Building a healthcare app is about more than just slick features and a great user interface. It demands an ironclad commitment to protecting the most sensitive kind of data there is: patient data. This is where HIPAA compliant app development comes in—it's the entire process of architecting and building software that lives up to the strict security and privacy standards of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
In simple terms, it means putting specific technical, physical, and administrative safeguards in place to make sure every piece of Protected Health Information (PHI) is handled with the utmost security. But getting it right, especially when you want to modernize your app with cool tech like AI, can feel tricky. That's why we built tools to make it easier. We've developed a prompt management system that plugs into your app, letting you innovate with AI without the compliance nightmares. We'll touch on this a bit more later.
Understanding The Stakes Of HIPAA Compliance

Starting a healthcare software project without a deep understanding of HIPAA is like building a hospital without fire codes. It’s not a question of if something will go wrong, but when. The entire regulation is built on two core pillars: the HIPAA Privacy Rule, which dictates how PHI can be used and shared, and the Security Rule, which spells out the safeguards needed to protect it.
Ignoring these rules isn't just a regulatory headache; it's a massive business risk. The financial fallout from HIPAA violations has skyrocketed. In February 2024 alone, organizations paid out over $137 million in penalties—a huge jump from previous years. By 2023, the average fine for a violation during mobile app development hit just over $2 million per incident. The numbers don't lie; cutting corners on compliance can be financially devastating.
Demystifying Core Compliance Concepts
Before you even think about writing a single line of code, your team needs to be fluent in a few non-negotiable concepts. It all starts with Protected Health Information (PHI). This is any health data that can be tied to an individual, from the obvious things like names and social security numbers to diagnoses and treatment histories.
Next up is the Business Associate Agreement (BAA). Think of this as a legally binding contract you must have with any third-party vendor who touches PHI on your behalf. This includes your app development partner, your cloud hosting provider—anyone. A BAA makes it official: your partners are just as responsible for protecting patient data as you are. For a deeper dive, you can learn more about the challenges of designing digital products for healthcare.
One of the most common mistakes we see is teams treating HIPAA compliance like a final checkbox to tick off before launch. True compliance is a mindset and a continuous process, woven into every stage of your app's lifecycle—from the first design sketch to ongoing maintenance.
Implementing Essential Technical Safeguards
This is where the rubber meets the road. Translating HIPAA's legal jargon into a concrete set of technical requirements is the core of building a compliant application. These are the non-negotiable security controls that need to be baked into your app's architecture from day one.

Think of Protected Health Information (PHI) like digital currency. You wouldn’t leave cash lying around for anyone to grab, and the same mindset must apply to patient data. Every architectural choice has to be filtered through the lens of protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI.
Fortifying Data With End-to-End Encryption
The absolute foundation of your technical safeguard strategy is strong, end-to-end encryption. It’s not just a good idea; it’s a mandate. Encryption makes PHI completely unreadable and useless to anyone without authorized access, whether it's sitting in a database or flying across the internet.
Your development team must tackle encryption in two states:
- Data in Transit: This protects PHI while it's moving between a user's phone, your servers, and any third-party services. The gold standard here is Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 or higher, which creates a secure, encrypted pipeline for all data.
- Data at Rest: This is about securing PHI when it's stored on servers, in databases, or on backups. For this, AES-256 encryption is the industry benchmark, providing a powerful shield against any direct attacks on your storage.
To get this right, you need to implement robust cybersecurity compliance solutions that treat these encryption standards as the bare minimum.
Mastering Access With Strict Controls
Encryption is only one piece of the puzzle. You also have to be incredibly strict about who can access PHI and what they're allowed to do with it. This is where you enforce HIPAA's 'minimum necessary' principle through powerful access controls.
Two mechanisms are absolutely critical:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Passwords alone are a relic of the past. MFA requires users to provide at least two forms of verification to log in, which dramatically cuts down the risk of an account takeover from stolen credentials.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Not everyone needs access to everything. RBAC ensures that users—be they patients, nurses, doctors, or admins—can only see the specific data and use the specific functions required for their role.
Implementing MFA is proven to prevent up to 99.9% of account compromise attacks. When you combine that with diligent, real-time audit logging and automatic session termination, you build a fortress around your data. These safeguards aren’t optional suggestions; they are core requirements of the HIPAA Security Rule.
