Choosing between Oracle and PostgreSQL is a pivotal decision for any business leader looking to build scalable, modern software. It's a choice between a commercially backed, all-in-one ecosystem and a powerful, flexible open-source platform. But the database is just the foundation. The real magic happens when you connect that data to artificial intelligence, a process that can be notoriously complex.
That's why at Wonderment Apps, we've developed a prompt management system designed to bridge this gap. It's an administrative tool that developers and entrepreneurs can plug into their existing apps—whether powered by Oracle or PostgreSQL—to modernize them for seamless AI integration. This guide will walk you through the database comparison, and later, we'll show you how our toolkit makes leveraging that database for AI surprisingly simple.
Choosing Your Enterprise Database: The High-Stakes Decision
Picking the right database management system (DBMS) is one of those foundational decisions that will ripple through every part of your application's lifecycle. Whether you lean toward a commercial giant like Oracle or an open-source champion like PostgreSQL will shape your performance, scalability, and—most importantly—your total cost of ownership. This isn't just a technical choice; it's a strategic move that locks in your tech stack and budget for years.
This guide is designed to cut through the noise and give you a clear, business-first comparison of Oracle vs. PostgreSQL. No matter which database you choose, a deep understanding of database management best practices is non-negotiable for success.
Oracle vs PostgreSQL At a Glance
To kick things off, let's look at the key differentiators in a simple, side-by-side view. This table summarizes the core trade-offs you'll be making.
| Attribute | Oracle | PostgreSQL |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing Model | Commercial, per-core licensing with costly add-ons | Open-source (PostgreSQL License), completely free to use |
| Total Cost | High initial and ongoing licensing and support fees | Lower TCO, costs shift to support contracts and expertise |
| Core Strength | Unmatched stability for mission-critical, large-scale systems | Extreme flexibility, extensibility, and community support |
| Support | Official, enterprise-grade 24/7 support from Oracle | Community-based and paid third-party commercial support |
| Key Features | Real Application Clusters (RAC), advanced security modules | Advanced SQL compliance, robust extensibility (PostGIS) |
While a table gives you the facts, sometimes a simple visual makes the choice even clearer.
This decision tree helps visualize the primary trade-offs at a glance. It really boils down to the core tension between your budget constraints and your need for guaranteed enterprise stability.
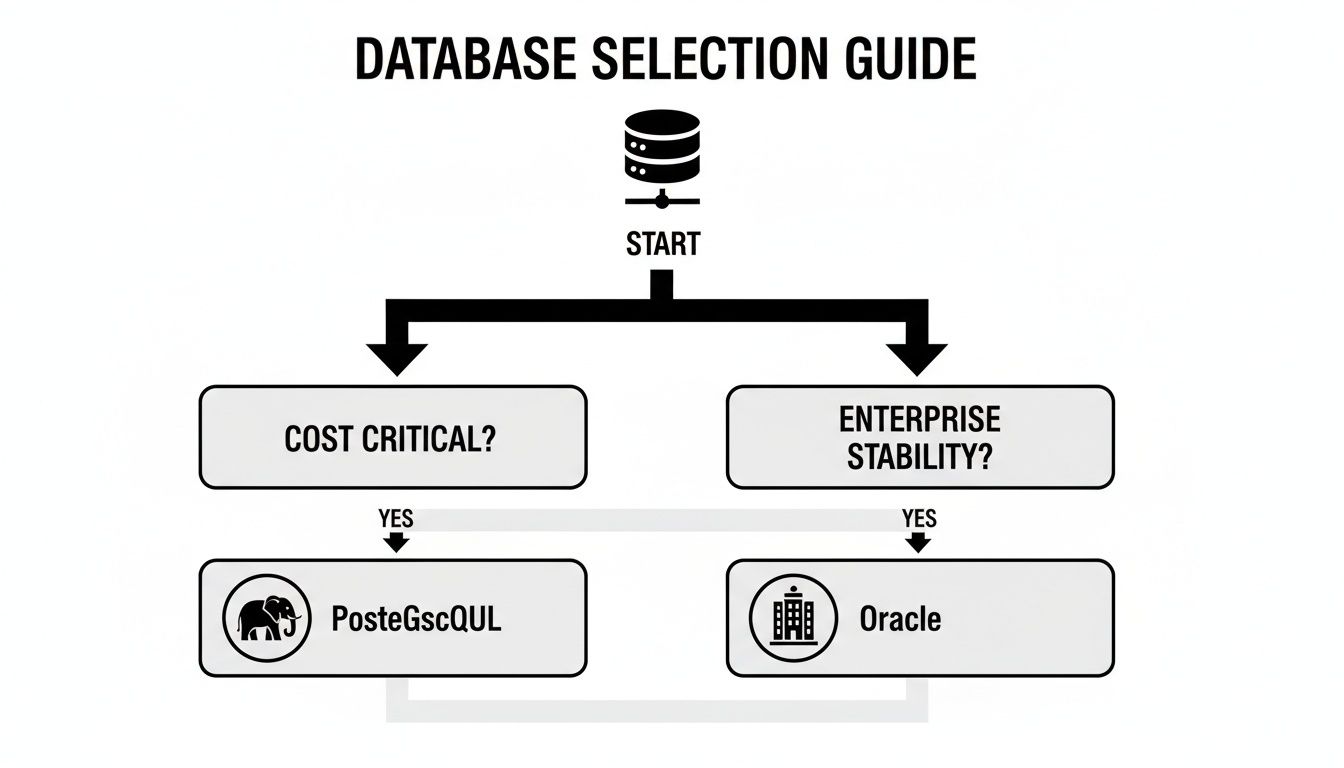
