Welcome to the world of AI-powered software. If you're looking to upgrade your application, you’ve probably come across supervised and unsupervised machine learning. But what's the real difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning, and how do you pick the right path for your business?
Here’s the simple version: Supervised learning is like a student studying with a detailed answer key. It trains on labeled data to predict specific outcomes, like forecasting sales numbers for the next quarter. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, is an explorer charting unknown territory. It dives into unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns you didn't even know existed, like entirely new customer segments.
At Wonderment Apps, we specialize in helping businesses integrate these powerful AI models into their custom software. If you're looking to modernize your desktop or mobile application, a key challenge is managing the connection to various AI models. That's why we developed a prompt management system—an administrative tool that developers and entrepreneurs can plug into their existing app to streamline AI integration. This guide will break down both machine learning approaches to help you make a smarter decision for your next project.
Understanding The Two Main AI Learning Models
The foundation of any great AI-powered software is choosing the right learning model for the job. Whether you want to predict future trends or uncover hidden customer behaviors, your choice between supervised and unsupervised learning will define your app's capabilities. The performance of many advanced AI models, especially for tasks like semantic search, often depends on solid infrastructure like a vector database.
With supervised learning, the model is trained on a dataset where every piece of input is already matched with a known output. This teacher-student dynamic is perfect for predictive tasks. For instance, in ecommerce, supervised learning helps giants like Amazon achieve 95% accuracy in product recommendations because it's driven by labeled data. This approach allows models to fine-tune their accuracy, often achieving up to 30% higher precision in classification tasks than their unsupervised counterparts. You can learn more about how AI is changing software development in our detailed guide.
Unsupervised learning works differently. It operates without any labeled data and is tasked with finding the underlying structure all on its own. It's the right tool for the job when you don't know the exact questions to ask but have a hunch that valuable insights are hiding in your data.
Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning at a Glance
To make the distinction clearer, here’s a quick side-by-side comparison. Think of this table as a cheat sheet for understanding the core identity of each learning model.
| Attribute | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Input Data | Labeled data (input-output pairs) | Unlabeled data (inputs only) |
| Primary Goal | Predict outcomes or classify data | Discover hidden patterns and structures |
| Common Tasks | Classification, Regression | Clustering, Association, Anomaly Detection |
| Feedback | Direct feedback (error correction) | No direct feedback; learns from data structure |
Ultimately, the choice isn't about which one is "better" but which one is right for your specific problem and the kind of data you have available.
How Supervised Learning Works for Predictive AI
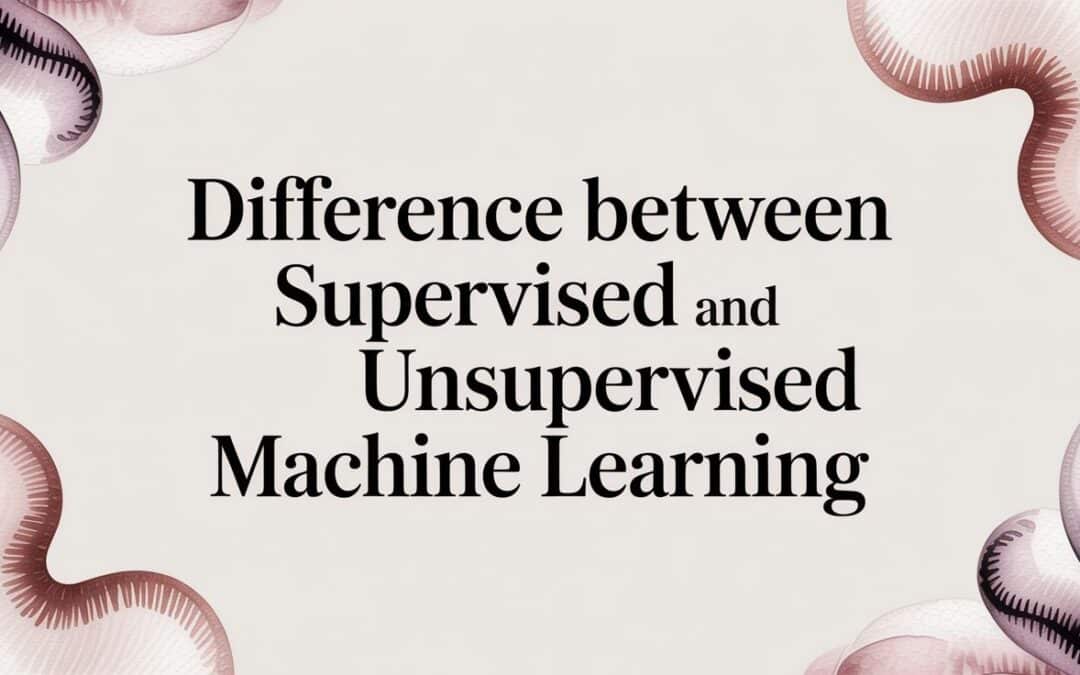
Let's start with supervised learning, the workhorse behind most of the predictive AI you probably use every day. The simplest way to think about it is like training a new employee. You wouldn't just point them to a desk and hope for the best; you'd give them an instruction manual and a stack of completed examples to learn from. That's exactly what we're doing here—teaching an AI model to handle a specific task by showing it thousands of labeled examples until it can reliably do the job on its own.
