When you're building software for the healthcare world, you're not just writing code—you're handling some of the most sensitive data imaginable. This is an industry where trust is everything. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) isn't here to slow you down; it's here to create a secure foundation so you can build amazing things on top of it.
Get it wrong, and you're looking at staggering fines, a ruined reputation, and a total collapse of patient trust. But if you get it right, compliance becomes a massive competitive advantage.
Your Guide to HIPAA Compliant Software
Think of HIPAA compliance less like a finish line and more like an ongoing promise to protect electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). This promise stands on three foundational pillars that every single piece of healthcare software needs to address.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what each one covers:
The Three Pillars of HIPAA Software Safeguards
| Safeguard Category | Core Focus | Example Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative Safeguards | The "human" side—policies, procedures, and training. | Conducting a thorough security risk analysis to identify vulnerabilities. |
| Physical Safeguards | Protecting the actual hardware and locations where data lives. | Implementing access controls for server rooms and data centers. |
| Technical Safeguards | The specific security measures baked directly into your software. | Encrypting all patient data, both when it's stored and when it's being sent. |
These aren't just suggestions; they're the core of building secure, trustworthy applications that can stand up against breaches and legal trouble.
The Growing Demand for Secure Solutions
The need for truly secure and compliant software has never been more intense, and the market shows it. The HIPAA compliance software market is already valued at around $1.5 billion in 2025 and is on track to explode to $5 billion by 2033.
That's a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15%, a clear sign that healthcare organizations are scrambling to keep up with threats and protect PHI. If you want to dive deeper into the nuts and bolts of building in this space, check out our guide to software engineering in healthcare. As cyberattacks get more sophisticated, the demand for well-built, secure software is only going to grow. You can discover more insights on the HIPAA compliance software market on datainsightsmarket.com.
A classic mistake is to treat compliance like a feature you can just bolt on at the end. Real HIPAA compliance has to be woven into the very fabric of your software development lifecycle—from the first sketch on a whiteboard to deployment and beyond.
Bringing modern tools like AI into your healthcare app adds another layer to this challenge. How do you integrate smart features while making sure every data interaction is secure and can be audited? This is where an administrative tool for AI is a game-changer. At Wonderment, we’ve developed a prompt management system that developers and entrepreneurs can plug into their existing app to modernize it for AI integration. A system with a prompt vault, parameter manager, and detailed logging gives you the auditable framework you need to innovate safely.
Throughout this guide, we’ll break down these requirements into actionable steps your development team can actually use.
The Three Core Safeguards Your Software Must Master
Building HIPAA-compliant software is a lot like constructing a digital fortress. You can't just throw up one tall wall and call it a day; you need multiple, layered defenses working in concert. HIPAA boils these defenses down into three core categories known as safeguards: Administrative, Physical, and Technical. Getting these right is non-negotiable for any application that touches patient data.
Let's stick with the fortress analogy for a second.
The Administrative Safeguards are your fortress's rulebook and guard training schedule. The Physical Safeguards are the actual walls, gates, and locks protecting the servers. And the Technical Safeguards are the high-tech surveillance systems, secret passcodes, and encrypted communication channels used inside the fortress walls. You absolutely need all three.
This diagram shows how these pieces fit together to create a cohesive defense for patient data.