As you can see, if budget is the main driver, PostgreSQL is almost always the starting point. But if your organization absolutely cannot compromise on proven, enterprise-grade stability and support, the path leads directly to Oracle.
Market Position and Future Trajectory
Understanding where each database stands in the market isn't just an academic exercise—it's about de-risking a long-term technology bet. A database's market position directly impacts the talent pool you can hire from, the richness of its third-party tool ecosystem, and the kind of community support you can lean on when things go wrong. Picking a platform with a strong, growing presence ensures you aren't left holding the bag with an obsolete system a few years down the road.
For decades, Oracle has been the undisputed heavyweight champion in the enterprise database arena. Its deep roots in mission-critical sectors like finance, healthcare, and massive retail operations speak volumes about its legendary reliability. For any organization where downtime is measured in millions of dollars per minute, Oracle's rock-solid stability and white-glove support provide a genuine sense of security. This long-standing dominance has created a powerful, self-reinforcing cycle of trust and adoption among the world's largest companies.
When you look at the competitive landscape, Oracle has consistently held its top spot. This isn't just perception; it's backed by metrics that track its influence across technical forums, job markets, and developer mindshare.
According to DB-Engines metrics, Oracle still wears the crown as the most popular DBMS globally, posting a commanding ranking score of 1244.08 as of June 2024. This score underscores its deep-rooted dominance in demanding enterprise environments. You can dig into more of these database popularity trends in Statista's research.
This market leadership means that finding experienced Oracle DBAs and developers, while not cheap, is a relatively straightforward task. The ecosystem is incredibly mature, with a vast array of proprietary tools and established best practices for almost any conceivable scenario.
The Rise of Open-Source Momentum
But while Oracle holds its ground, PostgreSQL has been on a remarkable upward tear, carving out significant market share with its powerful, open-source model. It's no longer just a "free alternative"; it has become the default choice for startups and modern enterprises building flexible, scalable applications. The momentum behind Postgres is impossible to ignore.
PostgreSQL's growth is consistently recognized, often earning it the title of "The World's Most Advanced Open Source Relational Database." Its impressive climb is fueled by a few key factors:
- A vibrant and active community that drives rapid feature development, a massive library of extensions, and exhaustive public documentation.