Every piece of data in this process is like a digital flashcard. On one side, you have the question (the input data), and on the other, you have the correct answer (the labeled output). For an e-commerce platform, the input might be a user's browsing history, and the label could be "purchased" or "did not purchase." The model crunches through these pairs, tweaking its internal logic over and over to minimize the gap between its predictions and the real answers.
This structured, goal-oriented approach is the core difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning. Supervised learning is guided and has a clear target, while unsupervised learning is all about exploration. Because of this, the quality of your labeled data is everything. Garbage in, garbage out isn't just a saying here—it's the law.
The Two Pillars: Classification and Regression
Supervised learning generally splits into two main problem types, each serving a totally different business purpose. Figuring out which bucket your problem falls into is your first real step toward building a useful AI feature.
Classification Models: Think of these models as digital sorters. They're trained to put data into predefined categories. The output is always a distinct label, like "spam" vs. "not spam" for an email filter or "fraudulent" vs. "legitimate" for a financial transaction. When you only have two choices, it’s called binary classification.
Regression Models: Instead of picking a category, regression models predict a continuous number. They're the fortune tellers of your data. Common examples include forecasting next quarter's sales revenue, estimating a house's price based on its features, or predicting a customer's lifetime value.
A simple way to remember the distinction is to ask what kind of question you want to answer. If the answer is "which category?" you need classification. If the answer is "how much?" you need regression.
Key Algorithms and Their Uses
Once you know your goal, you can pick from a whole toolkit of proven algorithms. Each has its own strengths, perfectly suited for different kinds of data and complexity. While the list of algorithms is massive, a few popular ones are the foundation for tons of real-world applications.
- Linear and Logistic Regression: These are the absolute workhorses of supervised learning. Linear Regression is for predicting continuous values (like sales) by drawing a straight line through the data. Logistic Regression is its cousin, used for binary classification (think yes/no decisions). They’re fast, easy to explain, and fantastic starting points.
- Support Vector Machines (SVM): SVMs are brilliant for classification problems where you need to find the best possible boundary to separate different data classes. It's incredibly effective when there's a clear margin between categories, making it great for things like text classification or basic image recognition.
- Decision Trees and Random Forests: A Decision Tree works like a flowchart, making predictions by asking a series of if-then questions. A Random Forest elevates this concept by building an entire ensemble of trees and letting them vote on the final prediction, which almost always leads to more accurate and stable results.
- Neural Networks: This is the powerhouse behind deep learning, with a structure inspired by the human brain. Neural networks are masters at finding incredibly complex, non-linear patterns in huge datasets. That makes them the go-to for advanced tasks like sophisticated image classification and natural language processing.