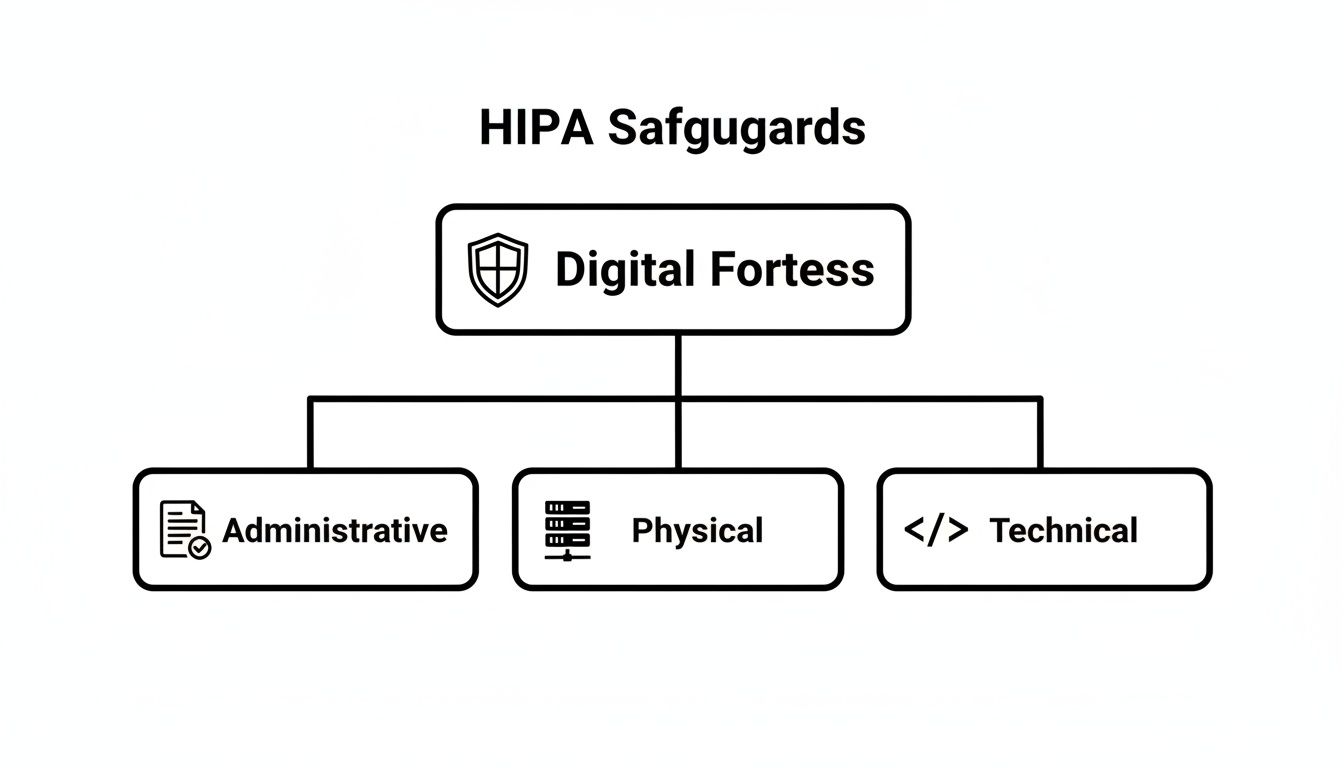
As you can see, each safeguard has a distinct role, but they all support the same mission: creating a secure environment for protected health information (PHI).
Administrative Safeguards: The People and Policies
This is the human element of HIPAA. It’s all about creating the policies, procedures, and training programs that govern how your team interacts with PHI. Frankly, these safeguards are arguably the most important, because even the most sophisticated tech can be completely undermined by simple human error.
Key administrative requirements include:
- Security Risk Analysis: You have to perform a formal, documented assessment to pinpoint potential risks and vulnerabilities to the PHI in your system. This isn't a one-and-done checkbox; it's an ongoing process.
- Security and Awareness Training: Every single person on your team who might come into contact with PHI—from junior developers to the CEO—needs to be trained on your security policies. This training has to be documented and repeated regularly.
- Contingency Planning: What's the plan if disaster strikes? You need a documented strategy for data backup, disaster recovery, and emergency operations to keep PHI safe and accessible no matter what.
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs): If you use any third-party vendor that handles PHI for you (think cloud providers like AWS or an analytics service), you must have a signed BAA in place. This is a legal contract that holds them to the same HIPAA standards you follow.
Physical Safeguards: Securing The Hardware
Next up are the Physical Safeguards, which are all about protecting the physical location of servers, workstations, and any other hardware storing or accessing PHI. Even though many of us rely on cloud providers for this heavy lifting now, you are still responsible for making sure your vendor is compliant and for securing your own office devices.
