When you're building an app, the debate over white-box testing vs. black-box testing is more than just jargon—it’s a main decision that directly impacts your budget, security, and ultimately, the user experience. The difference really boils down to perspective: white-box testing peeks under the hood at the code, while black-box testing acts like a real user, completely unaware of what’s going on inside. This isn't just a technical detail; it’s a strategic choice that can make or break your software, especially when modernizing it with AI.
At Wonderment Apps, we've seen firsthand how a smart testing strategy forms the bedrock of any successful app, particularly those integrating AI to scale and innovate. For business leaders looking to make their software initiatives successful, getting testing right is non-negotiable. That's why we developed a powerful administrative tool—a prompt management system that developers and entrepreneurs can plug into their existing apps to modernize them for AI. We'll allude to it here and dive into more detail later on how it helps streamline the development of excellent, scalable app experiences.
Choosing Your Software Testing Strategy
This guide will break down these essential testing methods, showing you how each one works, where they shine, and how they fit into a modern, scalable development lifecycle. For leaders aiming to integrate AI or modernize their platforms, getting this right is non-negotiable for a successful launch. Before we jump in, it helps to have a solid grasp of the big picture by understanding quality assurance in software development.
The Core Methodologies Explained
The heart of the white-box testing vs. black-box testing debate is all about what the tester can see. Each approach has a distinct job to do in making sure your app is both technically solid and a pleasure to use.
White-Box Testing gives testers a backstage pass to the source code and internal architecture. Think of it like a mechanic meticulously inspecting a car's engine to make sure every single part is working as designed. This method is perfect for sniffing out security vulnerabilities and optimizing code performance.
Black-Box Testing operates purely from the end-user's point of view, with zero knowledge of the internal code. Testers treat the software as an opaque "black box," focusing only on what goes in and what comes out. It’s all about confirming the app meets its functional requirements and delivers a seamless user journey.
Key Takeaway: White-box testing ensures the application is built correctly, while black-box testing ensures the correct application was built. A balanced strategy needs both to succeed.
A Quick Comparison
Seeing the high-level differences helps frame the strategic decisions you'll need to make for any software project.
| Aspect | White-Box Testing | Black-Box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Perspective | Internal (Code and Architecture) | External (User Interface and Functionality) |
| Knowledge Required | Programming and system knowledge | No programming knowledge needed |
| Primary Goal | Verify internal logic and security | Validate user experience and requirements |
| Performed By | Developers, Security Experts | QA Analysts, End-Users |
| Ideal For | Unit tests, security scans | User acceptance, end-to-end testing |
Ultimately, the best testing strategies don't pick a side. They combine both approaches to create a powerful feedback loop that strengthens the entire development lifecycle, from the first line of code to final user sign-off.
Understanding White-Box and Black-Box Testing
The core difference between white-box and black-box testing comes down to one question: How much do you know about what’s going on inside the software? Each approach gives you a totally different vantage point, and knowing when to use which is the bedrock of a solid QA strategy.
Think of your software as a high-tech, impenetrable vault. White-box testing is like handing the security expert the complete blueprints. They can trace every wire, inspect every lock, and analyze every internal mechanism to confirm it's built to spec.
Black-box testing, on the other hand, is like hiring a world-class safecracker. They don’t get the blueprints. They only know what the vault is supposed to do—protect the valuables inside. So they test the keypad, try to pry the door, and check the alarm system, all from the outside.
Defining White-Box Testing
White-box testing, which you might also hear called clear-box or structural testing, is the "blueprint" approach. Testers get full access to the application's source code, architecture, and internal pathways. It's all about getting under the hood to verify the code's internal logic and structure.
Testers are looking at specific code paths, loops, and conditional statements to make sure every single component works exactly as it was coded. This method is incredibly powerful for catching hidden bugs, security weak spots, and performance issues that you’d never spot from the user interface. Because it demands a deep technical understanding, white-box testing is almost always handled by developers or specialized security engineers.
Defining Black-Box Testing
Black-box testing comes from the complete opposite perspective: the end-user's. The tester knows nothing about the internal code, architecture, or database structure. They interact with the software just like a customer would, treating it as an opaque "black box."
Here, the entire focus is on inputs and outputs. Does the software do what it's supposed to when a user interacts with it?
If a user types in the right password, does the system let them in?
When a customer adds an item to their cart, does the total update correctly?
Does clicking "Forgot Password" actually send a reset email to the user's inbox?