- A growing talent pool as more developers and universities make PostgreSQL a core part of their curriculum. This makes hiring skilled professionals both easier and more affordable.
- An expanding ecosystem of third-party tools for monitoring, management, and high availability that now rivals many commercial offerings.
This open-source momentum is a critical factor for any business leader. It signals a future-proof technology backed by a global community that is deeply invested in its continuous improvement.
What Market Trends Mean for Your Business
So, what’s the takeaway from all this market analysis? In the Oracle vs. PostgreSQL debate, the decision really boils down to your company's risk tolerance, budget, and long-term vision.
Opting for Oracle means aligning with the established enterprise standard. You're buying into a predictable, stable ecosystem with a clear, single throat to choke for support. This is often a non-negotiable for organizations with strict regulatory compliance needs or risk-averse stakeholders. Of course, this path comes with a hefty price tag and the potential for vendor lock-in.
On the other hand, choosing PostgreSQL is a bet on the future of open-source innovation. It gives you far more agility, freedom from punishing licensing costs, and a lower total cost of ownership. This choice empowers your development team to build and scale without budgetary gatekeeping, tapping into a dynamic and collaborative global community. The "risk" here isn't about the technology's capability—it's about ensuring you have the right in-house talent or third-party expertise to manage it effectively.
Comparing Architecture and Performance Under Load
When the rubber meets the road, it’s a database's underlying architecture that dictates how it behaves under pressure. The architectural philosophies of Oracle and PostgreSQL are fundamentally different, and these differences have profound implications for performance, especially when handling thousands of simultaneous operations. Understanding this distinction is mission-critical for any CTO or engineering lead planning for scale.
Oracle’s architecture is famously process-based, built from the ground up for the high-concurrency, high-throughput demands of massive enterprises. It relies on a sophisticated model of shared server processes and background processes to juggle memory and user connections with maximum efficiency. This design truly shines in Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) workloads, where countless small, rapid transactions are the norm.
Picture an e-commerce giant during a flash sale. Thousands of users are adding items to carts, checking out, and updating inventory all at once. Oracle’s architecture is engineered to manage this intense, concurrent workload with predictable, stable performance, minimizing contention and guaranteeing transactional integrity across the board.
Concurrency Control: The MVCC Difference
PostgreSQL, on the other hand, traditionally uses a process-per-connection model. While this could be more resource-intensive at a massive scale, modern connection pooling solutions have largely solved this issue. The real star of PostgreSQL’s performance story, though, is its elegant implementation of Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC).
MVCC is a game-changer for environments with mixed read/write workloads. Instead of using locks that force readers to wait for writers to finish (and vice-versa), PostgreSQL gives each transaction a "snapshot" of the data as it existed when the transaction began. This means read queries never block write queries, leading to significantly higher concurrency in many real-world scenarios.
For a fintech application processing thousands of stock trades per second, this is huge. While traders are executing buy/sell orders (writes), analytics dashboards can run complex queries (reads) against the same tables without causing performance bottlenecks. This "readers don't block writers" principle is a core strength of PostgreSQL's design.
Scaling Out: Oracle RAC vs. PostgreSQL Replication
When a single server just isn’t enough, both databases offer powerful ways to scale out, but they take very different paths. Oracle’s flagship offering is Real Application Clusters (RAC), a shared-disk clustering technology that allows multiple servers to access the same database at the same time.
RAC provides exceptional high availability and scalability for OLTP workloads. Every node in the cluster is active, which means they can all process transactions. If one node fails, the others just seamlessly take over its workload. This active-active clustering is a premium, complex feature that underpins many of the world's most demanding financial and retail systems.
PostgreSQL handles high availability and read scalability through its robust built-in streaming replication. You can set up one or more standby servers (replicas) that get changes from the primary server in near real-time. This lets you offload read-heavy queries to the replicas, balancing the load and protecting the primary server for its main job: handling writes.