These safeguards cover things like:
- Facility Access Controls: This means limiting physical access to the rooms and buildings where PHI is stored. For a data center, that means security guards, key cards, and cameras. In your office, it means locking server closets and making sure employee laptops are secured.
- Workstation Use Policies: You need clear rules for how workstations that can access PHI are used. This includes policies on mandatory screen locks, password protection, and preventing "shoulder surfing" or unauthorized viewing of screens.
- Device and Media Controls: This governs how you handle any device containing PHI, like laptops, external hard drives, or even old-school USB sticks. It includes procedures for secure data disposal (like degaussing or physical destruction) and tracking the movement of devices.
Technical Safeguards: The Code-Level Controls
Finally, we get to the Technical Safeguards. These are the security measures you build directly into your software to protect and control access to PHI. For your development team, these are the most direct HIPAA compliant software requirements they'll be implementing.
The market certainly understands their importance. In the broader healthcare compliance software space, HIPAA-specific tools are expected to command a massive 28% market share in 2025. This is a key slice of a market projected to grow from $3.6 billion to $9.9 billion by 2034, with software components being the dominant force in automating PHI protection. You can read the full research on the healthcare compliance software market from Dimension Market Research.
These controls aren't just features; they are the digital locks, keys, and alarm systems of your application. They are the tangible proof that your software is designed for security from the ground up.
Essential Technical Safeguards include:
- Access Control: Your software must only allow authorized people to access PHI. This is usually done with unique user IDs, strong passwords, and role-based access control (RBAC), which ensures users only see the minimum data necessary to do their jobs.
- Audit Controls: You have to build mechanisms to record and examine all activity in systems that contain PHI. This means creating detailed audit logs that track who accessed what data, when they did it, and what actions they took.
- Integrity Controls: Your software must have a way to ensure PHI isn't improperly altered or destroyed. This often involves using checksums or other cryptographic methods to verify that data hasn't been tampered with in transit or at rest.
- Transmission Security: Anytime PHI is sent over a network, it must be encrypted. This applies to data sent to a user's browser, between your own servers, or to a third-party API, and is typically handled with modern standards like TLS 1.2 or higher.
Essential Policies and Documentation That Protect You
Building secure software is only half the battle. If you can't prove your software and operations are secure, you're just as exposed as if you'd written sloppy code. In the world of HIPAA, solid documentation isn’t just bureaucratic red tape; it's your armor during an audit and the blueprint for your entire security strategy.
Think about it. Imagine two companies facing a surprise HIPAA audit. Company A has brilliant developers who built a technically flawless app, but their documentation is a chaotic mess of outdated notes and verbal agreements. Company B, on the other hand, keeps a meticulously organized library of policies, risk assessments, and vendor contracts.
When the auditors arrive, Company A scrambles to justify their safeguards, trying to explain things on the fly. Company B simply hands over the proof. Guess which one walks away with a clean bill of health? This is where the real work of demonstrating HIPAA compliant software requirements happens—creating a living, breathing record of your commitment to protecting patient data.
The Security Risk Analysis (SRA)
The absolute cornerstone of your documentation is the Security Risk Analysis (SRA). This isn't a simple checklist you knock out in an afternoon. It's a comprehensive, methodical process of identifying every potential threat to ePHI and then evaluating the safeguards you have in place to stop them.
Think of it like hiring a professional home inspector to check every nook and cranny of your house for weaknesses before a hurricane hits. The SRA forces you to ask the tough questions:
- Where is every single piece of ePHI stored, transmitted, or processed?
- What could possibly go wrong with that data (e.g., ransomware, employee error, hardware failure)?
- How likely is each threat, and what would be the impact if it actually happened?
- Are our current security measures—like encryption or access controls—strong enough to handle these threats?
The final output is a detailed report that not only highlights your vulnerabilities but also provides a prioritized action plan to fix them. An SRA is a recurring activity, not a one-time event. Your software, your team, and the threat landscape are constantly changing, and your risk analysis has to keep up.
The Contingency Plan for Disaster Recovery
So, what happens when things inevitably go wrong? A server crashes, a natural disaster strikes, or a cyberattack knocks your system offline. A Contingency Plan is your detailed playbook for exactly these scenarios. It's the fire escape plan for your data, making sure you can recover quickly and maintain the integrity of ePHI.
