialized tests like penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and secure code analysis to ensure the application is fortified against common attack vectors and meets standards like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR, or SOC 2.
This discipline is one of the most critical quality assurance testing best practices, especially for organizations handling sensitive user information. For a healthcare platform, robust security testing is the key to achieving HIPAA compliance; for a payment processor, it’s a prerequisite for passing a PCI-DSS validation. Neglecting this step doesn't just create technical debt, it creates significant legal and financial risk, making proactive security validation a cornerstone of responsible software development.

How to Implement Security and Compliance Testing Effectively
To successfully integrate security and compliance, you must embed it into every stage of the software development lifecycle, not treat it as a final gate. This "DevSecOps" mindset ensures security is a shared responsibility from the start.
- Integrate Security into CI/CD: Utilize Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools directly within your CI/CD pipeline. This automates the scanning process for known vulnerabilities with every new build.
- Conduct Regular Penetration Testing: Schedule periodic penetration tests with third-party security professionals to simulate real-world attacks. This helps uncover complex vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss, providing a crucial external audit of your defenses.
- Leverage AI for Secure Modernization: When modernizing an application with AI, security testing is paramount. For example, you must test the AI integration points for prompt injection vulnerabilities. Using a prompt management tool like Wonderment’s platform can help by providing a secure layer that validates, logs, and sanitizes user inputs before they reach the AI model, mitigating a major risk vector. For a deeper dive into protecting your software, explore these application security best practices.
7. User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and Exploratory Testing
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and Exploratory Testing are critical final-stage validation techniques that connect technical quality with real-world business value. UAT involves end-users, such as business stakeholders or actual customers, validating that the software meets their requirements in realistic scenarios. Complementing this, Exploratory Testing empowers QA testers with the freedom to simultaneously design, execute, and learn from tests on the fly, uncovering defects that scripted tests might miss.
Together, these methods form one of the most essential quality assurance testing best practices because they bridge the gap between development and actual use. While automated tests confirm that code functions as designed, UAT confirms it functions as needed. For instance, a fintech platform might require UAT by compliance officers to validate regulatory features, while a healthcare system needs clinicians to confirm patient data workflows are both correct and intuitive. This human-centric approach is vital for ensuring usability and stakeholder buy-in before launch.
How to Implement UAT and Exploratory Testing Effectively
Success requires structured engagement with business users and a strategic balance between scripted and unscripted testing. It's about empowering human intuition within a controlled framework. For Wonderment clients, this is key for validating AI-driven features and ensuring they meet both business goals and user expectations.
- Involve Business Users Early: Don't wait until the UAT phase to engage stakeholders. Involve them during requirements definition to ensure test scenarios are aligned with business objectives from the start, which also improves the overall usability testing of a website or application.
- Use Test Charters for Exploration: Guide exploratory sessions with clear charters that define the mission, scope, and timebox for testing a specific feature. This provides focus without stifling the creative, investigative process needed to find obscure bugs.
- Balance with Automation: Maintain a healthy ratio where automated tests cover the core regression suite (around 80-85% of effort), freeing up your QA team to dedicate 15-20% of their time to high-impact UAT coordination and exploratory testing.
- Validate AI Behavior: Use UAT to confirm that AI-powered features, managed through tools like Wonderment’s prompt management system, deliver the expected business outcomes. Exploratory testing is perfect for stress-testing these systems to see how they respond to unusual or unexpected user inputs.
8. Mobile and Cross-Platform Testing
With mobile devices driving the majority of digital interactions, ensuring a flawless user experience across a fragmented ecosystem of devices, operating systems, and screen sizes is no longer optional. Mobile and cross-platform testing validates your application's functionality, usability, and performance on the specific hardware and software your customers use. This practice goes beyond simple emulation to uncover device-specific bugs related to memory, CPU, and network conditions.
This discipline is one of the most critical quality assurance testing best practices for any business with a mobile presence. It guarantees that whether a user is on the latest iPhone or a budget Android device, the experience remains consistent, responsive, and reliable. For ecommerce apps, this means a seamless checkout process on any phone; for banking apps like those used in fintech, it ensures security features work correctly across all supported iOS and Android versions.
How to Implement Mobile and Cross-Platform Testing Effectively
A successful mobile testing strategy requires a smart mix of real devices, emulators, and cloud services. Prioritize real-device testing for critical user flows like payments or onboarding, as emulators cannot fully replicate hardware-specific issues or OS-level interruptions.
- Prioritize Based on User Data: Use analytics to identify the most popular devices, operating systems, and screen resolutions among your target audience. Focus your primary testing efforts on this matrix to maximize impact and ROI.
- Leverage Cloud Device Farms: For extensive compatibility testing, use cloud-based device farms like Sauce Labs or BrowserStack. These services provide cost-effective access to a massive inventory of real devices, allowing you to scale your testing across hundreds of configurations without managing physical hardware.