Choosing the right algorithm is what separates a proof-of-concept from AI that delivers real-world accuracy for features like fraud detection systems or hyper-personalized recommendation engines.
Discovering Insights with Unsupervised Learning
While supervised learning is fantastic for making predictions when you already know the outcomes, its counterpart takes you on a completely different journey: an exploration into your data's hidden depths. Unsupervised learning is the detective of the machine learning world. It works with unlabeled data, meaning there are no predefined "correct answers" to guide its process. Its only mission is to dive into raw information and find inherent structures, hidden patterns, and surprising relationships all on its own.
Instead of predicting a specific target, this approach focuses on understanding the data's fundamental organization. Think of it like being handed a massive box of assorted LEGO bricks with no instruction manual. An unsupervised model would start sorting them by color, shape, and size on its own, creating logical groups without anyone telling it what a "red brick" or a "square piece" is. This is the heart of the difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning—one is built for prediction, the other for discovery.
This method is incredibly valuable for initial data exploration, helping you understand your users and operations on a much deeper level. It’s a powerful tool for modernizing applications, especially when the goal is to uncover insights you didn’t even know you should be looking for.
Key Tasks in Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning isn't a single technique but a whole family of methods, each designed to find a different kind of structure in your data. Three main tasks dominate this field, and each one solves a distinct business problem.
Clustering: This is the most common unsupervised task you'll encounter. Clustering algorithms group similar data points together based on their shared characteristics. An e-commerce platform, for instance, could use clustering to segment its customers into natural groups like "frequent high-spenders," "bargain hunters," or "occasional shoppers" without needing any prior labels.
Association: This technique is all about finding "if-then" rules. It identifies relationships between variables in huge datasets. The classic example is market basket analysis, where a retailer might discover that customers who buy hot dogs also tend to buy buns, leading to smarter product placement and promotions.
Dimensionality Reduction: Sometimes, datasets have hundreds or even thousands of features, which can make them nearly impossible to analyze. Dimensionality reduction simplifies this complexity by shrinking the number of variables while keeping the most important information, making the data far easier to process and visualize.
Popular Algorithms and Real-World Impact
Two algorithms really stand out as foundational tools in the unsupervised learning toolkit: K-Means Clustering and Principal Component Analysis (PCA). K-Means is a go-to for clustering, as it efficiently partitions data into a specific number of groups. PCA is a premier technique for dimensionality reduction, helping distill complex datasets into their most essential components.
The real-world impact of these methods is massive. Unsupervised learning, for example, has completely changed customer segmentation in retail. It powers Netflix's recommendation engine, which helps retain an incredible 80% of subscribers through sophisticated clustering algorithms.
Without the need for expensive, time-consuming data labeling, methods like k-means clustering can reduce data dimensionality by up to 90% while preserving key insights. This autonomy is a game-changer for media and SaaS clients launching content-rich apps. In fintech, anomaly detection can spot fraud in 95% of cases without any prior examples, saving companies millions.
To dive deeper, you can explore more about how these unsupervised methods are benchmarked on AWS.
Comparing Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Models
Once you get past the textbook definitions, the real difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning boils down to a few critical areas: goals, data needs, algorithmic complexity, and how you measure success. For anyone looking to build smarter applications, nailing these distinctions is key. One approach isn't inherently superior; the right choice is all about your specific problem and the resources you have on hand.
Supervised learning is direct and purposeful. It starts with a very specific question, like "Is this transaction fraudulent?" or "What's the projected lifetime value of this customer?" In sharp contrast, unsupervised learning is all about exploration. It begins with a much broader prompt, like "Are there any natural customer segments in our user base?" or "What does 'normal' network activity actually look like?"
Data Input and Preparation
The most significant operational hurdle is the data itself. Supervised models are hungry for labeled data—every single data point needs a known, correct answer attached to it. This can be an expensive, time-consuming slog, often demanding manual work from subject matter experts. The model's accuracy is a direct reflection of how good those labels are, making data prep a massive and often costly part of the project.
Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, works with unlabeled data. This lets you get started much faster because you can feed raw information straight into the model. The trade-off? Your data has to be exceptionally clean and well-structured. With no "answer key" to guide it, the model can easily get confused by noise or irrelevant information. The cost shifts from labeling to intense data cleaning and preprocessing.
The core tasks of unsupervised learning—clustering, association, and dimensionality reduction—are all designed to find meaning in this raw, unlabeled world.
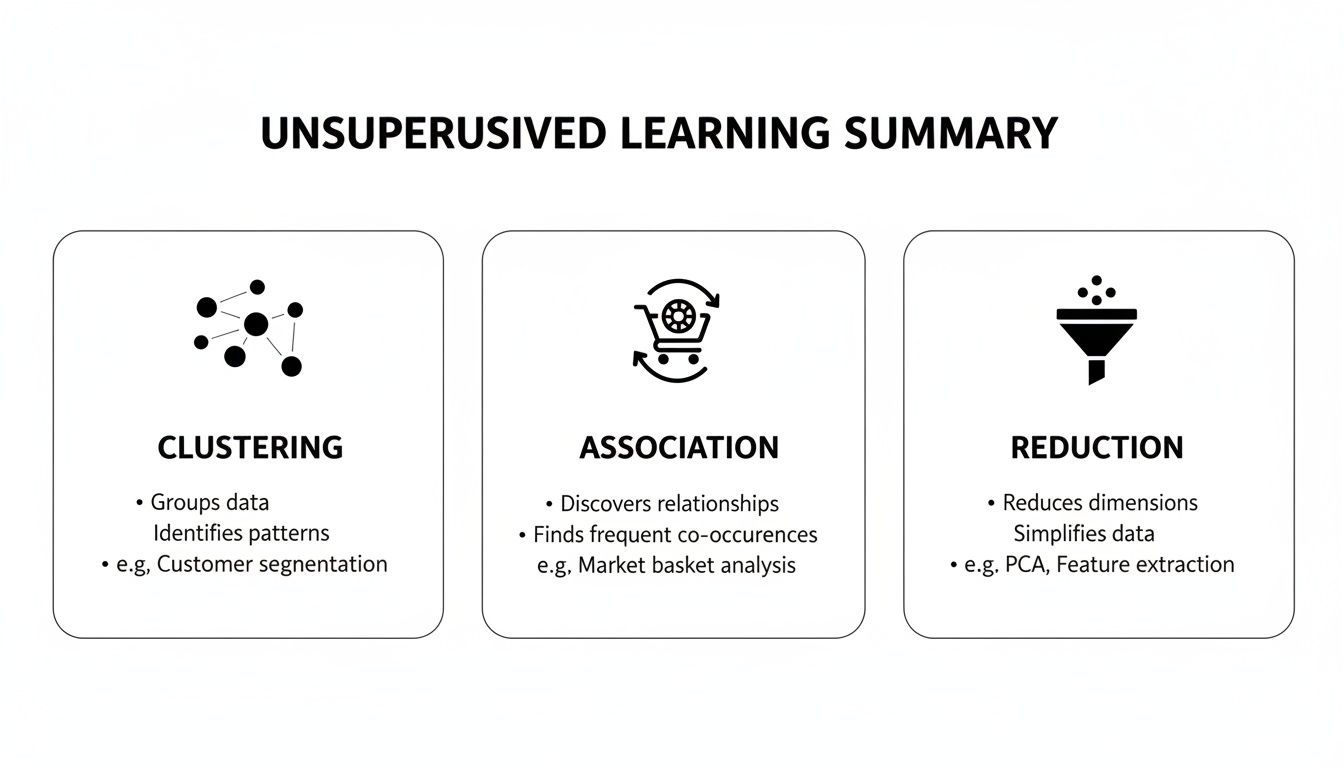
As you can see, these techniques are built to categorize data, spot relationships, and cut through complexity without any predefined labels.