A well-crafted Contingency Plan is the difference between a manageable incident and a catastrophic business failure. It demonstrates foresight and proves to auditors that you take the availability and safety of patient data seriously.
This plan has to cover key areas like data backup procedures, disaster recovery protocols to get critical operations back online, and an emergency mode operation plan so you can still function while systems are down. Without one, you’re just improvising during a crisis—and that’s a recipe for compliance violations and lost patient trust.
Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
You rarely build software in a complete vacuum. You almost certainly rely on cloud providers, analytics tools, and other third-party services. If any of these vendors, known in HIPAA-speak as Business Associates, handle ePHI on your behalf, you are legally required to have a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with them.
A BAA is a binding contract that forces the vendor to uphold the same HIPAA standards you do. It ensures they will properly safeguard patient data, report any breaches to you, and comply with all the necessary rules. Without a BAA in place, you are directly liable for their mistakes.
Ultimately, your documentation is what transforms your technical safeguards from abstract concepts into a defensible, auditable compliance program. For a deeper dive into creating clear and effective records, exploring technical documentation best practices can provide valuable insights that apply here as well.
A Developer Checklist for Building Compliant Software
Alright, this is where the rubber meets the road. Moving from high-level HIPAA rules to the actual code editor is how compliance becomes real. For the developers in the trenches and the leaders guiding them, a straightforward, actionable checklist is the bridge between dense regulations and tangible software features.
This isn’t just about ticking boxes to avoid fines; it's about building a fundamentally secure and trustworthy application from the ground up. Let's break down the most critical technical safeguards into concrete development tasks that shield protected health information (ePHI) at every turn.
Implement End-to-End Encryption
First things first: data must be completely unreadable to anyone without authorization, whether it’s sitting in a database or flying across the internet. This is one of the most foundational HIPAA compliant software requirements and it has zero room for error.
- Data at Rest: All ePHI stored in your databases, object storage, or on any server hard drive must be encrypted. This is your last line of defense if an attacker somehow gets their hands on the physical storage media.
- How to Do It: Use industry-standard algorithms like AES-256 for database-level encryption. Most modern cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer managed encryption services that handle all the heavy lifting, including key management.
- Data in Transit: Any ePHI transmitted over a network—whether from your server to a user's browser or between internal microservices—must be encrypted.
- How to Do It: Enforce Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 or higher across every single communication channel. You absolutely must configure your servers to reject connections using outdated protocols like SSL or old versions of TLS.
Design Granular Role-Based Access Controls
Just because someone works at a hospital doesn't mean they need to see every patient's full medical history. The Principle of Least Privilege is a core tenet of HIPAA, meaning each user should only have access to the bare minimum information needed to do their job.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is how you bring this principle to life in your code. It's about creating distinct roles—think 'Nurse,' 'Billing Specialist,' 'Physician,' 'Admin'—and attaching very specific permissions to each.
Think of RBAC like a digital keycard system. A nurse's keycard opens patient chart rooms, but a billing specialist's keycard only opens the accounting office. No single keycard should open every door in the building.
Your development team’s job is to build an authorization system where permissions are tied to these roles, not to individual users. This approach makes managing access scalable and auditable, which massively reduces the risk of data exposure.
Create Comprehensive Audit Logs
If a data breach happens, or even if an auditor just wants to check your work, you must be able to answer the question: "Who did what, and when?" Without comprehensive audit trails, that's impossible. Your software has to log every single interaction with ePHI.
At a minimum, your audit logs need to capture:
- Who: The unique user ID that performed the action.
- What: The specific action taken (e.g., 'view_patient_record', 'update_prescription').
- When: The exact timestamp of the event.
- Where: The IP address or system the action came from.
- On Whom: The specific patient record or data that was affected.
Crucially, these logs have to be immutable—meaning they can't be altered or deleted. They also need to be stored securely for at least six years, as HIPAA requires.