- Simulate Real-World Conditions: Don't just test on a perfect Wi-Fi connection. Use tools to simulate variable network conditions like slow 3G, intermittent connectivity, and offline mode. Also, test app behavior during interruptions like incoming calls, low battery warnings, and OS updates to ensure stability.
9. API and Integration Testing
In a world of microservices and interconnected systems, API and Integration Testing is no longer optional; it’s the backbone of reliable software. This practice validates that individual APIs function as documented and, more importantly, that different software components and third-party services communicate flawlessly. It ensures data flows correctly, authentication is secure, and error handling is robust across system boundaries, preventing catastrophic failures where services meet.
This is one of the most critical quality assurance testing best practices for modern applications, which often rely on a complex web of internal and external services. For a fintech platform integrating a payment gateway or a healthcare app using an external lab’s API, a single point of failure in an integration can bring the entire service down. Rigorous testing of these connections ensures data integrity, maintains functionality, and builds user trust.
How to Implement API and Integration Testing Effectively
Effective API testing requires a proactive and comprehensive strategy that starts early in the development lifecycle, not just before a release. The goal is to verify every aspect of the API contract, from request and response formats to performance under load.
- Document and Standardize: Create clear, comprehensive API documentation using standards like OpenAPI (Swagger). This documentation becomes the blueprint for your automated tests, ensuring you cover every endpoint, method, and expected status code (2xx, 4xx, 5xx).
- Isolate and Mock Dependencies: Use mocking and service virtualization to test components independently. This allows you to validate your application's logic without relying on the availability or stability of external third-party services, enabling faster and more reliable testing within your CI/CD pipeline.
- Test for Real-World Scenarios: Go beyond simple "happy path" tests. Validate schema and data types, test error conditions like invalid authentication or timeouts, and verify behaviors like rate limiting and pagination. For AI-powered apps, this includes testing integrations with multiple LLM providers, ensuring consistent performance and data handling, a process easily managed with a tool like Wonderment's prompt management system.
10. Test Data Management and Environment Strategy
Effective testing is impossible without realistic, reliable test data and stable, production-like environments. A Test Data Management and Environment Strategy is the practice of systematically creating, managing, and refreshing test data while provisioning isolated, well-governed test environments. This discipline ensures that tests are not only repeatable and accurate but also secure and compliant, preventing sensitive production data from being exposed.
This approach is fundamental to any mature list of quality assurance testing best practices because it directly impacts test validity. Without high-quality data and environments, even the best-written automated tests can produce false positives or miss critical defects. For organizations in regulated industries like healthcare or finance, this strategy is non-negotiable, as it provides the foundation for testing compliance controls like HIPAA or PCI-DSS without using actual sensitive customer information.
How to Implement a Test Data and Environment Strategy
Success hinges on treating your test data and environments as first-class citizens in the development lifecycle, not as an afterthought. This requires both technical tooling and clear governance processes.
- Automate Data Generation and Masking: Implement automated pipelines that refresh test environments with recent, anonymized production data. Use data masking techniques for sensitive fields like account numbers or patient identifiers to ensure compliance. For load testing, generate synthetic data that mirrors real-world distributions and edge cases.
- Isolate and Standardize Environments: Maintain separate, isolated environments for different testing stages like integration, user acceptance testing (UAT), and performance testing. Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or Ansible to define and version environment configurations, ensuring consistency and rapid provisioning.
- Establish Clear Governance Policies: Document who can access which environments and what kind of data they contain. Define a clear process for requesting, refreshing, and decommissioning environments. This governance is critical for security and for preventing teams from interfering with each other's testing activities, ensuring reliable and predictable results.