This approach is all about validating that the software meets its functional requirements and provides a smooth, intuitive user experience. It's typically carried out by QA analysts who are masters at thinking—and acting—like real-world users. To see how this fits into the bigger picture, you can explore the main types of software testing in our comprehensive guide.
Here's an easy way to remember it: White-box testing is about how the system works on the inside, while black-box testing is about what the system does on the outside.
By bringing these two perspectives together, you can be confident your application is not only engineered correctly but also delivers a flawless experience for your users.
Comparing Testing Methodologies Side-by-Side
To really get to the bottom of the white-box testing vs. blackbox testing debate, you have to look past the textbook definitions and see how they stack up in the real world. Their goals, the skills they demand, and the level of detail they get into are fundamentally different. One looks inward at the architecture, while the other looks outward at the user experience.
This isn't just some technical nitpick; it's a critical business decision. Picking the right approach at the right time directly impacts your budget, timeline, and the final quality of what you ship. Understanding where each one shines helps you put your resources where they’ll make the biggest impact and build a much more solid application.
This diagram breaks down the core differences between the two testing approaches at a glance.
As the visual shows, white-box testing is all about the code and deep analysis. Black-box testing, on the other hand, is user-centric and all about function, which really drives home how they’re two sides of the same quality coin.
Key Differences White-Box vs Black-Box Testing
To make these distinctions even clearer, let's break them down side-by-side. This table cuts through the noise and lays out the core attributes of each methodology.
| Attribute | White-Box Testing | Black-Box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Verify internal logic and structure. | Validate functionality against requirements. |
| Knowledge Required | Deep understanding of programming, code, and architecture. | No internal knowledge needed; focuses on user specifications. |
| Performed By | Primarily developers and specialized SDETs. | QA analysts, end-users, and dedicated testers. |
| Level of Detail | Microscopic (code paths, statements, branches). | Macroscopic (user flows, inputs/outputs, UI behavior). |
| Main Objective | Maximize code coverage. | Achieve high functional coverage. |
| Synonyms | Clear-box, glass-box, structural testing. | Behavioral, opaque, closed-box testing. |
This comparison highlights that the choice isn't about which one is "better," but which one is right for the specific task at hand. Both are essential for a comprehensive QA strategy.
Primary Goals and Objectives
The core purpose of each approach really dictates its scope and impact. At its heart, white-box testing is about verification—making sure the internal structure is built correctly. Black-box testing is all about validation—confirming the final product actually does what the user needs it to do.
White-Box Testing Goal: The main mission here is to hit high code coverage. This means making sure that as many lines, branches, and paths in the code get executed as possible. It’s all about digging up hidden logic errors, sniffing out security holes buried in the code, and optimizing clunky algorithms.
Black-Box Testing Goal: Here, the focus shifts entirely to functional correctness and the user experience. Testers are validating that the software meets its documented requirements, that user journeys feel intuitive and are bug-free, and that every input spits out the correct output, no matter what the code looks like under the hood.
Key Insight: White-box testing asks, "Did we build the system right?" It scrutinizes the craftsmanship of the code. Black-box testing asks, "Did we build the right system?" It ensures the finished product solves the user's problem.
Skills and Expertise Required
The human element is a huge differentiator here. The skills needed for each approach are highly specialized, which is why developers and QA analysts have such distinct—but equally vital—roles in any solid quality assurance plan. This is a key factor when deciding how to pick the right developers for your app project.
A developer’s intimate familiarity with the codebase makes them the perfect person for white-box testing. They can read the code, trace its logic, and write unit tests that zero in on specific functions or modules.
On the flip side, a QA analyst is a natural at black-box testing because they bring that crucial external, user-first perspective. They’re experts at designing test cases from requirements, thinking like a user, and spotting flaws in the interface that a developer, who is close to the code, might easily miss.
Level of Detail and Scope
The level of granularity is another major point of contrast. White-box testing is microscopic; it’s about peering into individual lines of code and internal pathways. Black-box testing is macroscopic, focusing on the big picture of end-to-end user flows and overall system behavior.
A white-box test might involve dissecting a single algorithm to see if it handles edge cases correctly or checking a database query to find a performance bottleneck. The scope is narrow and incredibly deep.
Black-box testing, in contrast, looks at a complete user journey, like a customer successfully buying a product in an e-commerce app. The scope is broad and entirely user-centric, covering multiple integrated pieces from the outside in.