Ensure Data Integrity and Transmission Security
Beyond just making data unreadable, you have to ensure it hasn't been secretly tampered with or corrupted. This is the 'I' in the classic CIA triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability) of information security.
- Integrity Controls: Implement mechanisms like cryptographic checksums or digital signatures. This allows your system to verify that data hasn't been altered since it was last saved, confirming its integrity every time it’s accessed.
- Transmission Security: We already covered using TLS for encryption, but it's also about hardening your API endpoints and communication channels against common network attacks that could compromise data integrity while it's in motion.
This checklist gives your development team a solid technical foundation. To make it even clearer, here's a quick summary of these essential controls.
Key Technical Implementation Checklist
This table breaks down the core technical controls, why HIPAA requires them, and how they are typically implemented in software development.
| Technical Control | HIPAA Purpose | Common Technology/Method |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Protects ePHI from unauthorized viewing. | AES-256 for data at rest; TLS 1.2+ for data in transit. |
| Access Controls | Enforces the Principle of Least Privilege. | Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with unique user IDs. |
| Audit Logging | Creates an accountable record of all ePHI interactions. | Immutable, detailed event logs stored securely. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures ePHI is not altered or destroyed improperly. | Cryptographic checksums and digital signatures. |
Nailing these four areas is a huge step toward building a truly compliant and secure healthcare application.
Modernizing Healthcare Apps with Compliant AI
Artificial intelligence is no longer some far-off concept; it’s becoming a practical, everyday tool in healthcare. We’re seeing it everywhere, from AI-powered diagnostic imaging to smart platforms that create personalized patient experiences. These features are opening doors to better outcomes and more efficient operations. But with that kind of power comes a huge responsibility, especially when protected health information (ePHI) is in the mix.
Bringing AI into a healthcare app adds a whole new layer of complexity to HIPAA compliant software requirements. Every single interaction with an AI model—every piece of data used to train it and every answer it generates—has to follow the same tough security and privacy rules. This means building compliance into your AI strategy from day one isn't just a smart move; it's an absolute must.
Building Compliance into AI from Day One
The biggest headache with AI in a HIPAA world is keeping track of the data. When a user sends a prompt containing ePHI to an AI model, you've just created a new data transmission that needs to be secured, logged, and tightly controlled. This calls for a completely different toolkit than what you’d use for traditional software.
Imagine a doctor using an AI assistant to get a quick summary of a patient's long medical history. The doctor's request—the prompt itself—is considered ePHI. The AI's response is also ePHI. You need a rock-solid system to track that entire conversation with the same diligence you'd apply to a database entry. Anyone looking to bring advanced tech into healthcare needs to understand the fine points of choosing and using the right HIPAA Compliant AI Tools.
This is where specialized administrative tools become absolutely essential for integrating AI securely. A purpose-built prompt management system gives you the auditable framework you need to innovate without putting data at risk.
Think of a dedicated AI management toolkit as a compliance control plane for your app's smart features. It delivers the visibility and governance required to prove that every AI interaction is secure, auditable, and perfectly aligned with HIPAA's technical safeguards.
The Role of a Prompt Management System
Picture a prompt management system as the central nervous system for your app’s AI features. It puts you in the driver's seat, giving you direct control over how your application talks to different AI models while maintaining a strict compliance posture.
Here’s a breakdown of how its key pieces support HIPAA requirements:
- Prompt Vault with Versioning: This securely stores and manages every prompt your app uses. Versioning is key because it creates an audit trail, showing the exact prompt version used for any given interaction—something that's invaluable during an incident investigation.
- Parameter Manager: This acts as a gatekeeper, controlling what data your app is allowed to send to an AI model. It helps enforce data minimization by stopping sensitive or unnecessary ePHI from ever leaving your secure environment in the first place.
- Integrated Logging System: Every prompt, every response, and every API call is logged, no matter which AI model you're using. This creates the kind of comprehensive, unchangeable audit trail HIPAA demands for monitoring who is accessing ePHI and how it's being used.
- Cost and Token Manager: While not a direct HIPAA rule, this feature gives you a clear view of AI usage and spending. That data can be a lifesaver for spotting weird activity that might signal a security problem, like a sudden, unexplained spike in API calls.