Creating Immutable Audit Trails
When a security incident happens—and you have to assume it might—you absolutely must be able to trace every interaction with PHI. This means you need a comprehensive, unchangeable audit trail that answers the who, what, when, and where for every action.
Think of your audit trail as a permanent, unchangeable historical record. It must capture every user login, file access, data change, and export. These logs are your first and best tool for forensic analysis after a breach and for proving your compliance during an audit.
These logs need to be protected from being altered and stored securely for at least six years. Another simple but crucial safeguard is automatic logoff. This feature ends a user's session after a set period of inactivity, which is a key defense against unauthorized access on a device that’s been left unattended.
Finally, your choice of hosting provider is a massive decision. Major cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer HIPAA-compliant hosting and will sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). They provide built-in tools for encryption, access control, and logging that can give your development process a significant head start. To brush up on the fundamentals, take a look at our guide on foundational data security concepts.
The table below breaks down the primary security safeguards you'll need to address.
HIPAA Security Safeguards Checklist
| Safeguard Type | Key Requirement | Example Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative | Conduct a risk analysis to identify vulnerabilities to PHI. | Perform regular security risk assessments and create a risk management plan. |
| Administrative | Implement a security awareness and training program for all staff. | Annual HIPAA training for all employees with access to PHI. |
| Physical | Control physical access to facilities where PHI is stored. | Secure server rooms with keycard access; implement workstation security policies. |
| Physical | Implement policies for the secure disposal of PHI. | Use certified data destruction services for old hard drives and media. |
| Technical | Implement access controls to limit access to PHI. | Unique user IDs, role-based access control (RBAC), and automatic logoff. |
| Technical | Encrypt PHI both in transit and at rest. | Use TLS 1.2+ for data in transit and AES-256 for data at rest. |
| Technical | Maintain audit logs of all activity involving PHI. | Implement a logging system that tracks all access, creation, and modification of PHI. |
| Technical | Ensure the integrity of PHI from alteration or destruction. | Use checksums or digital signatures to verify data integrity. |
This checklist is a great starting point, but remember that HIPAA compliance is an ongoing process of assessment, implementation, and refinement—not a one-time setup.
Budgeting for HIPAA Compliant App Development
Figuring out the real cost of a HIPAA-compliant app is a lot like budgeting for a new house. You don't just account for the lumber and drywall; you have to factor in the foundation, the high-tech security system, and the ongoing upkeep. If you only look at developer hours, you’re missing the bigger, more critical financial picture.