Goals and Algorithmic Complexity
The main goal of any supervised model is prediction. It learns to map specific inputs to known outputs and is fine-tuned to be as accurate as possible. Algorithms like Logistic Regression or Gradient Boosting Machines are built for this, delivering clear, measurable predictions.
Conversely, the goal of an unsupervised model is discovery. It's built to unearth hidden structures, patterns, and anomalies within the data. Algorithms like K-Means Clustering or Principal Component Analysis (PCA) act like explorers, mapping the data's internal architecture to reveal insights a human analyst might completely miss.
The core trade-off is simple: supervised learning offers high accuracy for known problems, while unsupervised learning offers powerful insights into unknown territory. One answers the questions you already have, while the other helps you discover the questions you should be asking.
Evaluation and Feedback
Figuring out if your model is actually working is another huge point of difference. For a supervised model, measuring success is straightforward. You can use metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall to compare the model's predictions against the true labels in your test data. This direct feedback makes it crystal clear how well the model is performing.
Unsupervised models are much tougher to evaluate. Why? Because there are no "right" answers to check against. Success is often subjective and requires a human in the loop. For a clustering model, you might use a metric like the Silhouette Score to check how tight your clusters are, but a domain expert ultimately has to decide if the discovered segments are actually meaningful and useful for the business.
To tie this all together, let’s break down these differences in a more structured way.
Detailed Feature Comparison: Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning
This table provides a comprehensive breakdown of the key differentiators between the two main machine learning paradigms, from data requirements to evaluation metrics.
| Comparison Criteria | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Predict a specific, known outcome (e.g., classify an email as spam or forecast sales). | Discover hidden, unknown patterns or structures (e.g., segment customers or detect fraud). |
| Input Data | Requires high-quality, labeled data where each input has a corresponding correct output. | Works with unlabeled data, requiring only raw inputs without predefined answers. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Learns through a direct feedback loop, correcting its errors based on the ground-truth labels. | Learns without direct feedback, identifying patterns based on the inherent structure of the data itself. |
| Evaluation Method | Performance is measured objectively using quantitative metrics like accuracy, precision, and F1-score. | Performance is evaluated more subjectively, often requiring human analysis or proxy metrics like cluster cohesion. |
| Algorithmic Complexity | Algorithms are trained to map inputs to specific outputs, often resulting in more direct and interpretable models. | Algorithms explore data relationships, which can lead to more complex and less intuitive results that need interpretation. |
Ultimately, choosing between them isn’t about which is "better," but which is the right tool for the job you need to get done.
Choosing the Right AI Model for Your Application
Knowing the theory behind supervised and unsupervised learning is one thing, but actually driving business value with it is a whole different ballgame. The real trick in understanding the difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning isn't just knowing what they are, but when to use them. This decision framework is designed to help you connect your business goals to the right AI strategy for your custom software.
The choice really boils down to your main objective. Are you trying to predict a specific, known outcome? Or are you digging through your data to find insights you don't even know exist yet? Answering that one question will usually point you in the right direction.
Think about an e-commerce platform that wants to predict customer lifetime value (CLV). They have a clear, measurable target. Because they also have historical data with known outcomes—how much customers have spent over time—this is a perfect job for a supervised regression model. On the flip side, a fintech app trying to spot weird transaction patterns for fraud detection would probably start with unsupervised learning. The goal there isn't to predict a pre-defined label but to figure out what "normal" looks like and then catch anything that deviates from it.
Key Questions to Guide Your Decision
To get from theory to a practical choice, you need to get your development and business teams in a room to answer a few critical questions. Your answers will build a strong case for either a supervised or unsupervised approach, making sure your investment in AI lines up with real-world goals.
- Do we have high-quality, labeled data ready to go? If you do, supervised learning is a strong contender. If not, are you prepared for the significant time and money it takes to label that data properly?
- What's our primary business goal? Are you focused on prediction (like forecasting inventory needs) or on discovery (like finding new customer personas)? Prediction points straight to supervised learning, while discovery is where unsupervised methods shine.