10-Point QA Best Practices Comparison
| Approach | Implementation complexity | Resource requirements | Expected outcomes | Ideal use cases | Key advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test-Driven Development (TDD) | Moderate–High (cultural change, training) | Developer time, test frameworks, CI integration | Higher code quality, safer refactoring, living tests | Complex systems, AI integrations, legacy modernization | Fewer defects, improved maintainability, regression safety |
| Automated Testing (Unit, Integration, E2E) | High (setup and ongoing maintenance) | Test infrastructure, automation tooling, test authors | Fast feedback, broad coverage, fewer regressions | High-scale apps, frequent releases, multi-platform projects | Speed, scalability, repeatability of tests |
| Risk-Based Testing Strategy | Medium (requires risk assessment process) | Stakeholder time, risk tools, targeted test allocation | Optimized QA ROI, focus on critical failures | Time‑constrained projects, legacy modernization, high-risk domains | Efficient resource allocation, business-aligned testing |
| Continuous Integration and Continuous Testing (CI/CT) | High (pipeline design, orchestration) | CI servers, automated tests, monitoring and reporting | Rapid feedback, fewer integration issues, faster releases | DevOps teams, frequent commits, large engineering orgs | Early defect detection, increased deployment velocity |
| Performance and Load Testing | Medium–High (scenario design, env setup) | Load generators, realistic data, monitoring tools | Validated scalability, identified bottlenecks, capacity data | Ecommerce peaks, fintech throughput, streaming services | Prevents outages, enables capacity planning, consistent UX |
| Security and Compliance Testing | High (specialized skills, continuous effort) | Security experts, scanning/pen testing tools, audit processes | Reduced breaches, regulatory compliance, audit readiness | Healthcare, fintech, government, regulated SaaS | Protects data, reduces legal risk, builds customer trust |
| User Acceptance & Exploratory Testing (UAT) | Medium (coordination with stakeholders) | Business users, skilled testers, realistic environments | Validated business requirements, improved usability | MVP launches, stakeholder sign-off, UX-critical features | Real-world validation, uncovers usability and edge-case issues |
| Mobile and Cross-Platform Testing | High (device fragmentation, OS permutations) | Device labs or cloud, cross-platform tools, test matrices | Consistent UX across devices, fewer device-specific bugs | Mobile apps, global user bases, responsive web | Improves retention, reduces platform-specific failures |
| API and Integration Testing | Medium (protocols, mocks, async behavior) | API tooling, mock services, schema docs, test data | Reliable integrations, validated data flows, backward compatibility | Microservices, third‑party integrations, AI inference APIs | Catches integration issues early, supports independent development |
| Test Data Management & Environment Strategy | High (data masking, provisioning, governance) | Data generation/masking tools, infra-as-code, storage | Realistic, repeatable tests while protecting sensitive data | Regulated industries, large-scale performance testing, parallel teams | Preserves privacy, improves test fidelity and repeatability |
From Best Practices to Business Impact
Navigating the landscape of modern software development requires more than just good code; it demands a deep, organizational commitment to quality. Throughout this guide, we've explored the ten pillars of effective quality assurance, moving beyond reactive bug-finding to a proactive, strategic approach. From establishing a solid foundation with Test-Driven Development (TDD) and a multi-layered automated testing strategy, to implementing the dynamic feedback loops of Continuous Integration and Continuous Testing (CI/CT), each practice serves a critical purpose.
The journey doesn't end there. Adopting a risk-based testing strategy ensures your efforts are focused where they matter most, while rigorous performance, security, and compliance testing protect your application from failure, threats, and regulatory pitfalls. By embracing both structured User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and the creative freedom of exploratory testing, you build a comprehensive understanding of your product's real-world usability and resilience. Ultimately, mastering these quality assurance testing best practices is what separates fragile, high-maintenance applications from robust, scalable, and market-leading solutions.
The Shift from Gatekeeper to Value Creator
The core takeaway is this: quality assurance is not a final checkpoint but a continuous, integrated discipline that accelerates value delivery. When QA is embedded throughout the development lifecycle, it ceases to be a bottleneck and becomes a strategic enabler.
- For Engineering Teams: Integrating these practices means catching defects earlier when they are exponentially cheaper and easier to fix. It leads to more stable builds, less rework, and a more predictable development velocity.
- For Product Teams: A mature QA process provides the confidence to innovate and iterate quickly. It delivers reliable data on user experience, performance, and security, ensuring that each new feature enhances the product rather than introducing instability.
- For the Business: The ultimate benefit is a direct impact on the bottom line. High-quality software improves customer retention, strengthens brand reputation, reduces support costs, and minimizes the financial and legal risks associated with security breaches or compliance failures.
Actionable Next Steps: Implementing a Culture of Quality
Transforming your QA process from a checklist to a cultural cornerstone requires deliberate action. Start by assessing your current state and identifying one or two high-impact areas for improvement.
- Start Small, Automate Smart: Don't try to boil the ocean. Begin by automating your most critical, repetitive regression tests. This frees up your team for more valuable exploratory and risk-based testing.
- Unify Your Tooling: Ensure your testing, CI/CD, and monitoring tools are integrated. A unified toolchain provides a single source of truth and streamlines the feedback loop from code commit to production deployment.
- Embrace AI, But Govern It: As you modernize your applications with AI, the testing paradigm shifts. The non-deterministic nature of AI models introduces new challenges in repeatability, data management, and cost control. Traditional QA methods are insufficient for validating AI-driven features.
This is where specialized tooling becomes not just a convenience, but a necessity. At Wonderment Apps, we've built a prompt management system specifically to address these challenges. It's an administrative tool that developers and entrepreneurs can plug into their existing app or software to modernize it for AI integration. Our system includes a prompt vault with versioning for repeatable testing, a parameter manager for secure internal database access, a unified logging system across all integrated AIs, and a cost manager that gives you a clear view of your cumulative spend. This comprehensive tool provides the structure needed to test, monitor, and scale your AI integrations with confidence.
Ready to modernize your application and master AI-driven quality assurance? The Wonderment Apps prompt management system provides the essential toolkit to test, manage, and scale your AI integrations effectively. Schedule a demo today to see how you can build quality into your AI initiatives from day one.