The total investment for HIPAA compliant app development goes way beyond just writing code. I've seen many founders and project managers get blindsided by the "hidden" costs—which are actually non-negotiable requirements for creating a genuinely secure and legally sound application. Trying to cut corners here isn't a savvy business move; it's a gamble that almost always leads to catastrophic costs down the line.
This simple flow shows how the two streams of work—development and compliance—merge to create the total investment needed.
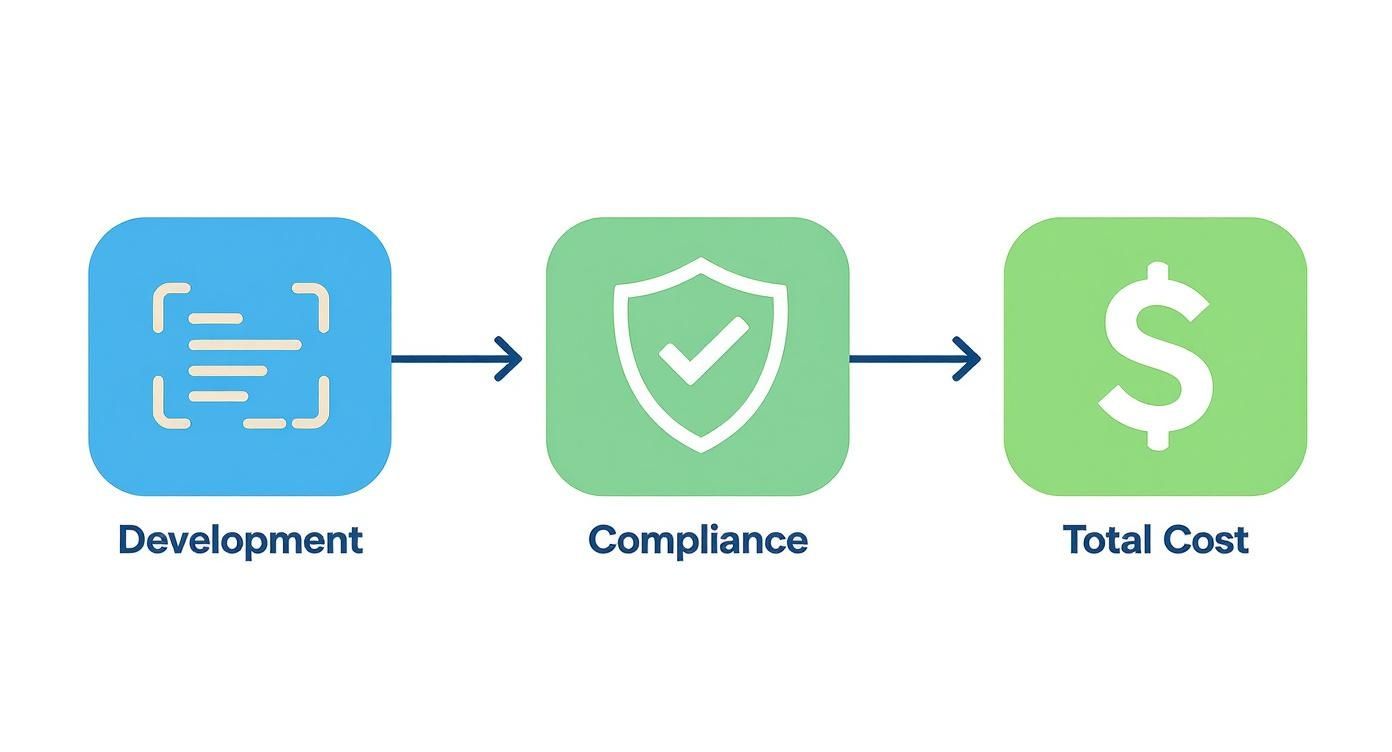
As you can see, compliance isn't something you tack on at the end. It's a parallel, equally important investment that has to be woven into the core development effort from day one.
Breaking Down the Core Cost Categories
To budget accurately, you need to think beyond your core development team. These are the areas where a smart upfront investment will save you from massive financial headaches later.
Here are the key cost centers you absolutely must factor in:
- Legal and Compliance Expertise: Before a single line of code is written, you need legal counsel to interpret HIPAA’s rules for your specific app. Compliance consultants then help translate those dense legal requirements into concrete technical specifications—a crucial step for avoiding expensive rework.
- Third-Party Security Audits: You can't just declare your app secure. Independent, third-party audits and penetration tests are essential for validating your safeguards. These audits catch vulnerabilities your team might have missed and give you the documentation to prove you’ve done your due diligence.
- Secure Hosting and Infrastructure: You’ll need a HIPAA-compliant hosting provider like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure that will sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). This specialized infrastructure naturally comes at a premium compared to standard hosting plans.
- Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance: HIPAA compliance isn't a one-and-done project. Your budget must include recurring operational expenses for ongoing security monitoring, regular risk assessments, and software updates to patch any new vulnerabilities that emerge.
Understanding Realistic Cost Ranges
So, what’s the real number? The investment can swing wildly depending on your app's complexity and the sensitivity of the data it handles. A recent analysis pegs the average cost for a fully featured HIPAA-compliant application somewhere between $100,000 and $250,000.
Just the compliance-specific requirements alone can tack on an extra 20–30% or more to the total development cost. This premium covers the non-negotiables: data encryption, secure authentication, audit trails, and granular access controls. For a deeper dive, you can discover more insights about healthcare app development costs.
Let me be clear: trying to save a few bucks by skipping a third-party audit or putting off a BAA is a recipe for disaster. The cost of a single data breach—from fines and legal fees to reputational ruin—can easily eclipse your entire initial development budget.
The biggest driver of your cost will always be complexity. A simple appointment scheduling tool will be far less expensive than a comprehensive telehealth platform with real-time video, EMR integration, and patient portals. The more Protected Health Information (PHI) you handle, the more robust—and therefore expensive—your security architecture must be. Planning for these costs transparently from the very beginning is the only way to build a sustainable and truly secure healthcare application.