- What happens if a prediction is wrong? In high-stakes situations like medical diagnostics, the explainability and high accuracy of supervised models are often non-negotiable.
This kind of structured thinking clarifies which model will best serve your application. For a deeper look at applying these ideas, check out our guide on leveraging machine learning for businesses.
Industry-Specific Scenarios
In regulated industries, the choice becomes even more obvious. Supervised learning clearly dominates in healthcare, claiming 75% of ML projects compared to unsupervised learning's 20%. This is all about the need for accuracy and compliance. Supervised models trained on labeled patient records can predict disease outbreaks with up to 92% precision, which is far better than what you’d get from exploratory clustering. While clustering is great for things like genomics, it can easily misgroup data without clear labels. For Wonderment Apps' wellness clients, this means we can build compliant apps that detect anomalies in vitals data, speeding up data processing by 40%.
When making your final call, you'll also have to balance competing priorities. You have to consider crucial factors like the inherent AI speed-accuracy trade-off; faster models don't always deliver the precision your application might demand.
Ultimately, picking the right model is a strategic move that defines your application's intelligence and its impact. By asking the right questions and understanding the trade-offs, you can ensure your AI projects deliver measurable results that modernize your software and get it ready for whatever comes next.
Modernize Your App with Smart AI Integration
Choosing between supervised and unsupervised learning is a critical first step, but it’s just the beginning. The real challenge—and where the value lies—is in the implementation. Integrating AI into custom software isn't just about plugging in an algorithm; it’s about building a scalable, manageable, and cost-effective system that actually grows with your business. This is where Wonderment Apps' prompt management system can be a game-changer.
Our team specializes in taking legacy software and seamlessly connecting it to the best-fit AI models on the market. We handle the heavy lifting on the engineering side, freeing you up to focus on what matters most: the user experience. But our support doesn’t stop once the initial build is complete.
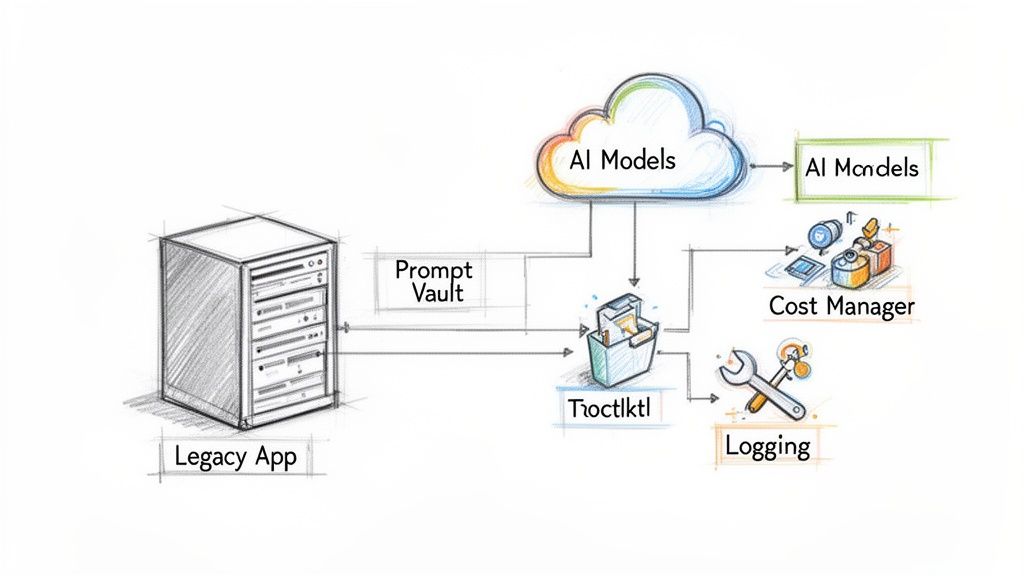
We provide a powerful administrative toolkit designed to give you total, long-term control over your AI integration. For any entrepreneur or developer looking to innovate responsibly, this system is an absolute necessity.