One of the biggest practical differences is the time commitment. White-box testing demands a lot more time than black-box testing because of its exhaustive code path analysis, which can stretch testing phases from days into weeks. Black-box, however, is much more efficient with techniques like equivalence partitioning. For a simple age validator, you might only need two test cases, which can slash your case volume by up to 80%. A recent QA report estimated that white-box tests take 2-3x longer per module than black-box tests—a critical data point for the 70% of agile teams pushing releases every two weeks. You can explore more data on testing timelines to see how this plays out in project planning. This time gap is a make-or-break factor in agile environments where speed is everything.
When to Use Each Testing Approach
Choosing between white-box and black-box testing isn’t about picking a winner. It’s about selecting the right tool for the job at hand. Making the right call at the right time saves resources, cuts down on risk, and helps you build an application that’s both technically solid and a pleasure to use.
Think of it this way: white-box testing makes sure the internals are right, while black-box testing confirms the externals work as expected. You absolutely need both to ship a great product.
Scenarios Demanding White-Box Testing
You’ll want to reach for white-box testing whenever the internal logic, security, and performance of your application are non-negotiable. This is the go-to method for developers and security specialists who need to get under the hood, dig into the code, and find problems that are totally invisible from the outside.
Here are a few prime situations where white-box testing is a must:
Security-Critical Applications: For any fintech, healthcare, or SaaS platform handling sensitive data, white-box testing is your first line of defense. It's the only way to conduct a deep vulnerability analysis, sniff out insecure coding habits, and shut down potential data breaches before they ever happen.
Complex Algorithm Tuning: When your app leans on a complicated algorithm—like a recommendation engine for an e-commerce store or a fraud detection system—white-box testing lets you verify its logic and tune its performance, function by function.
Unit and Integration Testing: During the main development cycle, developers rely on white-box unit tests to make sure individual components work perfectly in isolation. Catching bugs this early is fundamental to building a stable codebase.
Performance Bottleneck Identification: If your application feels sluggish, white-box testing is how you find the culprit. It can pinpoint the exact lines of inefficient code or slow database queries causing the lag.
Key Insight: Use white-box testing when the risk of an internal failure is high. It's an upfront investment in stability and security that prevents catastrophic issues down the road.
Situations Where Black-Box Testing Excels
Black-box testing is the perfect choice for validating software from the user’s point of view. It answers the single most important question: does this thing actually do what it’s supposed to for the person using it?
You'll want to choose black-box testing in these scenarios:
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): This is the final check before going live. Real users or QA analysts put the software through its paces to confirm it meets their needs and the business requirements, all without ever peeking at the code.
Validating User Interface (UI) and Experience (UX): For any app that real people will use, like a mobile banking app or an online store, black-box testing is ideal. It ensures the user journey is intuitive, functional, and free of weird visual bugs.
System and Integration Testing: When you need to be sure that different pieces of a large system play nicely together, black-box testing simulates real user workflows that cut across multiple modules or services.
Smoke Testing After Deployment: Right after a new build goes to a server, a quick round of black-box smoke tests can verify that all the critical features are up and running. It’s a fast way to get a pulse on the build’s stability.
To strengthen your overall defense, you can dive deeper into our guide on application security best practices, which nicely complements these testing methods.
Introducing Gray-Box Testing: The Best of Both Worlds
Sometimes, you need something in between. A purely white-box or black-box approach isn't always the most efficient path. That’s where gray-box testing comes into play. It's a powerful hybrid model where the tester has some, but not all, knowledge of the system's internal workings.
For instance, a tester might know the database schema to write more precise queries, or they might understand the API endpoints to design smarter integration tests.
Gray-box testing strikes a strategic balance. It blends the user-centric view of black-box with the technical depth of white-box, leading to more intelligent and targeted test cases. This approach can uncover deeper issues without needing full source code access, making it an incredibly efficient choice for many modern development teams.
Balancing Testing Speed and Thoroughness for Better ROI
In the constant push to get new features to market, the debate over white-box vs. black-box testing often boils down to a question of speed versus depth. Striking the right balance isn’t just a technical challenge; it's a critical business decision that directly impacts your return on investment (ROI). Every hour spent testing is an hour not spent shipping, but one catastrophic failure can erase months of progress.
On one hand, black-box testing is a clear accelerator for release cycles. It allows QA teams to quickly sign off on user-facing functionality and keep the development pipeline moving. But relying on it exclusively is like only checking a car’s exterior for dents while ignoring a potential engine flaw—you might miss a critical structural issue just beneath the surface.