A Practical Development and Deployment Playbook
Once you've settled on your budget and defined the necessary safeguards, it's time to shift from planning to action. Building a HIPAA-compliant app isn't a straight line; think of it more as a continuous cycle where security and privacy are baked into every single phase. This playbook is your roadmap for building, testing, and launching your app without ever putting compliance on the back burner.
This isn't just about checking off a list of requirements right before you go live. It’s about cultivating a compliance-first culture, from the very first wireframe all the way to post-launch monitoring. Every stage strengthens the one before it, resulting in a secure, resilient application that earns the trust of both patients and healthcare providers.
Privacy by Design: Your First Line of Defense
The costliest compliance mistakes almost always happen before a single line of code gets written. The discovery and design phase is your golden opportunity to weave security into the very fabric of your app. We call this 'privacy by design'.
What this means in practice is that every feature, every user journey, and every piece of data is scrutinized through a security lens. Don't start by asking, "What data do we need?" Instead, ask, "What's the absolute minimum data we need for this feature to work?" This principle, known as data minimization, is a cornerstone of HIPAA.
During this early stage, your team needs to get serious about a full-blown risk analysis. This isn't a quick meeting; it's a deep-dive to uncover every potential threat and vulnerability surrounding PHI.
- Map Every Touchpoint: Create detailed diagrams that trace the path of PHI from the moment it's collected to when it's stored, processed, and sent.
- Anticipate Threats: For each of those touchpoints, brainstorm what could go wrong. Think unauthorized access, data interception during transfer, or even accidental employee disclosure.
- Find the Weak Spots: Look at your proposed architecture and pinpoint weaknesses that a threat could exploit.
The result of this exercise is a risk management plan—a document that details specific controls to counter each risk you've identified. This becomes the bible for your development team.
Secure Development Isn't Optional
With a security-focused design locked in, it's time to start building. Here, secure coding practices are completely non-negotiable. Your developers need to be well-versed in writing code that stands up to common attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other vulnerabilities that hackers love to exploit.
Your responsibility doesn't end with your own code, either. You have to be incredibly thorough when vetting any third-party libraries or SDKs you plan to use. A single insecure component can compromise your entire system.
When you bring a third-party service into your ecosystem, you're also inheriting its security (or lack thereof). Always get a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) and do your homework on their security certifications and audit reports before you integrate.
Connecting to other systems, like Electronic Health Records (EHRs) or payment platforms, is another critical step. All of these integrations must use secure, authenticated APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that enforce strict access rules and encrypt every bit of data that moves between them.
The journey of building a HIPAA-compliant application can be broken down into several distinct stages, each with its own set of compliance-related tasks and priorities. From the initial idea to ongoing maintenance, security and privacy must be a central theme.
The table below outlines these key stages and the critical compliance activities that should happen at each point.
HIPAA App Development Lifecycle Stages
| Development Stage | Key Compliance Focus | Critical Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery & Design | Privacy by Design, Risk Identification | Conduct risk analysis, map PHI data flows, define access controls, principle of least privilege. |
| Development | Secure Coding, Vendor Management | Train developers on secure practices, vet third-party libraries, secure all APIs, demand BAAs. |
| Testing & Validation | Vulnerability Detection, Compliance Verification | Perform SAST, DAST, and penetration testing; conduct UAT on compliance workflows. |
| Deployment | Secure Infrastructure, Access Control | Harden servers, configure firewalls, implement robust logging and monitoring from day one. |
| Maintenance | Ongoing Vigilance, Incident Response | Monitor logs for threats, have an incident response plan, conduct regular audits and updates. |
Following a structured approach like this ensures that compliance is not an afterthought but a foundational element integrated throughout the entire development process, leading to a more secure and trustworthy application.
Put It to the Test: Rigorous Validation
You can't just hope your app is secure—you have to prove it. For a HIPAA-compliant application, the testing phase is far more intense than your typical functional and UX testing. It demands a dedicated, multi-layered security validation process.
Think of it as a series of hurdles designed to uncover any weakness:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Before the code is even compiled, automated tools scan it to find known vulnerabilities and bad practices.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Once the app is running, these tools simulate external attacks to find security holes in real-time.
- Penetration Testing: This is the ultimate stress test. You hire ethical hackers to do their best to break into your application, using the same tactics real attackers would. Their findings give you a priceless, real-world view of your defenses.