While PostgreSQL's native replication is primarily active-passive (one primary writer, multiple read replicas), a rich ecosystem of third-party tools like Patroni or Stolon can be used to build robust, automated failover and clustering solutions that rival commercial offerings. This gives organizations a ton of flexibility, but it does require more hands-on configuration.
Query Optimization and Indexing Strategies
Both databases have incredibly advanced query planners, but their philosophies have some key differences. Oracle's optimizer has decades of development behind it and offers a feature called "hints," which let developers manually guide the execution plan. This can be a powerful tool for forcing a specific, known-good plan when you know better than the machine.
PostgreSQL's planner, in contrast, is designed to work best without manual intervention. It relies on detailed statistics about your data to make the most efficient choice. While this approach works beautifully most of the time, the community developed the pg_hint_plan extension for those rare cases—often during migrations from Oracle—where forcing a plan is a must.
Both platforms also support a wide array of indexing strategies:
- B-tree: The default and most common index type for both.
- Bitmap: Excellent for low-cardinality columns, especially in data warehousing scenarios.
- GIN/GiST (PostgreSQL): Powerful indexing for complex data types like JSONB, full-text search, and geospatial data.
- Function-based/Expression-based: Lets you index the result of a function or expression, which is crucial for optimizing queries with complex
WHEREclauses.
Ultimately, effective database performance isn't just about the raw power of the engine; it's about how well you apply these tools. Mastering these techniques is fundamental to improving application performance regardless of the underlying database technology you choose.
Understanding the True Cost of Ownership
When you’re weighing Oracle against PostgreSQL, licensing is just the tip of the iceberg. The real story is told by the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). This isn't just about the price tag; it's the full financial picture, covering everything from support contracts and hardware to the specialized talent you’ll need to keep things running.
Getting a clear-eyed view of these long-term expenses is the only way to make a sound financial decision.
Oracle's Licensing: The Predictable Premium
Oracle’s pricing model is famously complex, and it represents a serious investment, both upfront and over time. Licensing is typically calculated on a per-core basis, which means your bill can climb fast as you scale up your hardware.
Worse, many of the features that enterprises consider essential—like high availability, advanced security, and partitioning—are sold as expensive, separate add-ons. It's an à la carte approach that can lead to some nasty budget surprises if you aren't planning carefully. Oracle's legendary stability and comprehensive, single-vendor support come at a premium, one that many large finance and healthcare organizations are willing to pay for predictability.
The main pieces of Oracle's cost structure are:
- Per-Core Licensing: This is the primary cost driver, tied directly to your servers' processing power.
- Annual Support Fees: Expect to pay a hefty percentage of your license cost each year just for access to patches, updates, and technical support.
- Pricey Add-On Features: Tools like Real Application Clusters (RAC) or the Advanced Security Option come with their own substantial licensing fees.
This model gives you a clear, albeit expensive, path if you need a fully supported, all-in-one solution without having to piece together components from different vendors.
The PostgreSQL "Free" Myth and Real-World Costs
PostgreSQL is open-source, so it’s completely free to download and use. This is a massive advantage right out of the gate, letting you sidestep the multi-million dollar licensing deals common with Oracle. But "free" software never means zero cost. The expenses just move from licensing over to operational spending.
You don't pay for the software, but you absolutely have to account for the resources needed to manage it well. While Oracle's database segment brought in billions through 2024, much of that came from premium add-ons. PostgreSQL, in contrast, lets your infrastructure grow without costs ballooning in proportion.
Here are the real-world costs of running PostgreSQL in an enterprise:
- Expert Talent: You need skilled PostgreSQL DBAs, and hiring or training them is critical. The talent pool is growing, but top-tier experts still command competitive salaries.
- Commercial Support: Many businesses choose third-party support from companies like EDB or Percona for 24/7 assistance. This becomes a recurring operational expense.
- Internal Resources: Your team will be the ones handling maintenance, performance tuning, patching, and setting up high-availability solutions that Oracle includes in its paid tiers.