The healthcare industry's shift to flexible, cloud-based tools is only making this more important. Cloud-based HIPAA compliance software is taking over the market, which is expected to jump from $3.7 billion in 2025 to $8.18 billion by 2032. This boom is happening largely because of the rise in remote care, where secure messaging and auditable data trails are non-negotiable.
By putting a robust administrative tool in place, you can confidently add powerful AI features to your application. It’s an approach that not only keeps you compliant but also builds a scalable and secure foundation for whatever you decide to build next. For a closer look at how these integrations work in the real world, you can explore our guide on AI solutions for healthcare.
Common Questions About HIPAA Software Development
Diving into HIPAA software can feel like trying to learn a new language, one filled with technical jargon and very specific rules. As leaders and development teams start working on healthcare projects, the same critical questions always seem to pop up. Getting these answers right is the key to avoiding costly mistakes and building an app that's genuinely secure.
Let's tackle some of the most common hangups and misconceptions about the HIPAA compliant software requirements we've walked through. It's time to clear up the confusion with some direct, practical advice.
Does a HIPAA Compliant Cloud Provider Make My App Compliant?
This is probably the biggest misconception out there, and the answer is a hard no. Using a HIPAA-eligible cloud provider like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure is an essential first step, but it only handles their side of the "shared responsibility model."
They give you the secure foundation—the locked-down data centers and protected hardware that meet the Physical Safeguards. But you are 100% responsible for correctly configuring their services and building all the necessary Administrative and Technical Safeguards into your own application.
Think of it like renting a high-security bank vault. The bank provides the impenetrable room with armed guards, but you're still responsible for managing who has the key, what you put inside, and how you track every entry and exit.
What Is the Biggest Mistake Companies Make with HIPAA Compliance?
The most common—and most expensive—mistake is treating compliance like an afterthought. Teams get excited about features, build out a whole application, and then try to "bolt on" security and HIPAA controls at the end of the development cycle.
This approach just doesn't work. It’s incredibly inefficient, almost always leaves critical security holes, and costs a fortune to fix compared to building security in from day one. Real compliance has to be woven into the software development lifecycle from the very first design sprint.
When you adopt a "compliance-by-design" mindset, security becomes a core feature, not a final hurdle. The result is a product that's fundamentally more secure, scalable, and trustworthy.
Do I Need an Official HIPAA Certification for My Software?
Here's another point that trips people up: there is no official government "HIPAA certification" for software. The government doesn't hand out a badge or a certificate that says your application is "HIPAA Certified."
Compliance isn't a one-time award you can frame on the wall; it's an ongoing process of sticking to the HIPAA Security and Privacy Rules. You prove your compliance through constant, diligent effort.
This includes things like:
- Rigorous risk assessments performed on a regular basis.
- Comprehensive documentation of every single safeguard you have in place.
- Successful third-party audits and penetration tests.
An attestation report from a reputable security firm can serve as powerful proof of your due diligence, but it is not a formal certification from a government body.
How Should We Handle Data from Wearables and Other Apps?
Pulling in data from outside sources like patient wearables or other third-party apps demands a crystal-clear and disciplined game plan. You can't just open an API and let the data flow in unprotected.
First off, you must have a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with any vendor that sends or processes PHI for you. This is a legal requirement with no wiggle room.
Second, your application has to use secure, encrypted APIs to get that data, enforcing modern standards like TLS 1.2 or higher. The moment that data hits your system, it's your responsibility. It has to be protected with the same strict access controls, tough encryption, and detailed audit logging as any other piece of PHI you manage, ensuring you have a consistent security posture across your entire data ecosystem.
At Wonderment Apps, we specialize in building complex, secure, and scalable applications for the healthcare industry. Modernizing your software with AI while maintaining strict HIPAA compliance is our expertise. Our administrative toolkit, featuring a prompt vault, parameter manager, and integrated logging, provides the control plane you need to innovate safely. A built-in cost manager even allows you to see your cumulative AI spend across all integrated systems.
Schedule a demo to see how we can help you build your next compliant healthcare application