Finally, User Acceptance Testing (UAT) must include specific scenarios to confirm your compliance rules are working. For instance, have testers try to access data they shouldn't have permissions for, confirming your role-based access controls are ironclad.
Go-Live and Stay Alert
After navigating the complexities of development and testing, you’ve made it to launch day. The last technical step is ensuring a secure server configuration. Your infrastructure team needs to harden servers, set up firewalls, and confirm that all logging and monitoring systems are fully operational from the moment you flip the switch.
But launch day is just the beginning. HIPAA compliance is a marathon, not a sprint. Post-launch, your focus has to shift to constant vigilance. This means:
- Continuous Monitoring: Keep a close eye on your system logs for any suspicious activity and set up immediate alerts for potential security incidents.
- A Ready-to-Go Incident Response Plan: You need a clear, documented plan for what to do if a breach occurs. This should cover everything from containing the threat to notifying users and regulatory bodies.
- Regular Audits: Don't set it and forget it. Conduct periodic internal and external audits to make sure your security controls are still effective and that you're prepared for new and evolving threats.
By following this playbook, you ensure compliance is a foundational pillar of your app's success, not just a box to check.
Modernizing Your Healthcare App with Compliant AI
Artificial intelligence isn't a sci-fi concept anymore; it's a real tool that can dramatically improve patient care and make clinical workflows much smoother. We're talking about everything from AI-powered diagnostic tools to smart chatbots that handle routine patient questions. The possibilities are huge.
But adding AI, particularly large language models (LLMs), into a healthcare app brings a whole new layer of compliance challenges to the table.
The central problem is straightforward: how do you let an AI model process data without ever exposing Protected Health Information (PHI)? The second any PHI leaves your secure system to hit a third-party AI service, you’ve created a potential compliance nightmare. This is a massive hurdle in HIPAA compliant app development that forces us to rethink data security from the ground up.
The AI Compliance Frontier
Your standard safeguards like encryption and access controls are still crucial, but they’re not enough when AI is in the mix. LLMs work by processing and learning from data, which creates a serious risk that PHI could be accidentally saved or used to train the model—a clear HIPAA violation.
To use AI safely, you need to build a secure, controlled "airlock" between your application and the AI model itself. This system has to be able to:
- Scrub PHI: Automatically find and either remove or anonymize sensitive patient data before it gets sent to the AI.
- Control Prompts: Carefully manage the instructions (prompts) you send to the AI, ensuring they're safe and don't ask for sensitive information.
- Log Everything: Keep a detailed and unchangeable audit trail of every single interaction with the AI, including what was sent and what came back.
Trying to build this kind of middle layer from scratch is a heavy engineering lift. It demands deep knowledge not just of AI, but of the specific quirks of healthcare data security. As you think about adding these advanced features, a good guide to HIPAA compliant AI tools can be invaluable for making sure your approach meets the strict regulatory standards.
A Smarter Way to Integrate Compliant AI
This is the exact problem we designed the Wonderment Apps prompt management system to solve. Think of it as a secure toolkit that plugs into your software, acting as a smart, compliant gateway between your app and various AI models. It’s built to give you all the benefits of AI without the compliance headaches.
Our system provides the critical oversight you absolutely need for using AI in a regulated space. For a deeper dive on this, check out our post on powerful AI solutions for healthcare.
Modernizing a healthcare app with AI isn't about just plugging into a model's API. It's about building a secure, auditable buffer zone that protects patient data no matter what. Your AI integration is only as compliant as the controls you build around it.
This approach lets you innovate with confidence. Instead of seeing AI as a compliance risk, you can start treating it as a strategic asset—one that’s managed with the same discipline as the rest of your secure infrastructure.
The core features of our tool are built specifically for the demands of HIPAA:
- Prompt Vault with Versioning: Create, test, and deploy pre-approved, safe prompts. You get strict version control, ensuring only vetted interactions happen between your app and the AI, which helps prevent accidental PHI exposure.
- Parameter Manager: This feature securely connects prompts to your internal databases. It dictates exactly what data the AI can access, enforcing the principle of least privilege right at the data level.
- Comprehensive Logging System: We give you a unified log of every single call made to any integrated AI. This creates the immutable audit trail that HIPAA requires, giving you total visibility for security reviews and compliance checks.