The decision ultimately hinges on where you prefer to spend your budget: on predictable, high-cost licenses with Oracle, or on skilled personnel and operational support with PostgreSQL. Understanding the full scope of your project is key, as the nuances of the cost of software development can influence which TCO model makes more sense.
When you're running either database in the cloud on AWS, managing runtime is another huge TCO factor. It's worth looking into automating savings by scheduling AWS RDS instances to keep those costs from spiraling. In the end, PostgreSQL almost always delivers a lower TCO, but it demands a real commitment to building or bringing in the right technical expertise.
Diving Into Features and Extensibility
Beyond the specs for performance and cost, a database's real value shows up in its features and how well it can adapt to new problems. This is where Oracle and PostgreSQL really show their different personalities. One gives you a massive, all-in-one suite, while the other offers a lean but powerful foundation that you can build on top of.
Oracle has a reputation for its incredibly rich, out-of-the-box toolkit. For big companies, this is a huge selling point. You get a whole universe of advanced features, all neatly integrated and backed by a single company. This includes things like mature data warehousing tools, sophisticated analytics functions, and beefy security modules that are good to go from day one.
The Power of PostgreSQL's Extensibility
PostgreSQL goes in a completely different direction, making extensibility its main event. Instead of trying to cram every possible feature into the core database, it provides a remarkably solid extension system. This lets developers plug in specialized functions whenever they need them, keeping the core database nimble while opening the door to almost endless possibilities.
This ecosystem of extensions is one of PostgreSQL’s greatest strengths. A few of the heavy hitters include:
- PostGIS: The undisputed champion for handling geospatial data. It essentially transforms PostgreSQL into a full-blown geographic information system (GIS).
- Foreign Data Wrappers (FDWs): These are fantastic. They let you query other databases—like Oracle, MySQL, or even NoSQL systems—as if their tables were sitting right inside your PostgreSQL instance.
- TimescaleDB: An incredibly popular extension that adds first-class support for time-series data. This is a must-have for IoT platforms and financial analytics applications.
The ability to tailor the database for specific jobs is a game-changer for modern development, particularly when you're pulling together all sorts of data for things like AI-driven analytics.
Procedural Languages and Modern Data Types
Both databases have powerful procedural languages for embedding complex business logic right into the database layer. Oracle’s PL/SQL is a well-established, feature-packed language that’s been the engine for enterprise apps for decades. It’s undeniably powerful, but it's also a major source of vendor lock-in. Migrating a mountain of complex PL/SQL packages is no small feat.
PostgreSQL offers PL/pgSQL, which feels very familiar if you're coming from Oracle and is more than capable enough for almost any task. The real advantage, though, is that PostgreSQL also supports other procedural languages, like Python (PL/Python) and JavaScript (PL/V8). This gives development teams a lot more flexibility.
One of the most critical differentiators for modern apps is native support for JSON. PostgreSQL’s JSONB data type is celebrated for its performance and deep feature set, including advanced indexing with GIN indexes. This makes it a go-to choice for applications dealing with semi-structured data, which is common in just about every SaaS and mobile backend today.
When you weigh the features, the choice between Oracle and PostgreSQL really boils down to this: do you want an all-inclusive, proprietary suite, or a flexible, open ecosystem? Oracle puts everything in one box for you. PostgreSQL gives you the building blocks to assemble the exact database you need, which is often a much better fit for teams that need to move fast and innovate.
Modernizing Your Application Stack with AI
Whether your team lands on Oracle’s enterprise stability or PostgreSQL’s open-source flexibility, the next strategic step is the same: building intelligent, future-proof software. The "Oracle vs. PostgreSQL" decision is foundational, but true competitive advantage comes from using that data to power smarter features. For that, AI integration is the key.
This is where many projects hit a wall. Connecting your existing database to modern AI models involves serious complexity—from managing prompts and securing data access to controlling unpredictable costs. At Wonderment Apps, we built a solution specifically to eliminate this friction.