A Toolkit for Sustainable AI Growth
Effectively managing an AI-powered application means constantly tracking performance, keeping a tight rein on expenses, and optimizing every interaction. Our administrative tool is built specifically for these challenges, giving you a central command center for your entire AI ecosystem. If you want to dig deeper into the foundations, our guide on the best language for machine learning is a great place to understand what's happening behind the scenes.
Our toolkit is built around four essential components:
- Prompt Vault with Versioning: This is your secret weapon for testing and perfecting every AI interaction. You can experiment with new prompts, compare their performance, and roll back to previous versions instantly—all without losing your work history.
- Parameter Manager: This feature lets you securely manage how your AI models tap into your internal databases. Your application can leverage proprietary data for personalized results without ever putting your security at risk.
- Unified Logging System: Get a complete, bird's-eye view of every single AI interaction across all platforms. Our logging system tracks performance across all integrated AIs, making it far easier to hunt down bugs and spot usage patterns.
- Cost Manager: No more surprise bills. Our cost manager provides total transparency into your AI spend, offering a clear, cumulative view of token usage and associated expenses so you can manage your budget effectively.
This integrated system gives entrepreneurs and developers the control they need to build with confidence. It transforms AI from a complex, black-box technology into a manageable and measurable business asset.
If you're ready to elevate your application with intelligent features and build software that’s truly designed to last, our approach gives you the tools for success. Schedule a demo of our administrative tool to see how we can help you modernize your app the smart way.
Your Top ML Model Questions, Answered
Once you get the hang of the core concepts, the real-world questions start popping up. It's one thing to know the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning, but it's another to know how they fit into your software modernization goals. The best approach always comes down to your data, your resources, and what you’re ultimately trying to achieve.
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions our teams hear.
Can You Mix Supervised and Unsupervised Learning?
Definitely. Not only is it possible, but it’s also a powerful strategy called semi-supervised learning. Think of it as getting the best of both worlds.
A common tactic is to start with an unsupervised method, like clustering, on a massive, unlabeled dataset. This lets the machine do the heavy lifting, finding natural groups in your data without you lifting a finger. For instance, you could let an algorithm group your entire customer base into segments based on behavior.
From there, you can take a small, manageable sample from each cluster and label it manually. Now you have a high-quality, representative dataset for a supervised model, without the soul-crushing cost of labeling everything. This combination of discovery and prediction is incredibly efficient.
Which One Is More Expensive to Implement?
This is a classic "it depends" scenario, and where you spend the money is the real story. Supervised learning usually has a higher price tag upfront. Why? Data labeling. It’s often a manual, time-consuming process that requires people with deep domain expertise, and that doesn't come cheap.
Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, skips the labeling costs but can rack up expenses elsewhere. It might demand more raw computational power to chew through huge datasets. It also often requires more hours from your data science team to actually interpret the patterns the model finds—the results aren't always self-explanatory. The long-term costs for either path will also depend on model maintenance, infrastructure, and how often you need to retrain.
Where Does Reinforcement Learning Fit In?
Reinforcement learning is the third major player in the machine learning world, and it operates on a totally different wavelength. It’s not about labeled data like supervised learning, nor is it about finding hidden patterns like unsupervised learning. Reinforcement learning is all about an "agent" learning through trial and error.
Imagine training a puppy. You give it treats for good behavior. The agent works the same way, taking actions in an environment to earn the biggest possible cumulative reward. This makes it the perfect tool for dynamic problems where the feedback is about performance over time, not just a simple right-or-wrong label. You'll see it powering everything from robotics and complex game-playing AI to real-time systems that allocate resources on the fly.
At Wonderment Apps, we help you navigate these choices to build intelligent, scalable, and cost-effective software. Our administrative toolkit provides the control you need to manage prompts, secure data, and monitor costs, ensuring your AI integration is a sustainable success.
Ready to modernize your application? Schedule a demo with Wonderment Apps today.