- Cost Manager: AI integrations come with variable costs. Our tool includes a real-time dashboard to watch your total spend across all models, helping you manage your budget and avoid surprises as your app scales.
By using an administrative tool like this, you’re not just tacking on a feature. You're building a sustainable, scalable, and compliant AI strategy that truly modernizes your application and prepares it for the future of healthcare.
Answering Your Big Questions About HIPAA App Development
Diving into HIPAA compliant app development can feel a lot like trying to assemble complex furniture with instructions written in a different language. It’s completely normal for everyone, from business leaders to developers, to have a laundry list of questions before kicking off a healthcare project. Getting clear, no-nonsense answers is the first real step toward building a secure and successful app.
This section cuts through the noise to tackle the most common—and most critical—questions we get from our clients. The goal here is to demystify these topics and give you practical insights you can start using immediately.
What's the Real Difference Between HIPAA Compliance and HITRUST Certification?
This is a great question, and it comes up all the time. The simplest way to think about it is this: HIPAA is the law, while HITRUST is a specific, structured framework for proving you're following that law (and others).
HIPAA is the U.S. federal regulation that lays down the legal requirements for protecting patient data. Being HIPAA compliant isn't optional; it's a legal must-have. HITRUST, on the other hand, is a certification framework from a private organization. It provides a highly rigorous, standardized, and certifiable way to show that you're compliant with HIPAA and other security standards.
You can be fully HIPAA compliant without ever getting HITRUST certified. However, earning that certification is often seen as the gold standard in the industry. It gives your partners, clients, and users an extra layer of confidence, showing them your security measures aren't just in place—they've been independently verified.
Do I Really Need a BAA with Every Single Third-Party Service?
Yes, absolutely—if that service will ever create, receive, maintain, or transmit Protected Health Information (PHI) on your app's behalf. Any vendor that touches PHI is legally considered a Business Associate, whether it's your cloud host like AWS, an analytics tool, or an external API.
Having a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with every one of these vendors is completely non-negotiable. This is a formal contract that legally binds them to protect PHI with the same high standards you're held to. Think of it as a critical link in your compliance chain that makes them accountable for safeguarding the data they handle for you.
Can We Use a Database Like MongoDB or PostgreSQL?
You sure can. The database technology itself isn't what makes an app compliant or non-compliant. It’s all about how you configure, manage, and lock it down. You can definitely use popular open-source databases like MongoDB or PostgreSQL for a HIPAA-compliant app, as long as you put the right controls in place.
This means you’ll have to:
- Enable strong encryption for data both at rest (sitting on the disk) and in transit (moving across the network).
- Set up strict, granular role-based access controls (RBAC) to enforce the "minimum necessary" principle.
- Make sure you have robust auditing and logging for all database queries and administrative actions.
- Host the database infrastructure inside a secure, HIPAA-compliant environment, like a properly configured VPC on a major cloud provider.
What Are the Most Common Mistakes We Should Avoid?
Having guided countless projects from concept to launch, we’ve seen a few recurring tripwires that can seriously derail a healthcare app. Steering clear of these common pitfalls will save you a world of time, money, and headaches.
One of the single biggest mistakes is treating compliance as a checkbox to tick off at the end. Retrofitting security is always more painful, more expensive, and far less effective than building it in from the very first wireframe.
Here are a few critical mistakes we see teams make all too often:
- Forgetting 'Privacy by Design': As mentioned, they treat compliance like a final inspection instead of baking security and privacy into the app's architecture from day one.
- Skipping the BAA: They integrate with third-party vendors without getting a signed Business Associate Agreement first, opening up a massive liability gap.
- Implementing Weak Audit Logs: They create flimsy or non-existent audit trails. This makes it nearly impossible to investigate a potential data breach or prove compliance when an auditor comes knocking.
- Neglecting Ongoing Compliance: They launch the app and assume the work is done. They forget that compliance is a continuous effort that requires regular security monitoring, risk assessments, and updates.
Ready to build a modern, scalable, and compliant healthcare application? Wonderment Apps is your dedicated engineering partner, specializing in UX-driven delivery and AI modernization. Let us help you navigate the complexities of HIPAA while building an exceptional product. Schedule a demo today to see how our expertise and tools can accelerate your project.