Simplify AI Integration with a Powerful Toolkit
We developed an administrative toolkit that plugs directly into your application, creating a seamless bridge between your data—whether in Oracle or PostgreSQL—and the power of AI. It lets your developers focus on building valuable features instead of getting bogged down in complex AI plumbing.
Our system is designed to give you complete control over your AI operations through a few core components:
- Prompt Vault: A centralized, version-controlled repository for all your AI prompts. This ensures consistency, simplifies updates, and lets you track the evolution of your AI interactions.
- Parameter Manager: Securely manages how AI models access your internal database, ensuring that sensitive data is handled properly and only necessary information is exposed.
- Unified Logging: Provides a comprehensive logging system across all integrated AI models. You get a single, clear view of all AI activity for easier debugging and performance monitoring.
- Cost Manager: Gives you a real-time dashboard to see cumulative token spend. This transparency is crucial for managing budgets and preventing surprise costs.
By streamlining the technical overhead, our toolkit empowers you to build intelligent applications that drive real business value. It handles the backend complexity so your team can innovate faster, no matter which database you've chosen.
Ultimately, the goal is to make AI integration a straightforward process. If you want to learn more about a strategic approach, check out our guide on how businesses can leverage artificial intelligence for growth. Our toolkit is the practical implementation of that strategy, turning your database into a powerful engine for innovation.
Oracle vs PostgreSQL: Answering the Tough Questions
When you're down to the final decision between Oracle and PostgreSQL, a few persistent questions always seem to pop up for both the technical folks and the business leaders. Getting straight, practical answers is key to moving forward with confidence. We’ve rounded up the most common ones we hear from teams making this exact choice.
Is PostgreSQL as Secure as Oracle for Enterprise Applications?
Absolutely. PostgreSQL comes loaded with robust, enterprise-grade security features right out of the box. We’re talking powerful tools like row-level security, granular access controls, and full SSL support for encrypting data in transit.
Oracle has a reputation for its advanced security modules, but those often come with a hefty price tag. In contrast, PostgreSQL’s security is highly configurable and more than capable of handling the vast majority of enterprise needs. When configured correctly by a diligent team, it can comfortably meet tough compliance standards like HIPAA and GDPR. The security is there; it just requires a commitment to proper management.
Which Database Is Better for Cloud-Native Applications?
For cloud-native development, PostgreSQL is almost always the preferred choice, and for good reason. Its open-source DNA, container-friendly nature, and excellent first-party support from all the major cloud providers—think Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, and Azure Database for PostgreSQL—make it a perfect match for modern infrastructure.
PostgreSQL's flexibility and lack of licensing headaches are ideal for the dynamic scaling and microservices architectures that define cloud-native apps. While Oracle has cloud solutions, they often bring along a level of complexity and cost that feels at odds with the agile spirit of the cloud.
How Hard Is It to Actually Migrate from Oracle to PostgreSQL?
Let's be direct: migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL can be a serious project, but it's a well-trodden path. The biggest headache usually comes from the application's reliance on Oracle-specific features, especially years of accumulated PL/SQL procedural code.
You can find automated tools that do a decent job of moving the schema and raw data over. The real work is in the business logic—that complex PL/SQL often needs to be manually rewritten into PostgreSQL's PL/pgSQL. A successful migration boils down to meticulous planning. Many teams find that bringing in partners who live and breathe database migrations is the best way to sidestep risks and minimize downtime. For most, the long-term payoff in lower costs and greater freedom makes the upfront effort more than worth it.
Choosing the right database is the foundation, but the real goal is building intelligent, modern software on top of it. Wonderment Apps gives your team a powerful administrative toolkit that plugs right into your application. It simplifies AI integration with tools like a version-controlled prompt vault, a secure parameter manager for database access, and a cost manager to keep an eye on AI spending.
See how our tools can help you modernize your application stack. Schedule a demo with Wonderment Apps today.