Conversely, white-box testing is the deep-dive inspection. It’s meticulous and often slower, but its ability to uncover security vulnerabilities and complex logic errors before they hit production provides immense long-term value. Preventing a single major data breach or system failure delivers an ROI that far outweighs the initial time investment.
Challenging Old Assumptions About Efficiency
For years, the consensus was that the code-level access of white-box testing made it inherently superior for finding faults, even if it took longer. However, recent analysis has challenged this long-held belief, suggesting that a well-designed black-box strategy can be surprisingly effective. This is a game-changer for teams trying to optimize resources without sacrificing quality.
A landmark 2016 study found that top-tier black-box methods performed nearly on par with established white-box strategies, showing a maximum difference in fault detection of only 4%. The research also revealed that the most critical 10% of test suites from both approaches identified at least 60% of the same faults. This proves you don’t always need to know the code to get excellent results. You can discover more about these testing efficiency findings to see how this data is reshaping traditional QA thinking.
Building a Hybrid Strategy for Maximum Impact
This evidence doesn't mean one method replaces the other. Instead, it empowers businesses to build smarter, hybrid QA strategies that blend the speed of black-box testing with the precision of white-box testing. By allocating resources strategically, you can get more comprehensive coverage, more efficiently.
Such a balanced approach is key to effective quality assurance. For practical methods to improve both efficiency and coverage in your testing processes, consider how to approach automating regression testing. This ensures that new features don't inadvertently break existing functionality—a common headache in rapid development. You can also read our guide on how automating regression testing saves time and money to get a deeper look.
The ROI Equation: True ROI in testing isn't just about launching faster. It's about launching with confidence, knowing you've minimized the risk of costly rework, reputational damage, and user churn.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a testing framework that is both rigorous and agile. By combining automated black-box tests for user flows with targeted white-box analysis for high-risk areas—like payment gateways or data processing algorithms—you get the best of both worlds. This integrated approach gives your team the ability to deliver high-quality software that stands up to real-world demands.
Modernizing Your QA Strategy with AI
A modern testing strategy has to be smart, scalable, and woven directly into your development lifecycle. Simply combining white-box vs. black-box testing isn't enough anymore. Today's applications demand an approach that fully embraces AI to stay competitive, meaning your QA framework needs to be as dynamic as the software it's validating. This is how you use AI to modernize your software application and build it to last for many years to come.
At Wonderment Apps, this is exactly what we help businesses build. We blend time-tested, traditional testing principles with the power of AI to create excellent app experiences that can scale to meet the size of any user audience.
Integrating AI with Unprecedented Control
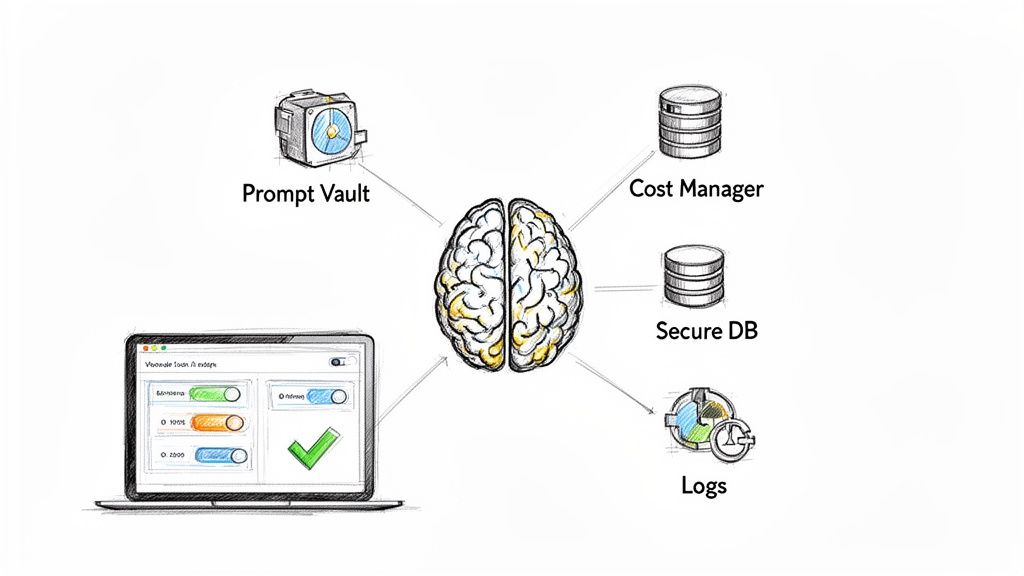
The real challenge today isn't just adding AI features—it's managing them effectively. An AI-powered application brings new complexities in performance, cost, and reliability. This is precisely why a comprehensive QA strategy is non-negotiable, and it's why we developed our own prompt management system—an administrative tool developers can plug into their existing app to modernize it for AI integration.
This toolkit puts a suite of powerful management features in your team's hands:
Prompt Vault: Keep all your AI model prompts in one centralized place with full versioning, ensuring consistency and making updates a breeze.
Parameter Manager: Give your AI models secure, controlled access to your internal database so they can retrieve the data they need without ever compromising security.
Comprehensive Logging System: Track every single interaction across all integrated AI models. This gives you a clear audit trail for debugging, performance tuning, and ensuring reliability.
Cost Manager: Monitor your cumulative spend on AI services in real-time. You can prevent surprise bills and make smarter budget decisions to maximize ROI.
By integrating this tool, you're not just modernizing your app—you're gaining unparalleled control over its performance, cost, and reliability. Everything is validated by a QA strategy that truly understands the nuances of both white-box and black-box testing.
A Future-Proof Approach to Quality
This level of control is essential for any business that's serious about building software that lasts. Our approach ensures that as you add new AI capabilities, your testing framework grows right alongside them. Your team can confidently test the internal logic of AI integrations (a white-box approach) while simultaneously validating the end-user experience (a black-box approach).
When you partner with us, you get more than a development service; you get a strategic partner dedicated to building a resilient, scalable, and intelligent application. Our mix of expert teams and advanced tools ensures your software isn’t just ready for today's market but is built for the innovations of tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you’re trying to pin down the differences between white-box vs. black-box testing, a lot of questions pop up. Getting straight answers is the only way to build a quality assurance strategy that actually protects your application and keeps users happy. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones.
Can Black-Box Testing Completely Replace White-Box Testing?
Not a chance. While it’s tempting to simplify and pick just one, they serve entirely different—and equally critical—purposes. Think of black-box testing as your front-line check; it validates the user experience and confirms the software does what it’s supposed to from an external perspective.
But white-box testing is what gets you under the hood. It’s the only reliable way to uncover security vulnerabilities, performance bottlenecks, and thorny logic errors buried deep in the source code. Any truly robust QA strategy uses a thoughtful mix of both to make sure every single layer of the application has been put through its paces.
Which Testing Method Is Better for Agile and DevOps?
Both are absolutely essential in fast-moving development environments. They each play a distinct, vital role in a modern CI/CD pipeline.
White-box testing, especially automated unit tests, is a cornerstone of continuous integration (CI). It gives developers near-instant feedback, catching bugs right at the code level before they ever get merged into the main branch.
Black-box testing, particularly automated end-to-end tests, is indispensable for continuous delivery (CD). This is your final guardrail, ensuring new features haven't inadvertently broken existing user-facing functions, which gives teams the confidence to release code frequently.
In short, the rapid feedback from black-box tests fits perfectly with Agile and DevOps release cycles, while white-box testing keeps the underlying codebase stable and secure.
How Do You Choose Between a Developer or QA Analyst for Testing?
The choice really comes down to the type of testing you’re doing. Each role brings a unique skill set perfectly suited for one approach over the other. White-box testing is a developer’s game—or a Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET)—since it requires someone who can read, understand, and analyze source code. This is an important consideration when you're looking to pick the right developers for your software project.
For black-box testing, a dedicated QA analyst is invaluable. They are masters at thinking like an end-user, building test cases straight from product requirements, and spotting usability flaws that a developer might naturally overlook. The most effective teams don’t choose one over the other; they leverage both, creating a powerful balance between technical rigor and a user-centric perspective.
Is One Method More Expensive Than the Other?
The costs can be deceiving if you only look at the surface. White-box testing might seem more expensive upfront. It demands skilled developers' time and can be more intensive to set up per test case. But its real value is in prevention—catching a single critical security flaw early can save a company millions down the road.
Black-box testing, on the other hand, is generally quicker to execute and easier to scale, especially with the right automation tools. The smartest, most cost-effective strategy is always a risk-based approach. Focus intensive white-box testing on high-risk components (like payment gateways or data handling), and use black-box testing to ensure broad functional coverage across the rest of the application.
At Wonderment Apps, we help you build a QA strategy that balances speed, thoroughness, and cost, ensuring your application is not only well-engineered but also perfectly aligned with user needs.
Ready to modernize your application with a robust, AI-ready testing framework? Schedule a demo of our administrative toolkit to see how we can help you gain control over your AI integrations and deliver flawless software.
